Chemistry News
The latest chemistry stories, summarized by AI
Featured Chemistry Stories

"Chemistry's Workhorse Separates Mirror-Image Molecules"
Chemists have demonstrated the use of mass spectrometry to separate chiral molecules, which exist as mirror-image structures with different properties. This breakthrough could streamline the laborious process of separating enantiomers, crucial in drug discovery, by allowing for quick determination of enantiomeric excess and confirmation of molecular structures. The technique, described in Science, has the potential to simplify and expedite the preparation of pure samples of enantiomers in larger quantities, with implications for drug design and discovery.

More Top Stories
"Oxygen's Impact on Nickel Catalysts in Methane Reforming"
Phys.org•2 years ago
"Real-time Observation of Catalytic Chemistry in Ammonia Production"
Nature.com•2 years ago
More Chemistry Stories
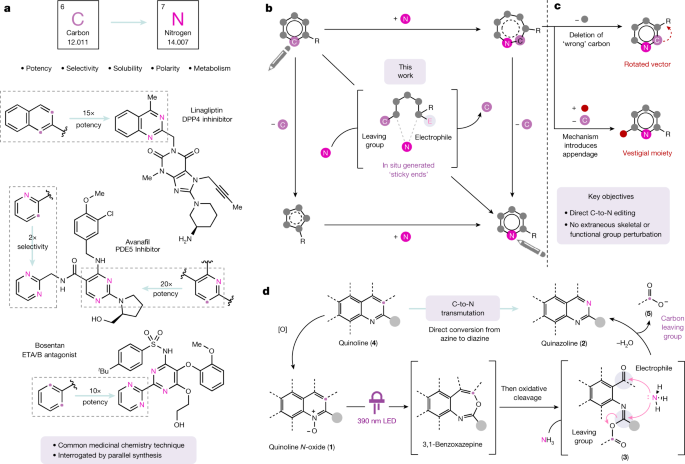
Advancements in Atom-Swap Chemistry Revolutionize Drug Discovery
Researchers have developed a method for the carbon-to-nitrogen single-atom transmutation of azaarenes, which are important building blocks in drug discovery and the synthesis of nitrogen heterocycles. This breakthrough in chemical synthesis opens up new possibilities for the creation of diverse nitrogen-containing compounds, which are crucial in the development of pharmaceuticals. The technique involves the use of photochemical carbon deletion and subsequent nitrogen insertion reactions, providing a powerful tool for the modification and functionalization of azaarenes. This advancement has the potential to significantly impact the field of drug discovery and the synthesis of nitrogen-containing compounds.

"The Illusion of an Essential Substance: Debunking Chemistry's Misconception"
A team of researchers investigating the use of sulfide solutions to reduce mercury emissions made a surprising discovery: the S2– ion, which was assumed to exist in aqueous form and had been a part of chemistry calculations for decades, does not actually exist. Using a Raman spectrometer, the team found no evidence of S2–(aq). The mistake, which occurred decades ago, has led to incorrect chemistry calculations and the researchers recommend that the ion be "comprehensively banished" from the chemical community.
"Efficient Halodealkylation of Fully Alkylated Silanes with Arenium-Ion Catalysts"
Researchers have developed a new method for the halodealkylation of fully alkylated silanes using arenium-ion catalysis. This approach offers a more sustainable and efficient route for the synthesis of methylchlorosilanes, which are important precursors in the production of silicones. The study provides insights into the catalysts, mechanisms, reaction conditions, and reactor designs involved in this process, highlighting the potential for further advancements in the field of molecular catalysis and the silicone industry.
