JWST Uncovers Sulfur Clues That Redefine How Giant Exoplanets Form
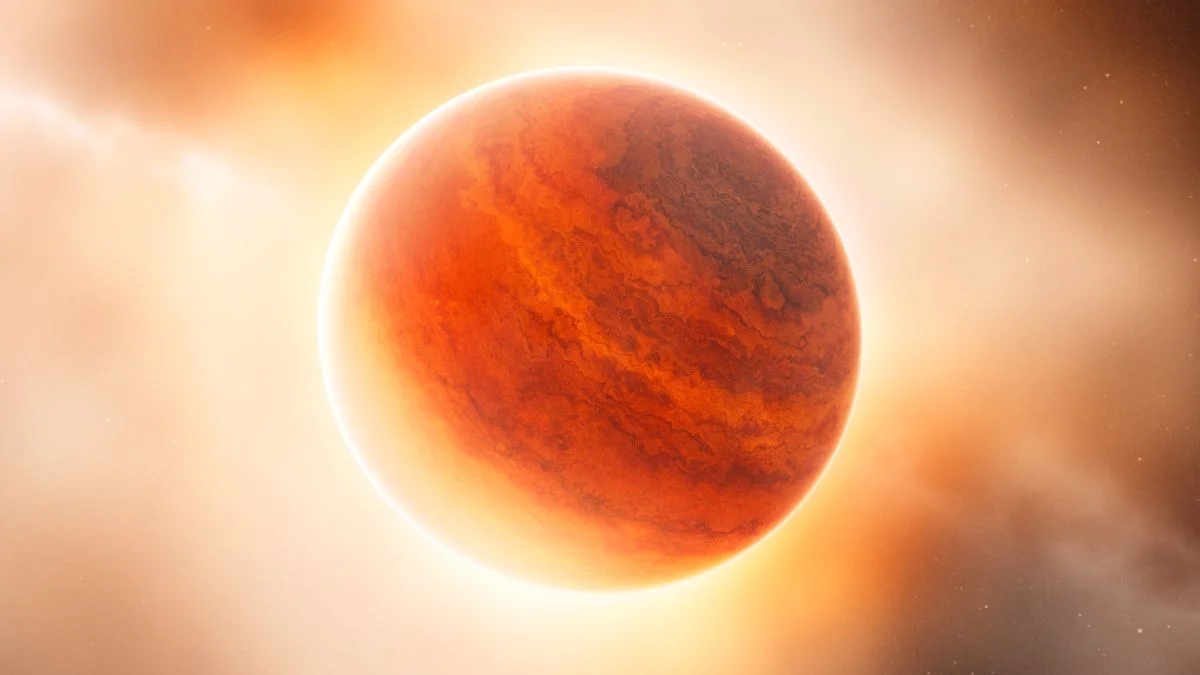
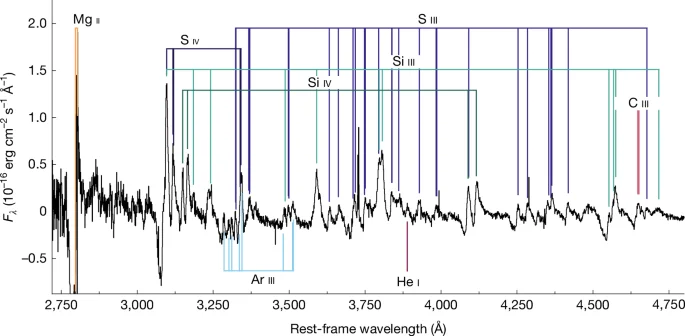
A JWST study of HR 8799’s three inner gas giants detects hydrogen sulfide in their atmospheres, revealing heavy-element enrichment consistent with solid-material accretion during formation. The finding suggests these 5–10 Jupiter-mass planets may have formed in a Jupiter-like way despite their wide, distant orbits, challenging simple core-accretion models and hinting at a more complex, potentially mixed formation path; the results were published in Nature Astronomy.