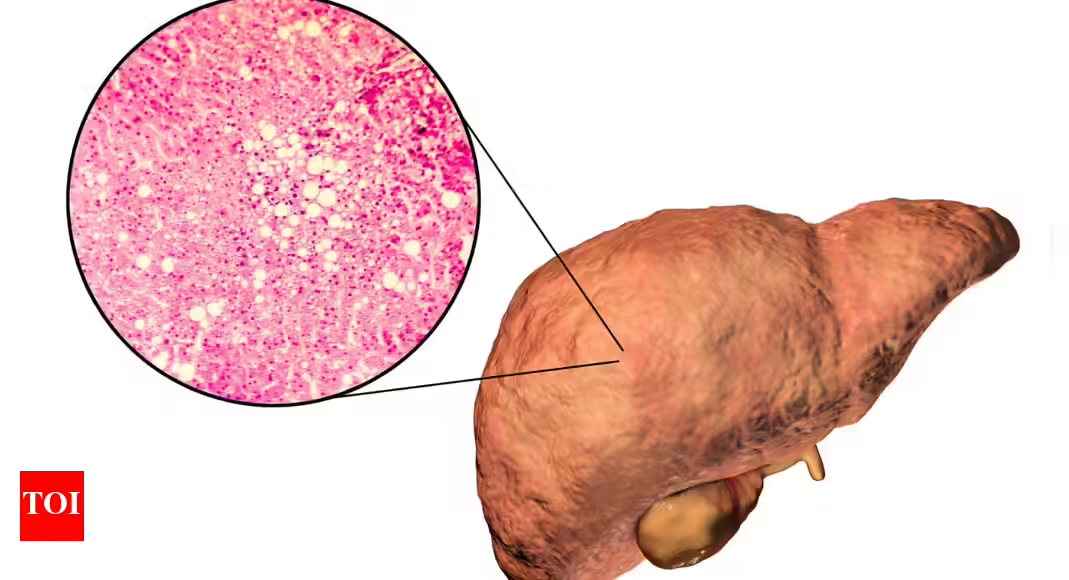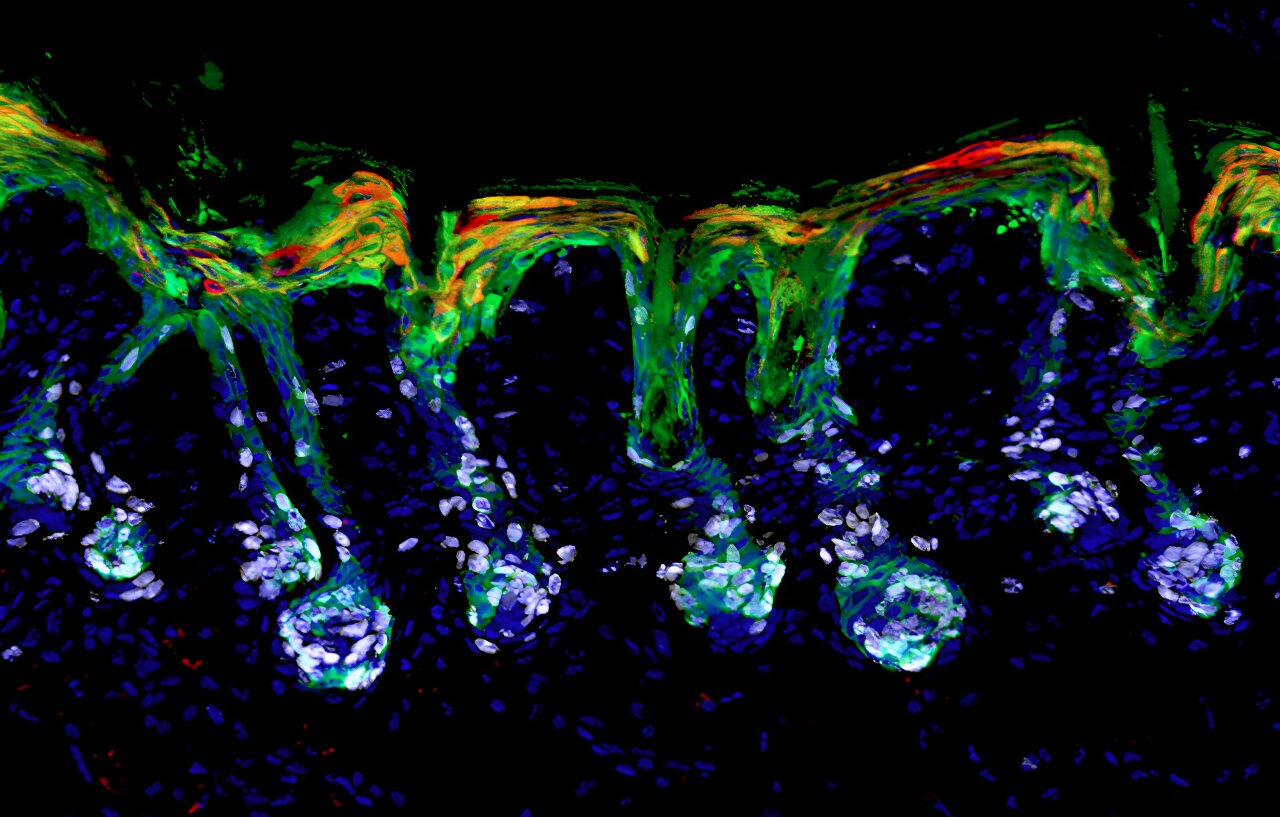
Vitamin A's Role in Tumor Immune Evasion and New Cancer Treatment Avenues
Scientists have discovered that a vitamin A metabolite, retinoic acid, can suppress the immune system's ability to fight cancer by promoting immune tolerance. They developed inhibitors that block this pathway, restoring immune responses and improving cancer vaccine efficacy, paving the way for new immunotherapy treatments.