Las Vegas raid mirrors California biolab case, prompting questions about federal response
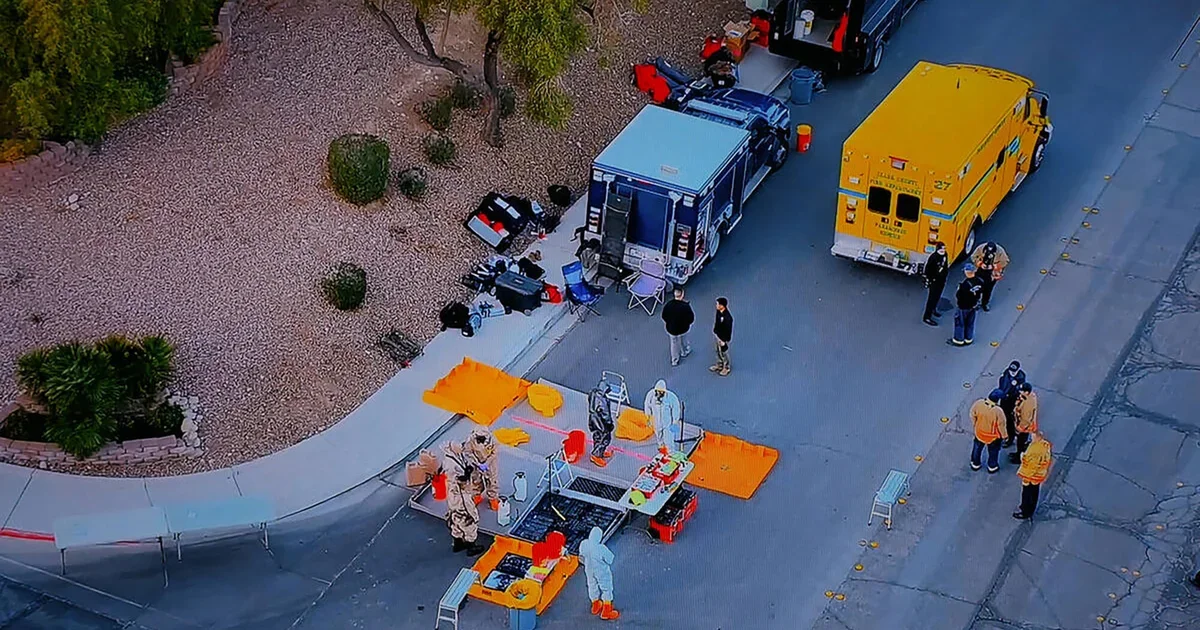
A Las Vegas home raid uncovered a lab setup with refrigerators, a freezer and lab equipment similar to a Reedley, California facility found in 2023, including pathogen-labeled containers and about 1,000 mice. The Las Vegas case is linked to Jia Bei Zhu, indicted in 2023 for distributing adulterated and misbranded medical items; authorities collected more than 1,000 samples and sent them to Maryland’s National Bioforensic Analysis Center. Officials say there may be more labs, while California officials criticized the federal response; a second Las Vegas home was searched with no suspicious materials found and a property manager, Ori Solomon, was arrested on an initial hazardous-waste disposal charge.