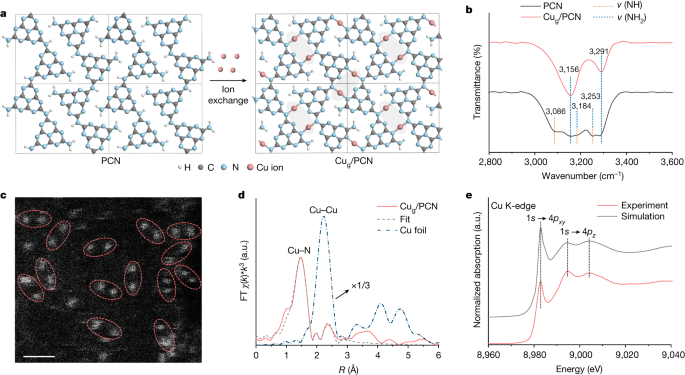
Revolutionizing Cross-Coupling: Geminal-Atom Catalysis Unleashed
Researchers have developed geminal-atom catalysis, a new approach for cross-coupling reactions in organic synthesis. This method bridges the gap between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis by utilizing heterogeneous single-metal-site catalysts. Geminal-atom catalysis offers potential advantages such as improved selectivity, recyclability, and scalability, making it a promising tool for sustainable organic synthesis. The data for this study are available in the manuscript and supplementary information, as well as in the Zenodo repository.
"Cyclic Sandwich Compounds: Synthesis and Remarkable Properties"
Researchers have synthesized and studied various cyclic sandwich compounds, including multidecker lanthanide-cyclooctatetraene clusters, lanthanide organometallic sandwich nanowires, and transition metal-benzene sandwich polymers. These compounds exhibit interesting properties such as ferromagnetism and potential for spin transport. The synthesis and characterization of these compounds provide insights into their electronic structures and bonding. Additionally, the study of cyclic ferrocene tetramers and other related compounds has contributed to the understanding of their reactivity and potential applications.
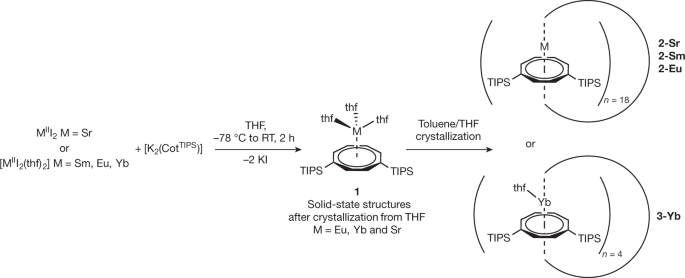
Nano-rings: Synthesis and Properties of Multidecker Sandwich Compounds
Researchers have extended the chemistry of sandwich compounds by assembling nano-rings from 18 identical sandwich-type building blocks, in which two planar molecular rings sandwich a metal ion 'filling' between them. This advancement opens up new possibilities for molecular assembly and has implications for various fields of chemistry research.
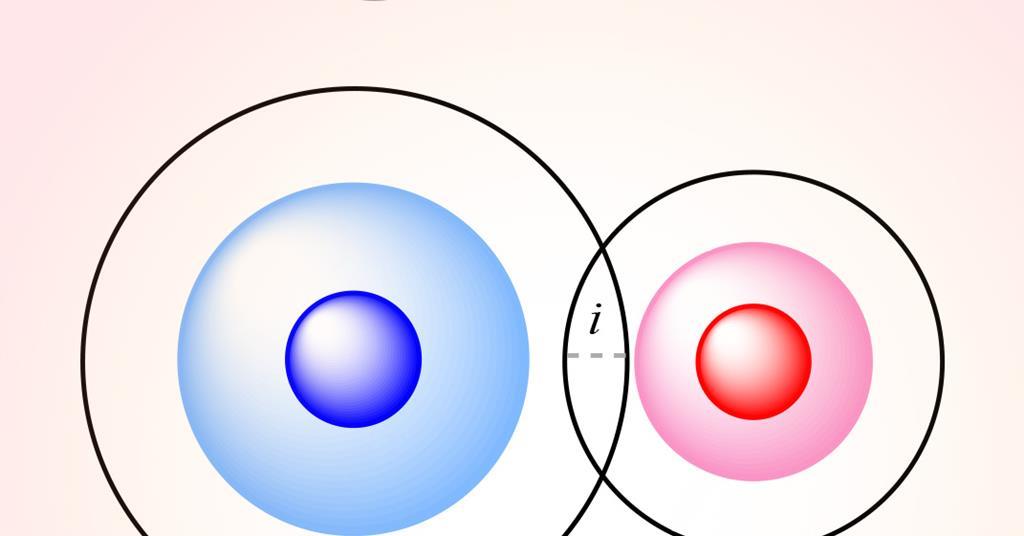
"Unveiling the Hidden Power of Van der Waals Crust in Describing Chemical Bonds"
Researchers in Spain have developed a new parameter called the penetration index, which describes the degree of interpenetration of the van der Waals crusts of two atoms. This parameter can replace previous distance measurements and be applied to a wide range of chemical bonds. The penetration index provides a quantitative measure of the degree of interaction between atoms, independent of their size. It has been successfully applied to hydrogen bonding and other bonding interactions, allowing for more precise descriptions and a better understanding of chemical bonding and structure. However, the method has some limitations when applied to ionic crystals due to its reliance on covalent radii rather than ionic radii.
