Synthetic DMT Trials Hint at Rapid Depression Relief With Guided Therapy
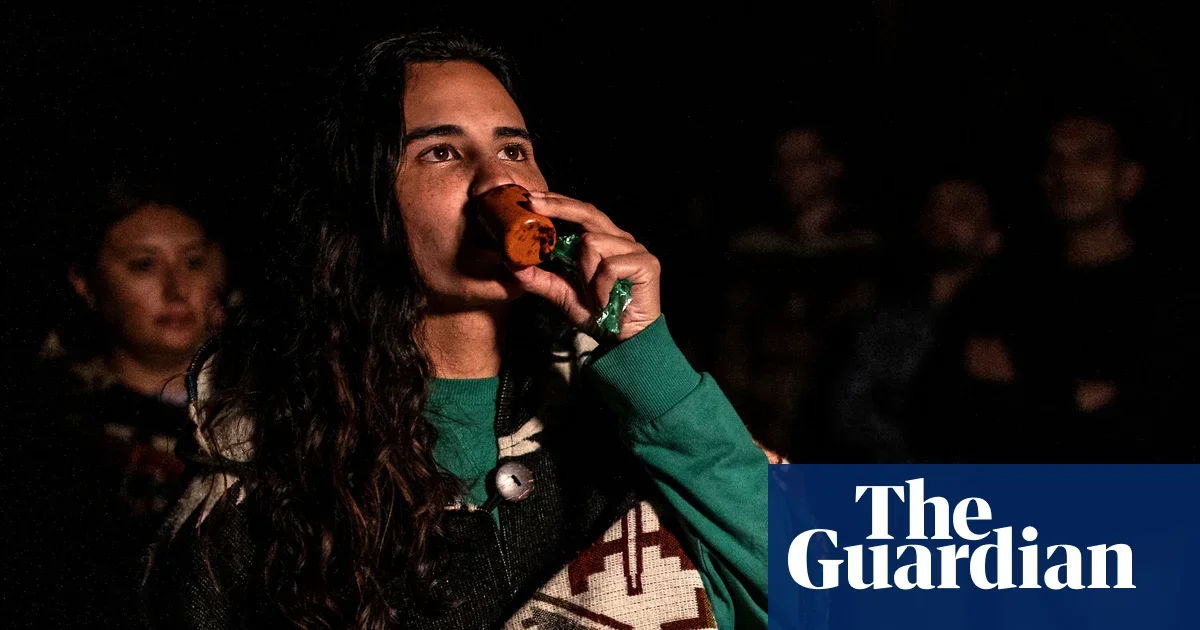
A phase II trial sponsored by Small Pharma (now Cybin UK) found a synthetic DMT formulation, delivered by injection with psychotherapeutic support, reduced depressive symptoms more than placebo after two weeks in 17 treated vs 17 controls. The study emphasizes the therapists’ role and notes the synthetic DMT yields a short, ~30-minute experience without vomiting (unlike traditional ayahuasca). While promising, the results are preliminary and require clinic-based administration, with broader context including FDA-approved ketamine therapy and ongoing psychedelics research.