Early markers could spot osteoarthritis risk in young adults before symptoms
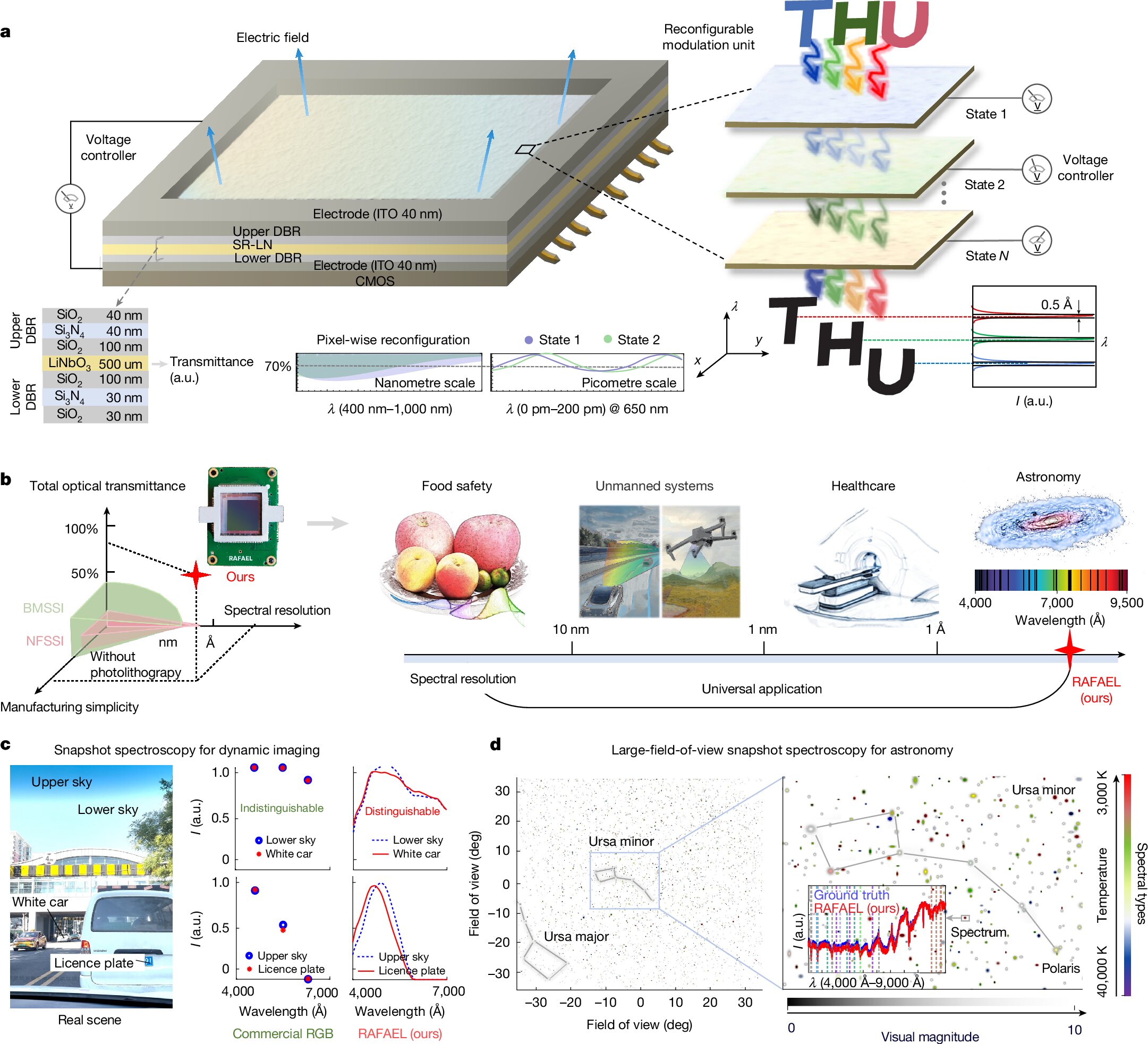
The article highlights that osteoarthritis is increasingly diagnosed in younger, active individuals and discusses how emerging diagnostic techniques—such as spectral fingerprinting using spectroscopy to analyze blood biomarkers—could detect risk before pain or joint damage appears. This early detection could enable preventive actions like targeted exercise, weight management, and injury prevention, potentially reducing long-term disability and healthcare costs. Current treatments focus on symptom management and may involve injections or, in severe cases, joint replacement, but early identification could shift care toward prevention and preservation of joint health.