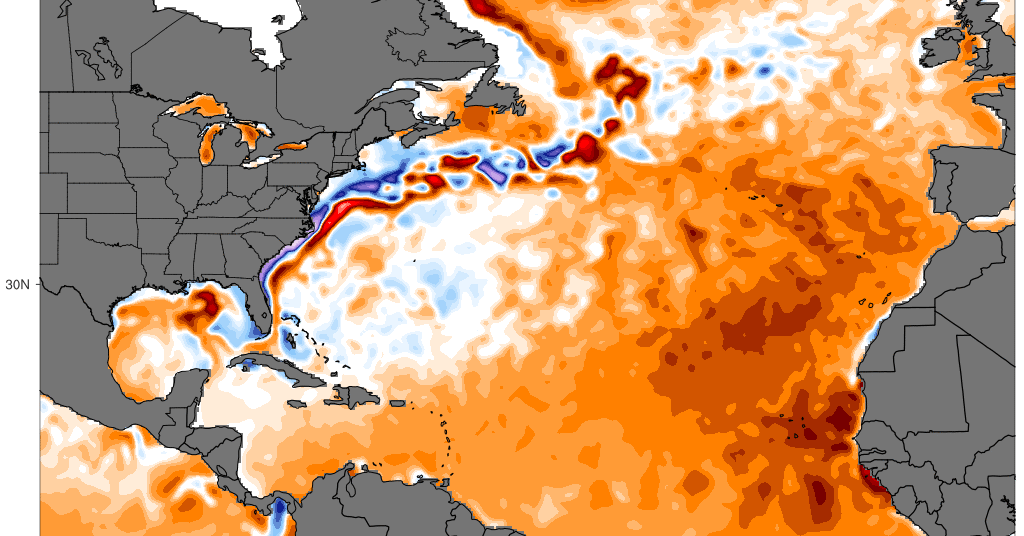
Record-Breaking Ocean Temperatures Signal Escalating Climate Crisis
