Human-Specific Regulatory Mechanism Identified in Early Embryo Development
TL;DR Summary
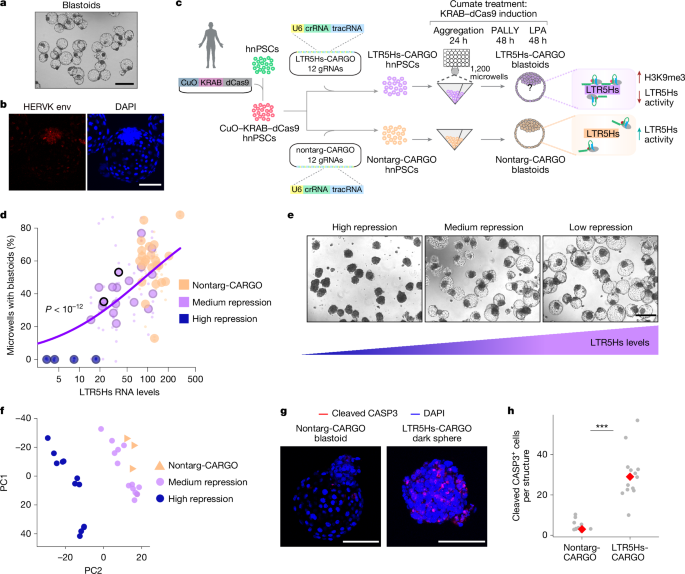
The study uncovers a human-specific regulatory mechanism involving endogenous retroviruses (ERVs), particularly HERVK LTR5Hs, which influence gene expression and lineage specification during early human development, using a stem cell-based blastoid model. Repression of LTR5Hs impairs blastoid formation, alters lineage allocation, and affects the expression of key genes like ZNF729, a human-specific gene regulated by a nearby LTR5Hs insertion that is essential for blastoid formation and proliferation. The work highlights the evolutionary role of ERVs as enhancers shaping human-specific developmental features.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
2
Time Saved
80 min
vs 81 min read
Condensed
100%
16,081 → 80 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature