Alzheimer's Gene Network Map Reveals Hidden Brain Drivers
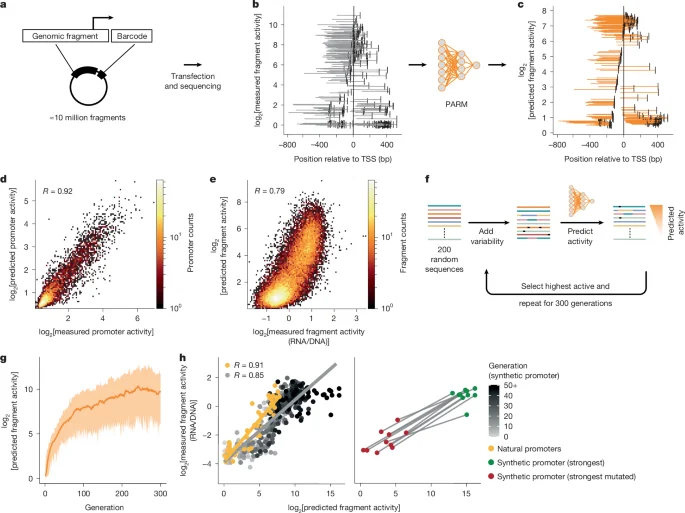
A team used a new machine-learning tool called SIGNET to build a cell-type-specific map of gene regulation in brains from 272 Alzheimer's patients, identifying hub genes and thousands of causal interactions—especially in excitatory neurons—offering potential drug targets while noting that causality isn’t proven and comparisons with non-AD tissue are planned.