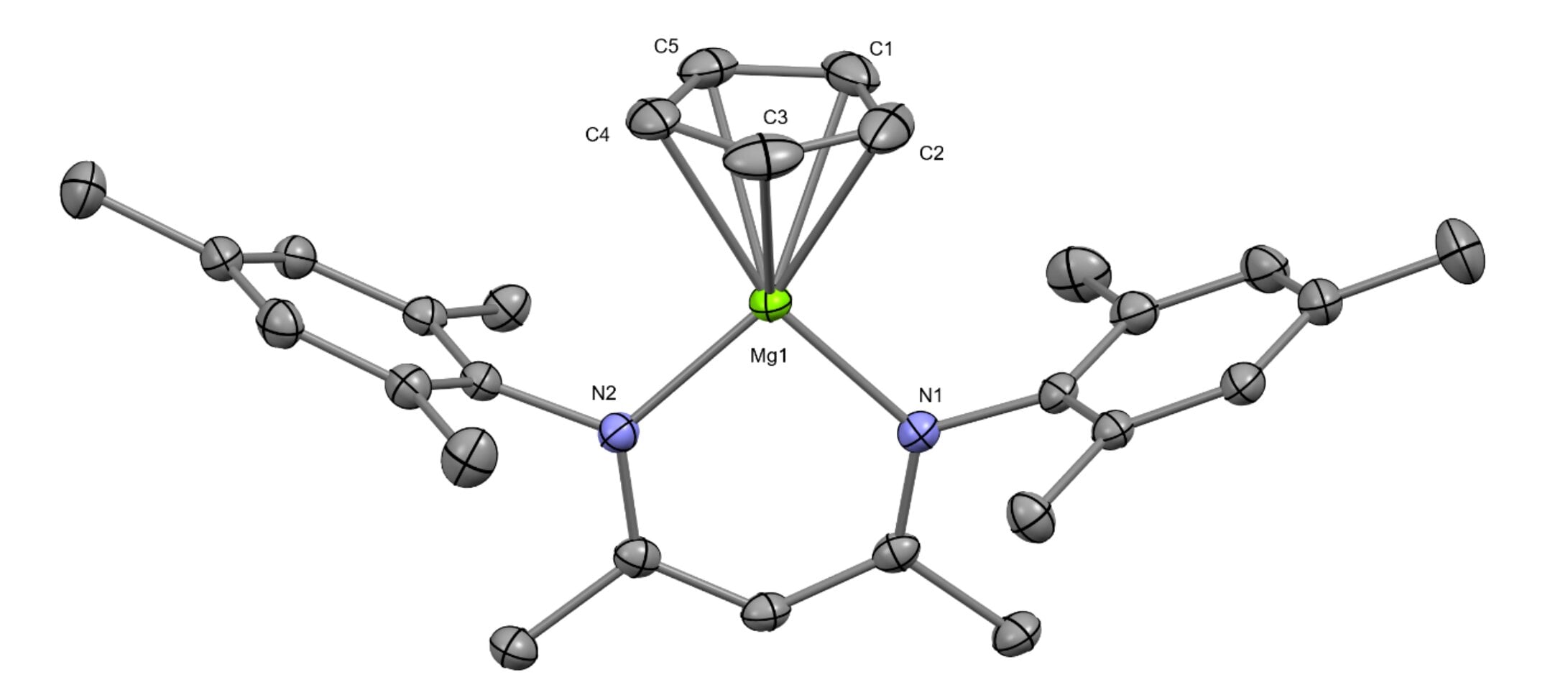
First-ever metallic bond formed between beryllium atoms.