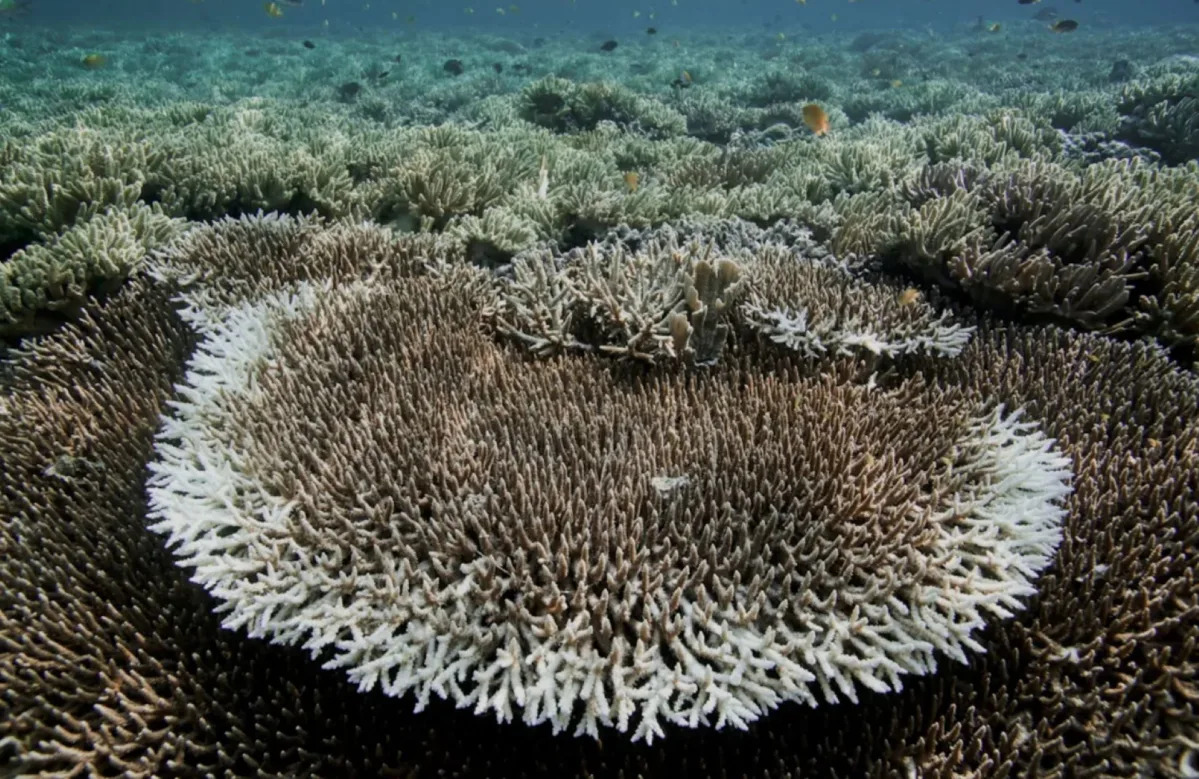
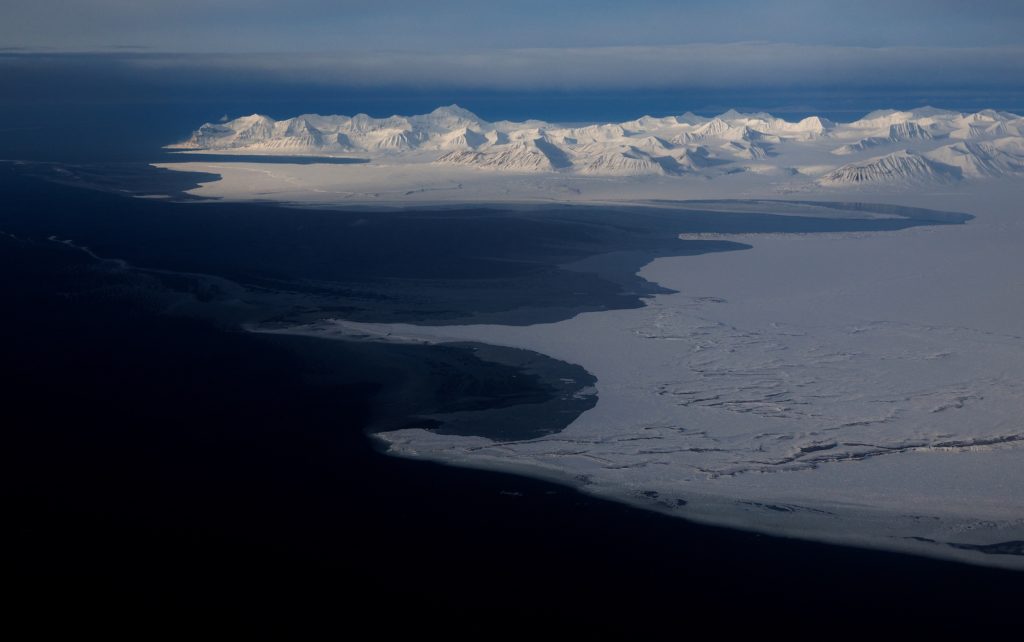
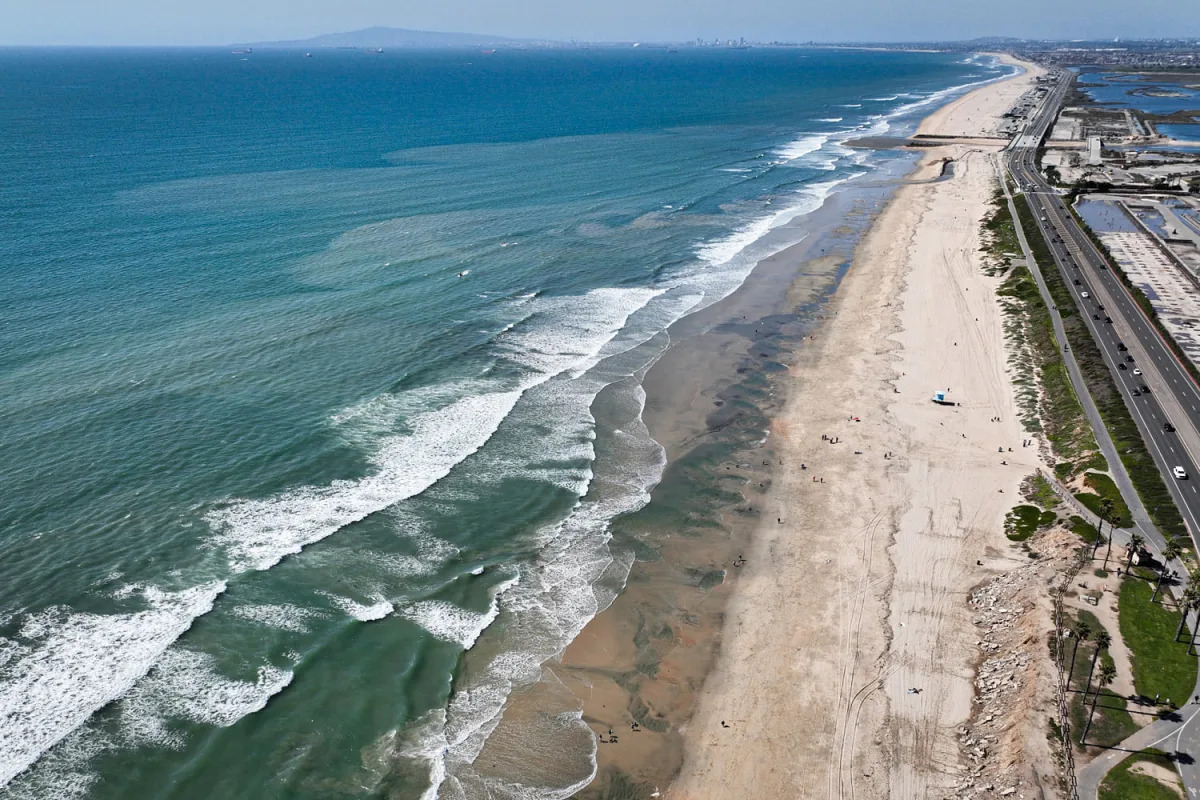
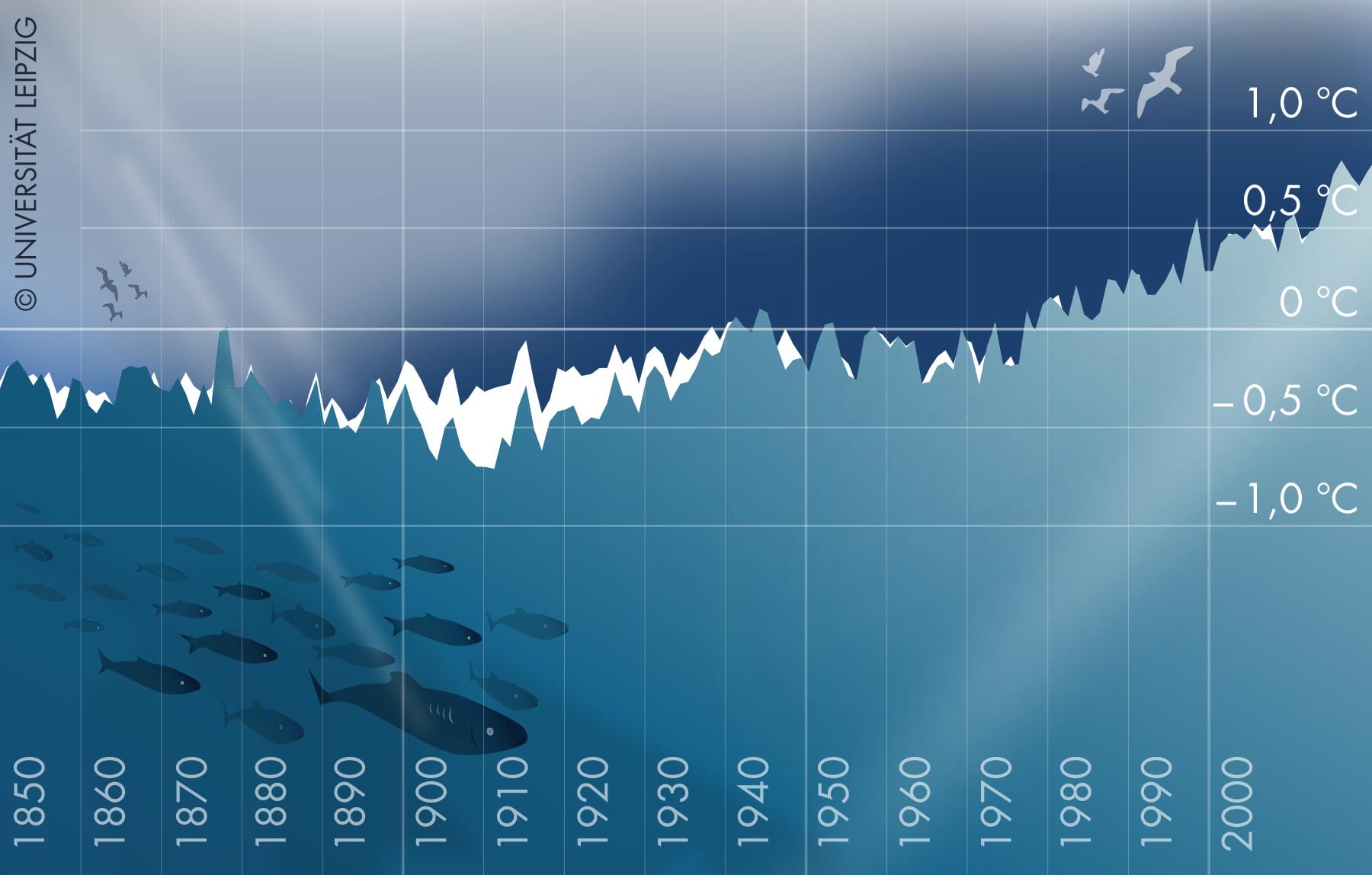
