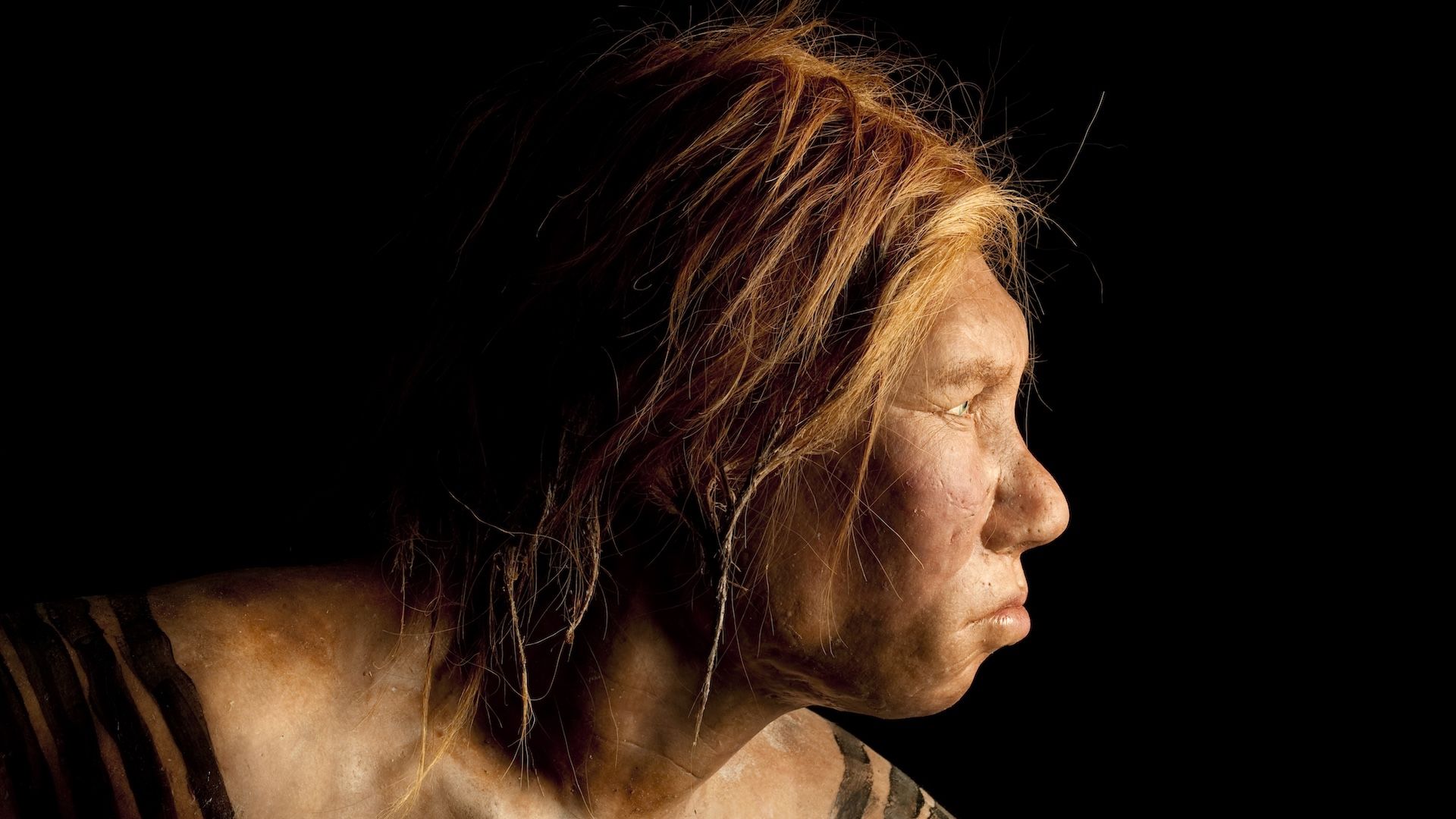
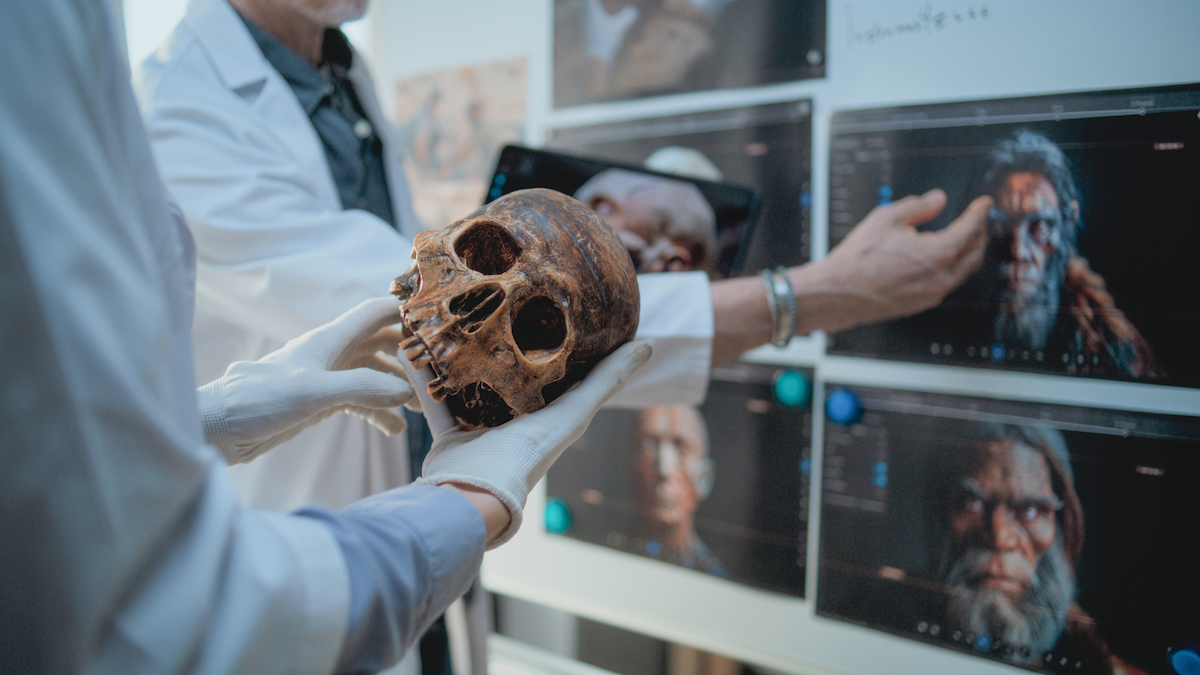
Neanderthals' vulnerability to lead poisoning gave humans an evolutionary edge
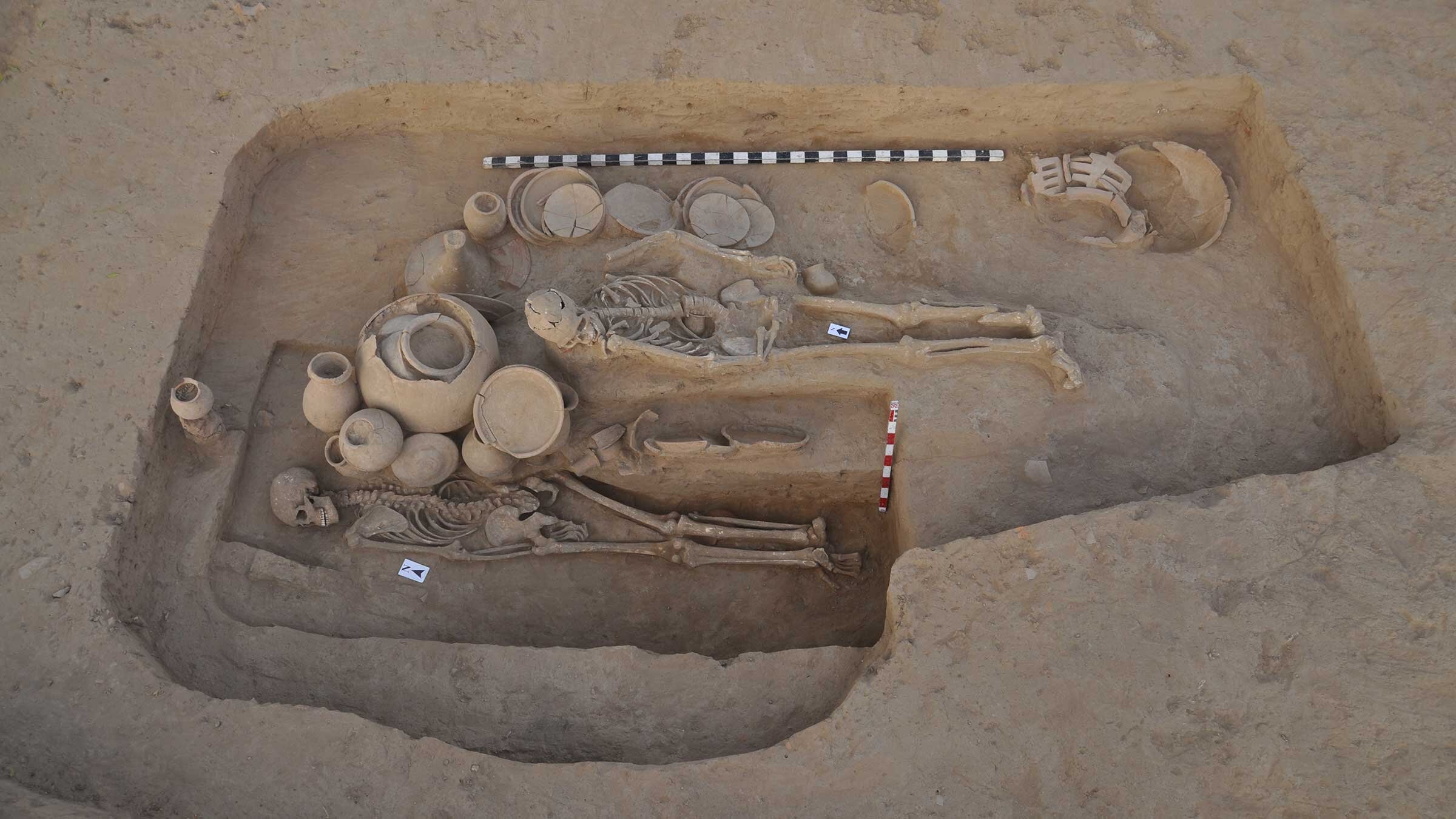
Research shows that Neanderthals were more susceptible to lead poisoning than modern humans, which may have influenced our species' communication abilities and provided an evolutionary advantage. The study suggests that exposure to lead, a toxin present for millions of years, impacted brain development and language skills, with modern humans developing gene variants that offered better protection against lead's toxic effects.