Molecule Found in Star-Birth Cloud Could Seed Life on New Worlds
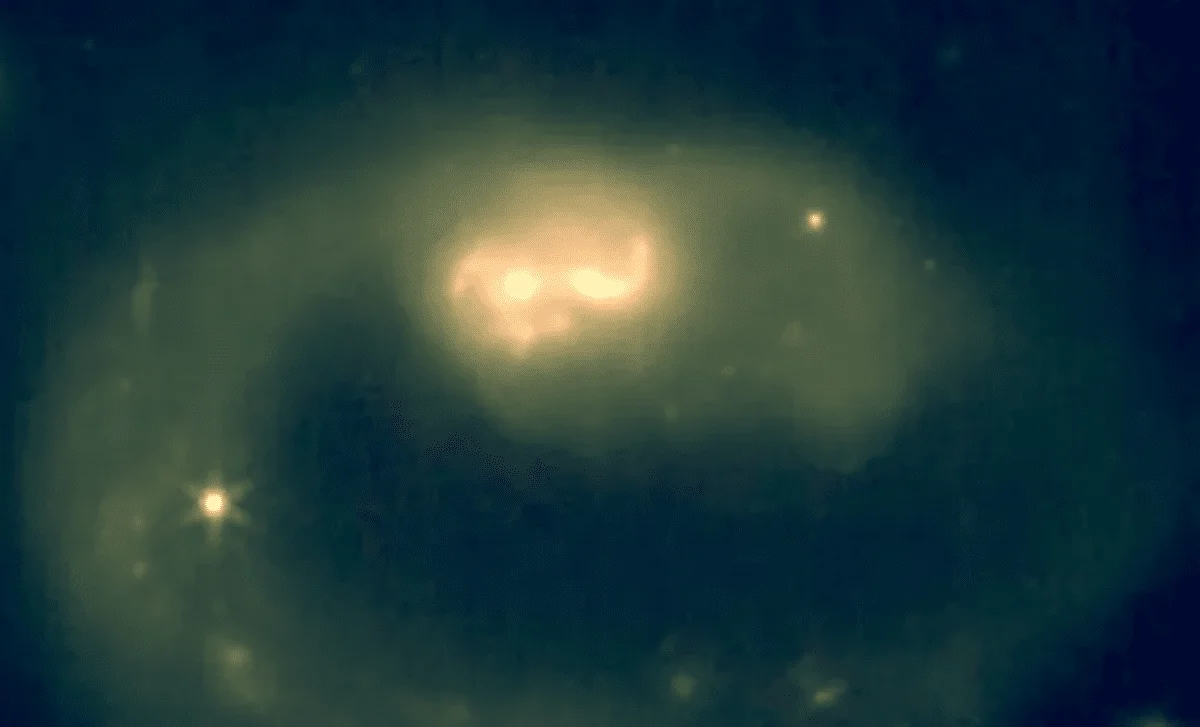
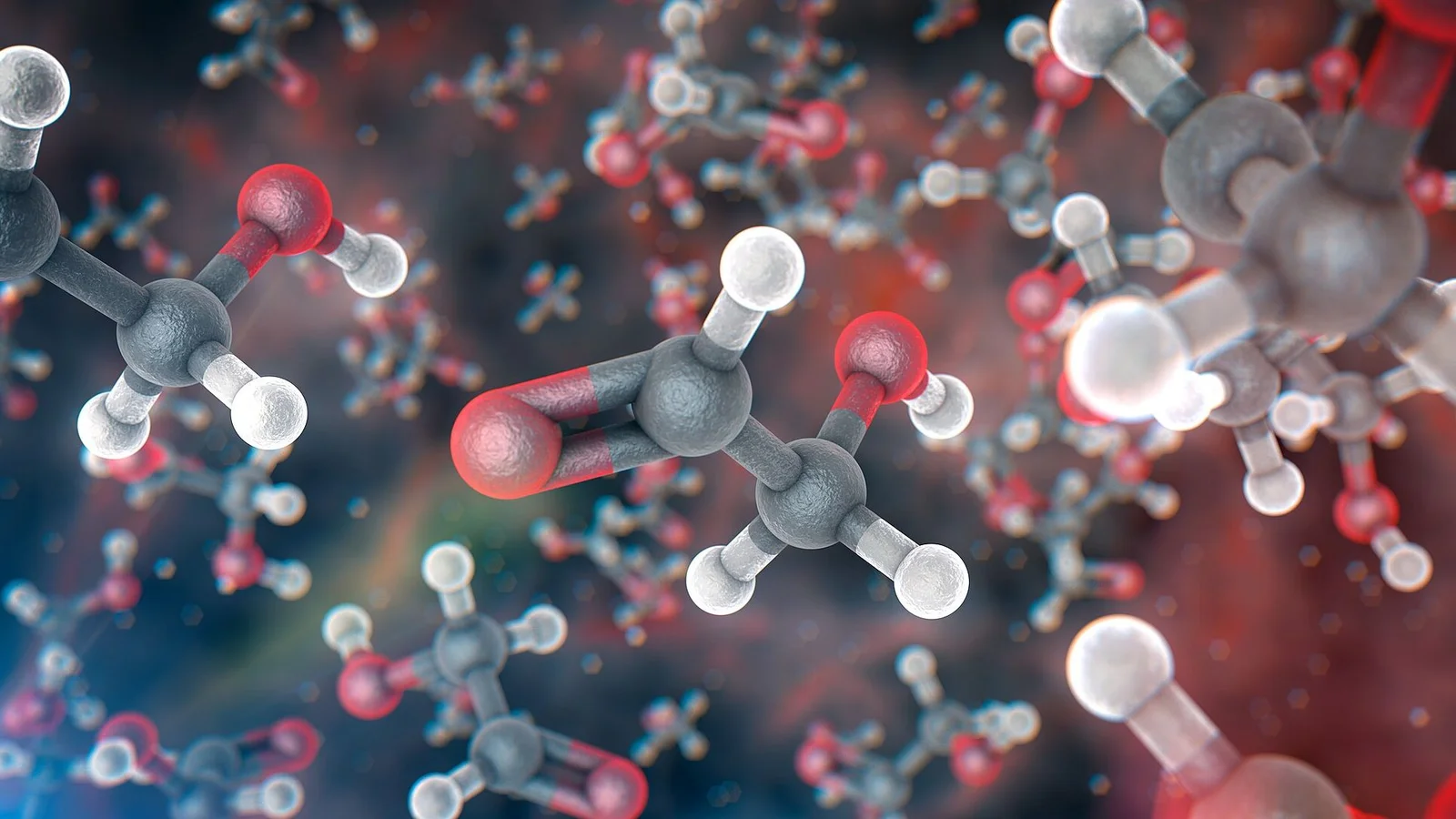
Astronomers detected methanimine, a simple organic molecule, in the L1544 pre-stellar core about 554 light-years away, suggesting that the chemistry needed for life begins before star formation and could seed planets forming from the cloud with life's building blocks.