Plant Mimics Ants to Attract Pollinators
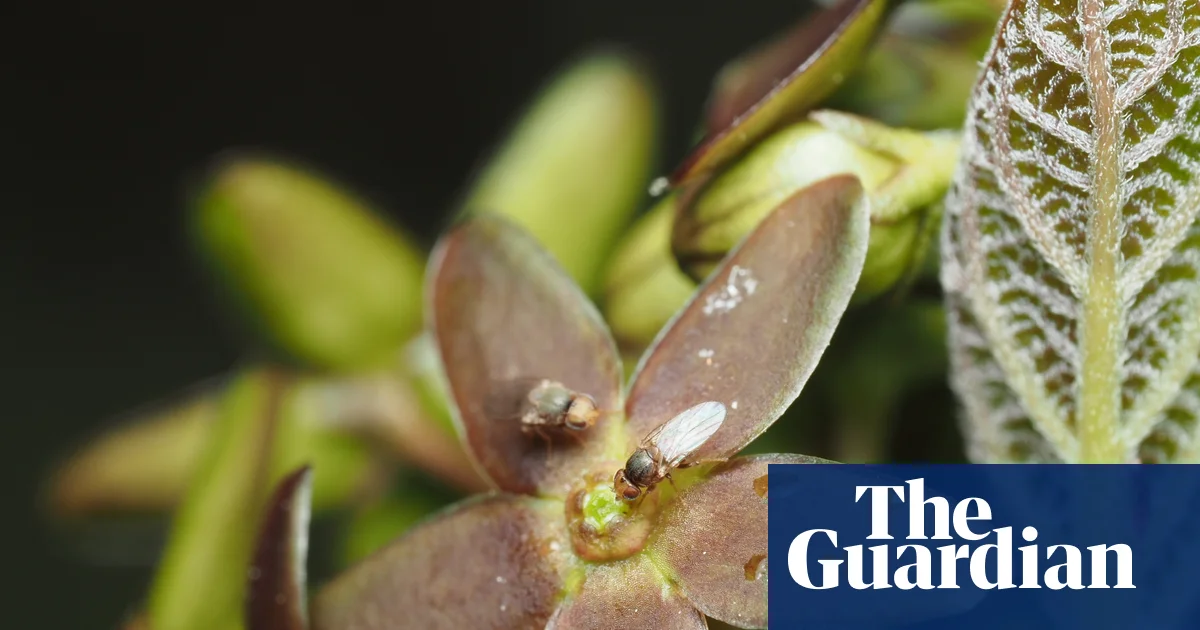
Scientists documented a Japanese plant, Vincetoxicum nakaianum, that mimics the smell of injured ants to attract flies that inadvertently pollinate it, revealing a sophisticated form of floral deception based on scent rather than visual cues.