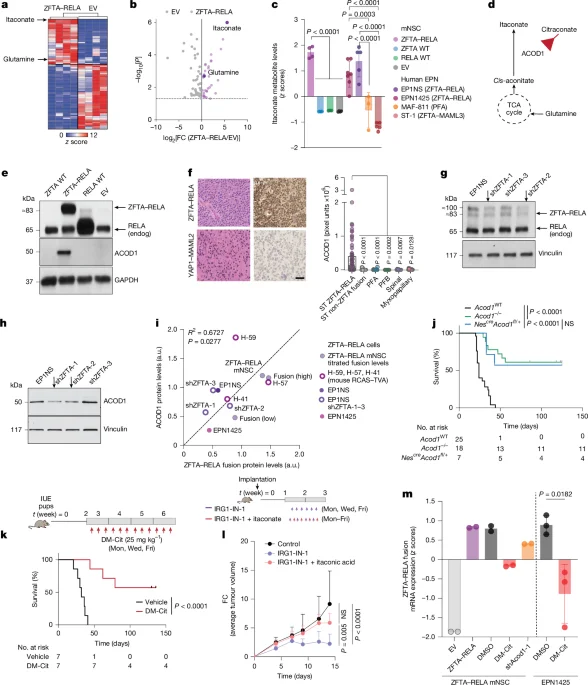
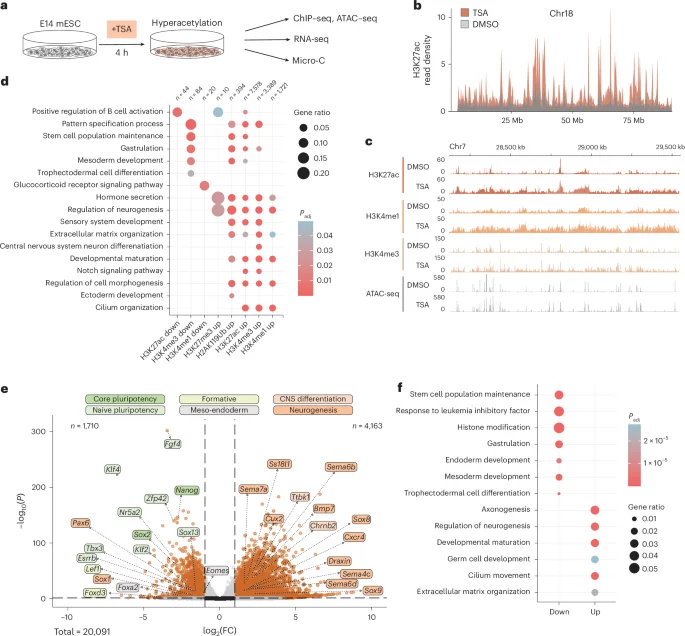
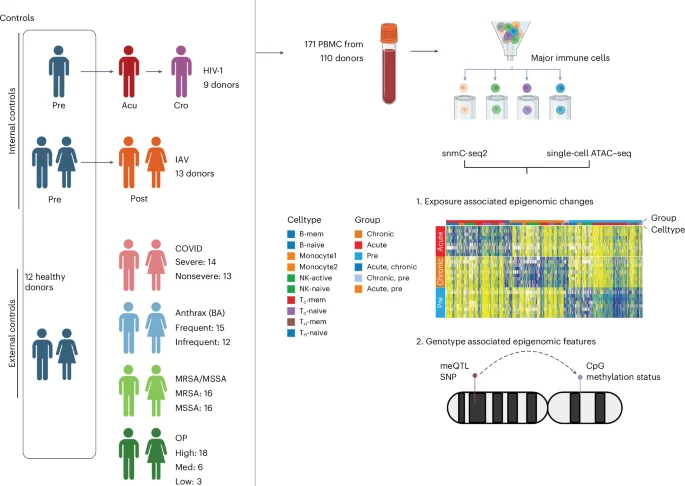
Fungicide Exposure Echoes through 20 Rat Generations via Epigenetic Inheritance
A Washington State University study in rats shows that a single in-utero exposure to the fungicide vinclozolin can imprint disease risk that persists for 20 generations, with birth-related mortality rising in later generations. The inherited effects are germline-based epigenetic changes, suggesting long-term implications for human disease and highlighting the potential for epigenetic biomarkers to enable preventative medicine decades before disease onset.