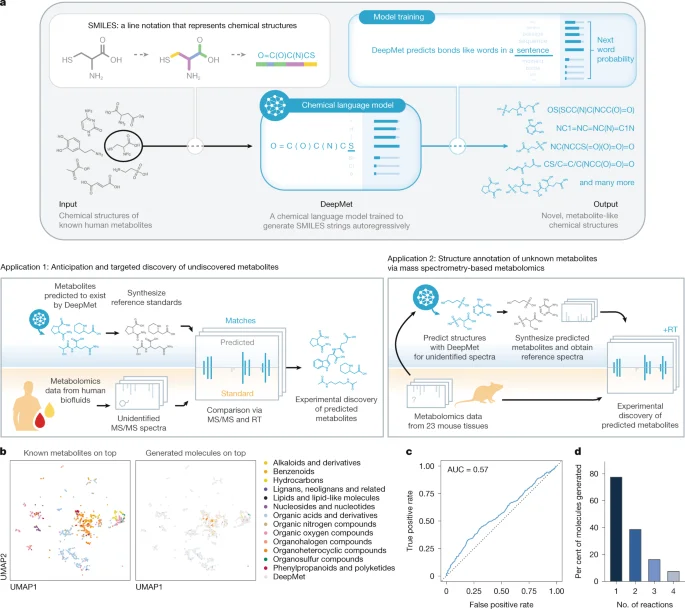
DeepMet: AI models illuminate unseen mammalian metabolites
A new chemical language-model approach, DeepMet, learns from known human metabolites to generate metabolite-like structures and prioritize plausible, yet-unrecognized mammalian metabolites. By coupling DeepMet with mass-spec data and MS/MS prediction (CFM-ID), the method enables de novo generation and targeted discovery of metabolites, identifying 16 previously unrecognized mouse tissue metabolites and 17 metabolites in human biofluids, and correctly predicting 252 of 313 HMDB 5.0 additions (81%). The team further improves annotation with a meta-learning framework that integrates retention times and isotope patterns, achieving about 70% accuracy in a mouse dataset. They also release a web app and Snakemake pipeline to extend the approach, highlighting DeepMet’s potential to fill gaps in mammalian metabolome maps while noting limitations such as its focus on metabolite-like chemical space and isomer ambiguity.