Super agers keep generating young neurons into old age
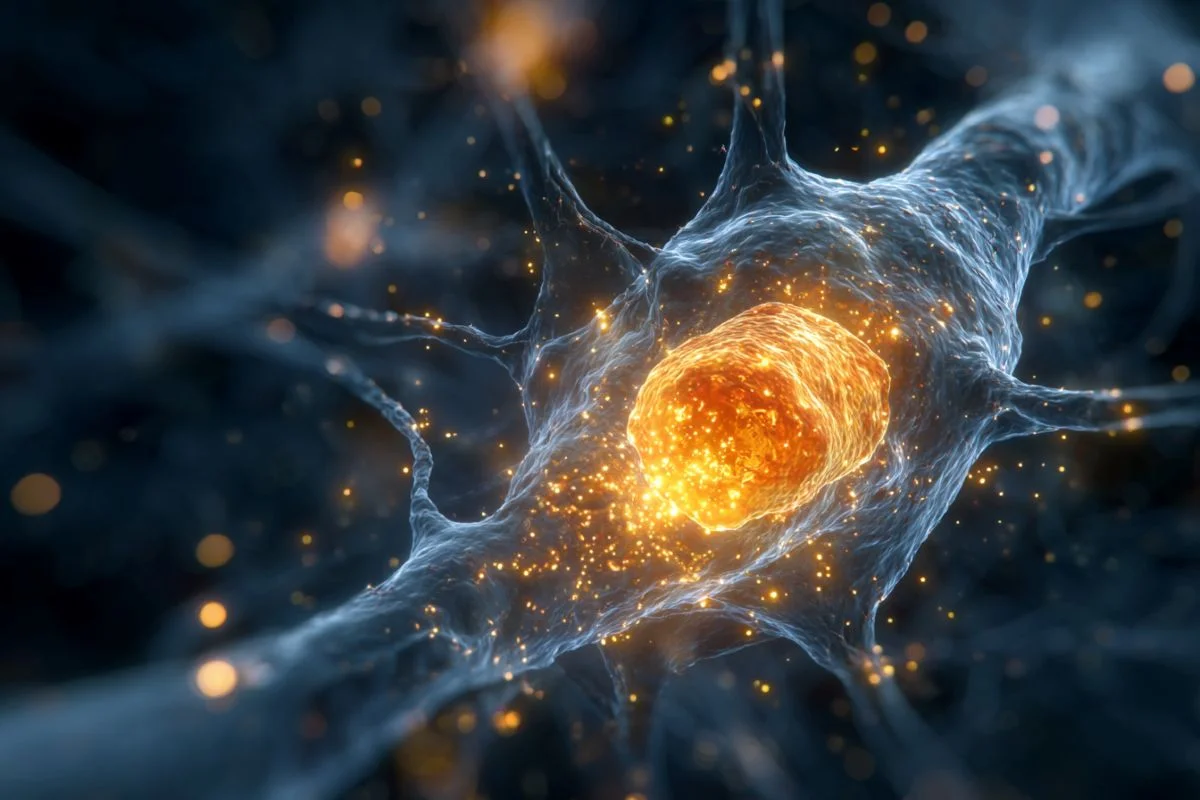
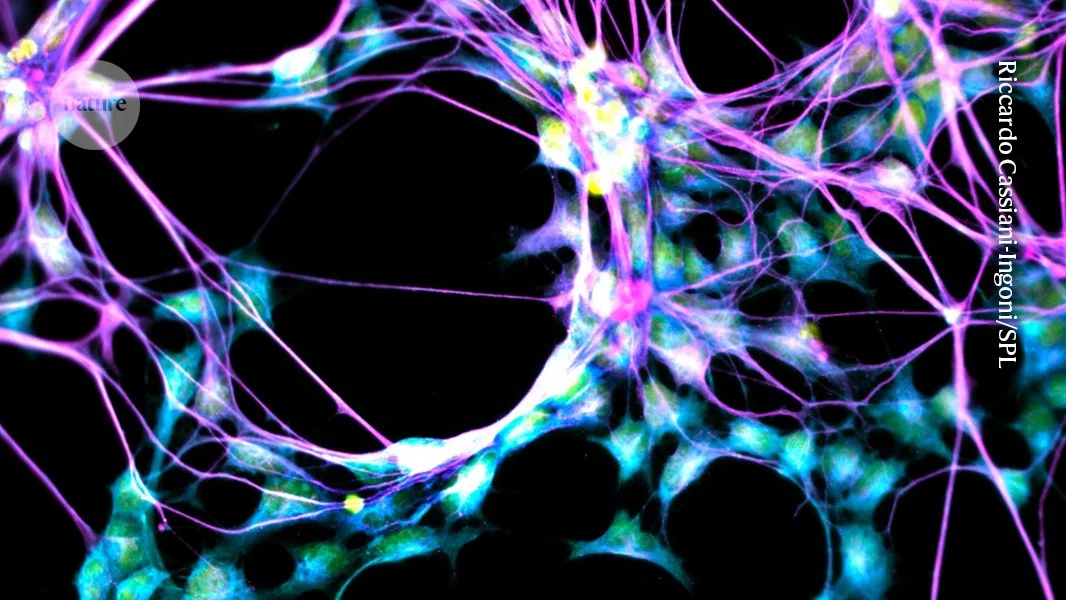
New Nature study finds that older adults with healthy cognition, including 'super agers', continue to produce immature neurons in the hippocampus at higher levels than those with cognitive decline, suggesting persistent neurogenesis may support memory; the neuron fraction is tiny (~0.01%), and the small sample sizes mean results should be interpreted cautiously; researchers hope to harness this process to develop therapies that boost neurogenesis in aging and Alzheimer's.