Health And Science News
The latest health and science stories, summarized by AI
Featured Health And Science Stories

Vitamin A's Role in Tumor Immune Evasion and New Cancer Treatment Avenues
Scientists have discovered that a vitamin A metabolite, retinoic acid, can suppress the immune system's ability to fight cancer by promoting immune tolerance. They developed inhibitors that block this pathway, restoring immune responses and improving cancer vaccine efficacy, paving the way for new immunotherapy treatments.

More Top Stories
Genetic and Microbiome Insights into Achieving a Century of Life
Indian Defence Review•2 months ago
2025's Top Medical Breakthroughs Transforming Healthcare
ABC News•2 months ago
More Health And Science Stories
Aging Immune Cells Alter DNA to Maintain Inflammation
Research shows that aging immune cells, specifically macrophages, can sustain a heightened inflammatory state through a pathway involving GDF3 protein, which may worsen responses to severe infections like sepsis; targeting this pathway could lead to new treatments for age-related inflammatory conditions.

Scientists Confirm Creatine's Benefits for Brain, Heart, and Muscle Health
Recent scientific research confirms that creatine, a common supplement traditionally associated with athletic performance, also significantly benefits brain and heart health by supporting cellular energy and neurotransmitter function, with studies showing it is safe for general use and potentially crucial for addressing creatine deficiency disorders.
Watching Brain Surgery for Alzheimer's Cure Research
The article explores cutting-edge Alzheimer's research, including brain surgery to collect tissue, laboratory studies on toxic proteins, and promising drug developments, suggesting that curing Alzheimer's may be achievable in the future.
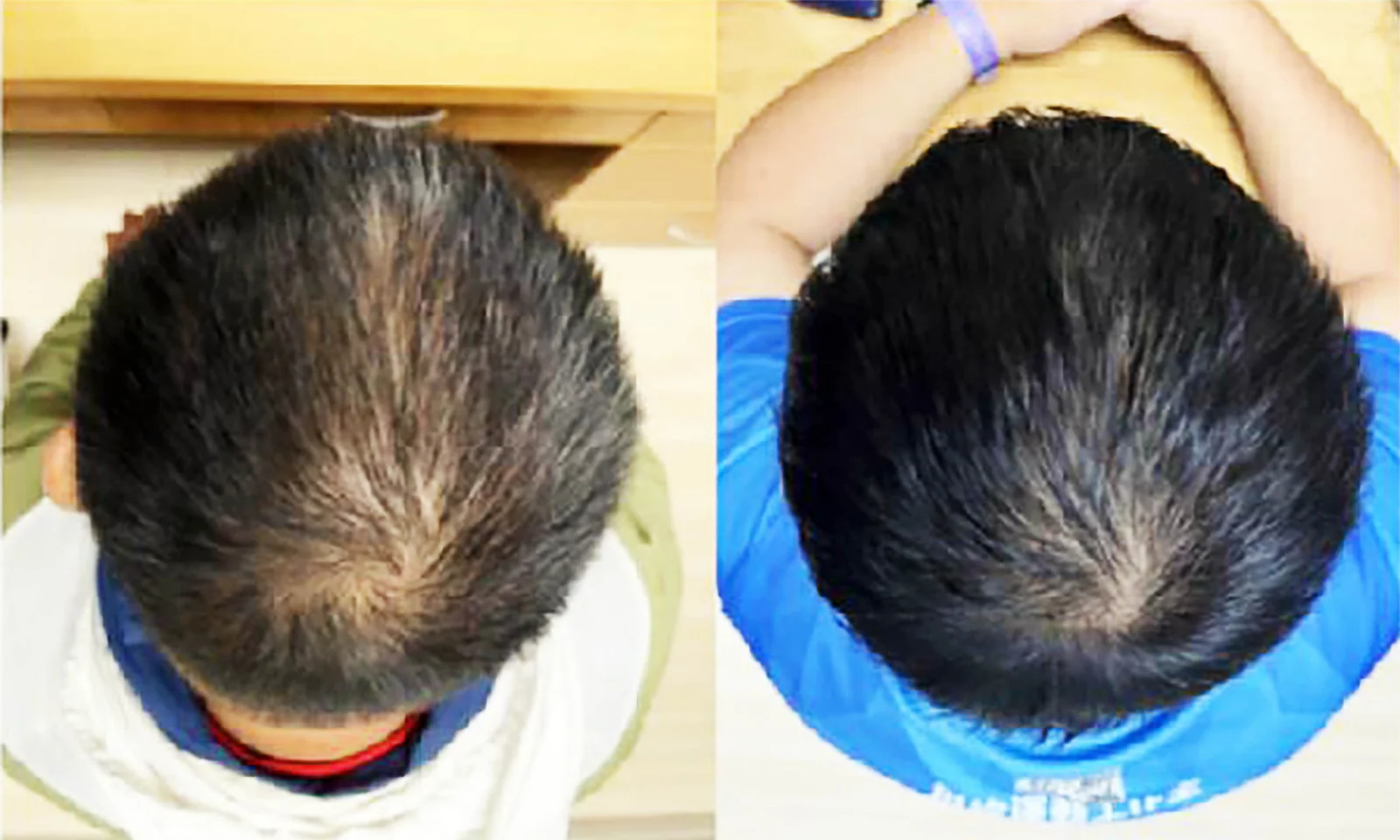
Plant-Based Serum Promotes Rapid Hair Regrowth, Scientists Find
Scientists developed a plant-based hair serum containing Centella asiatica extract, which showed a 25% increase in hair thickness in a short, 8-week trial, suggesting potential for hair regrowth, though further research is needed to confirm efficacy and safety.

Secret Brain Hack to Simplify Exercise
Research suggests that applying vibration to tendons can alter sensory signals sent to the brain, making exercise feel easier and allowing individuals to exert more effort without perceiving increased difficulty, potentially encouraging more physical activity.

The 'Hercules Gene': A Double-Edged Sword for Sports Stars
The article explores the 'Hercules gene' or myostatin deficiency, which leads to increased muscle mass and strength, highlighting cases like sprinter Harry Aikines-Aryeetey and animals like Belgian Blue cattle, discussing its implications for sports, health, and potential doping risks.

Exercise Boosts Brain Hormone Delivery
Research from Touro University reveals that vigorous exercise increases extracellular vesicles in the blood that transport hormone precursors like POMC more efficiently across biological barriers, including the blood-brain barrier, potentially impacting stress, mood, metabolism, and drug delivery.

Engaging in Creative Activities May Help Slow Brain Aging
Engaging in creative activities like dancing, music, art, or playing strategy video games is linked to a younger-looking brain and slower brain aging, with long-term practice providing stronger benefits. Even short-term creative training can improve brain aging markers, suggesting that regular creative engagement supports neural health and cognitive resilience.

Prenatal Exposure to Fatty Food Cues and Childhood Obesity Risk
Early life exposure to fat-related sensory cues, independent of nutritive content, can prime neural and metabolic responses that increase susceptibility to obesity and metabolic syndrome in adulthood, with effects observed across different diets and sex-specific differences in timing sensitivity.

Scientists Unveil Sedentary Weight Loss Method
Scientists have discovered that restricting methionine in the diet can increase energy expenditure and promote fat burning in mice, similar to cold exposure, without requiring exercise. This finding suggests potential new dietary strategies for obesity management by enhancing the body's natural heat production and fat utilization, which could complement existing treatments.