Chemists at the University of Oxford have successfully bonded two beryllium atoms for the first time using a multi-stage process that involves building two molecules with each made up of a single beryllium atom and several carbon and hydrogen atoms. The team mixed the two molecules together with a chemical made by bonding dual magnesium atoms together, resulting in the creation of a crystal compound called diberyllocene. The team established safety protocols to conduct the procedure safely and found that math models used to make predictions decades ago proved to be correct.
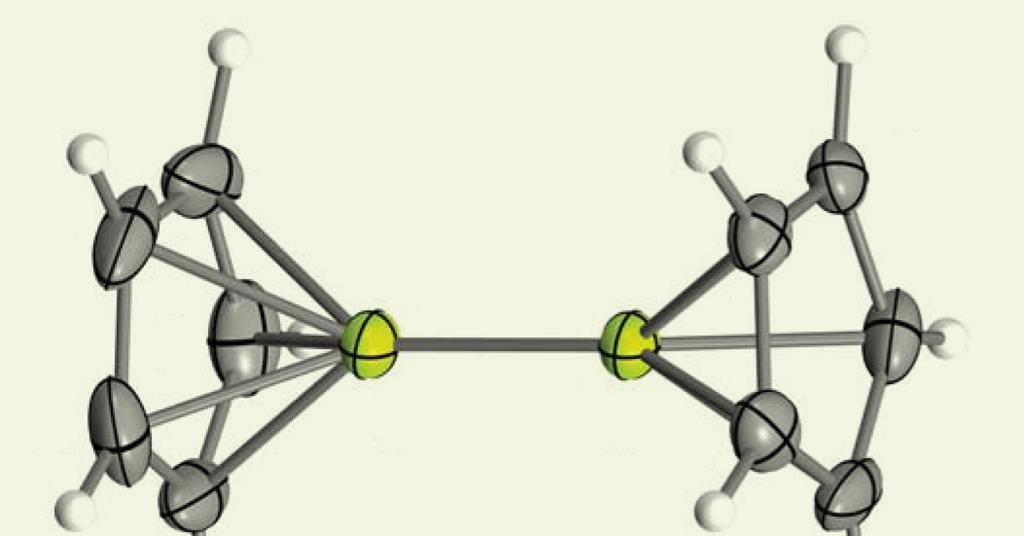
Chemists achieve stable beryllium bond after 50-year quest
Researchers at the University of Oxford have successfully isolated the first stable compound with a beryllium-beryllium bond, diberyllocene, using a dimeric magnesium(I) complex. The synthesis of diberyllocene will help answer questions about the fundamental nature of beryllium-beryllium bonding that were posed over a century ago. The compound features two half-sandwich (cyclopentadienyl)beryllium units linked through a beryllium-beryllium bond, which was found to be 2.05Å in length. The researchers also concluded that diberyllocene was a reductant that could be used to synthesise other beryllium-metal bonds.
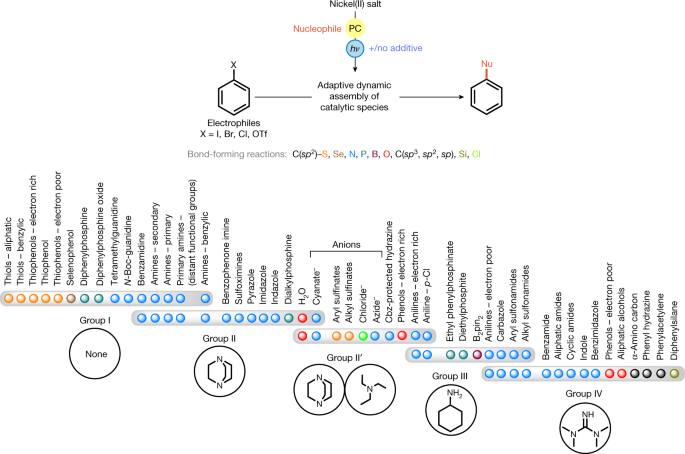
Advancements in Catalysis for Controlling Chemical Reactions.
Researchers have developed a unified and practical method for carbon-heteroatom cross-coupling using nickel/photo dual catalysis. The method involves the use of adaptive dynamic homogeneous catalysis, which allows for the acceleration of reaction generality and mechanistic insight through additive mapping. The team also used machine learning to predict reaction performance in C-N cross-coupling. The method has potential applications in drug design and medicinal chemistry.