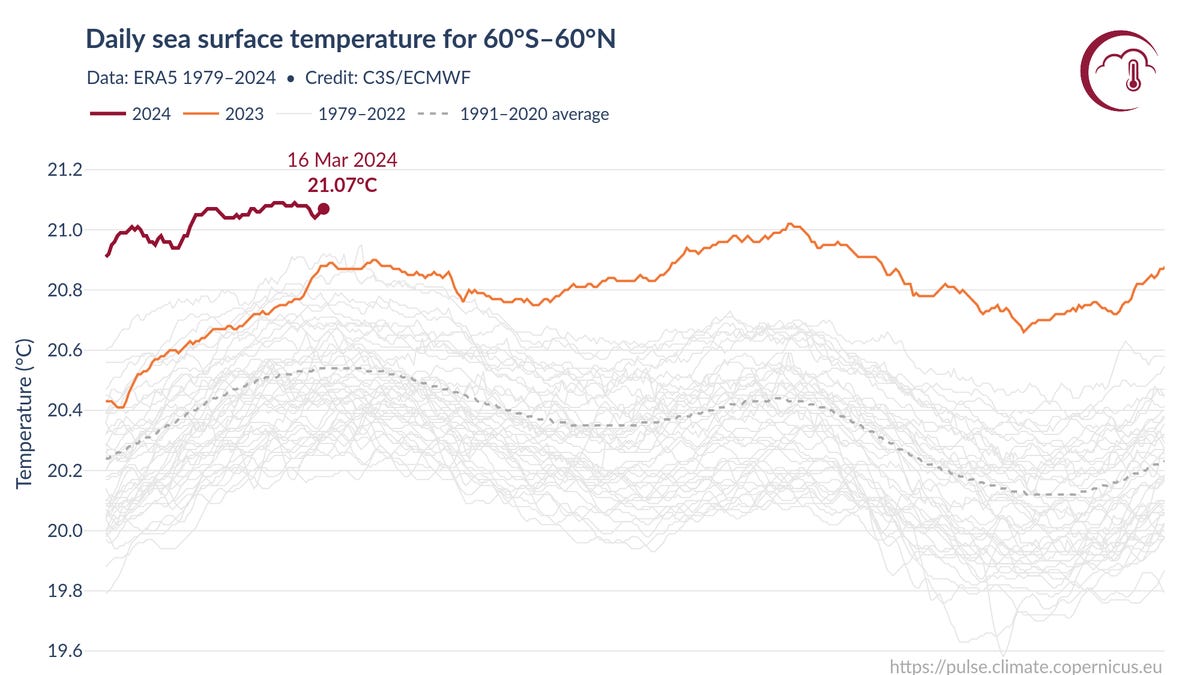
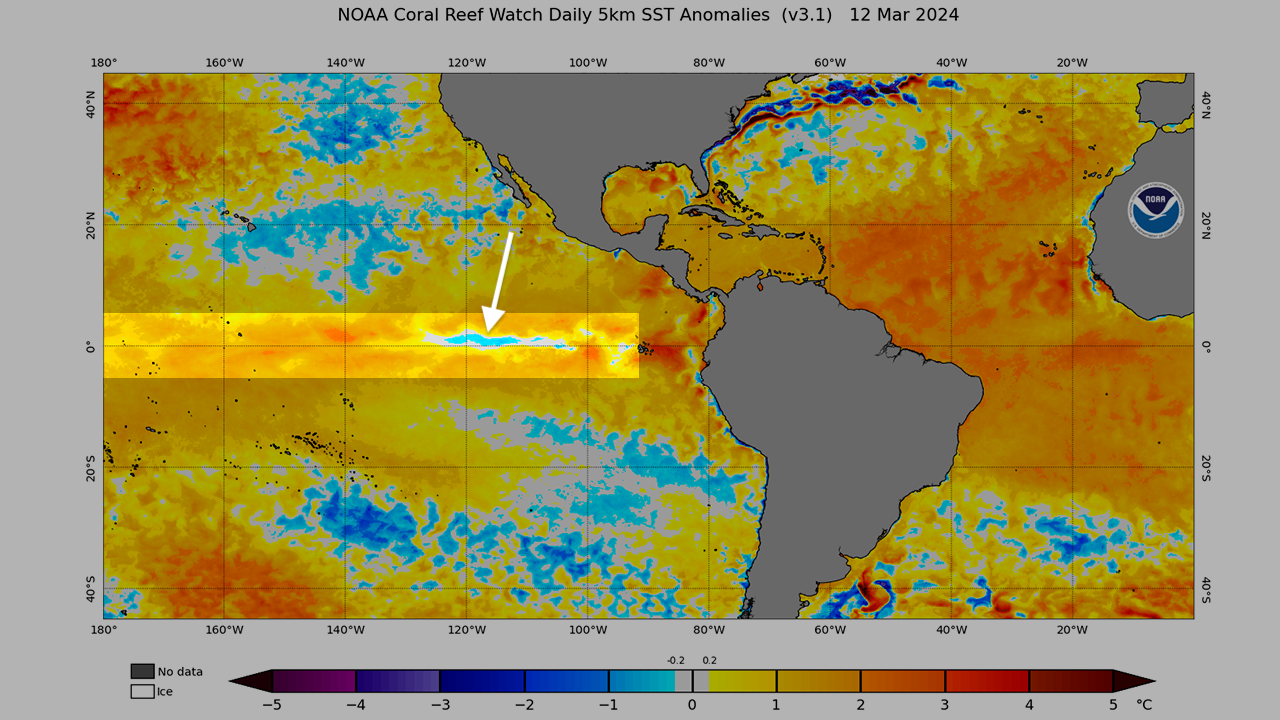
In 2025, Earth's oceans reached a record-high heat content, absorbing 23 Zetta Joules of energy, which accelerates climate change impacts such as stronger storms, rising sea levels, and more extreme weather events, with uneven warming across regions fueling unpredictable weather patterns.