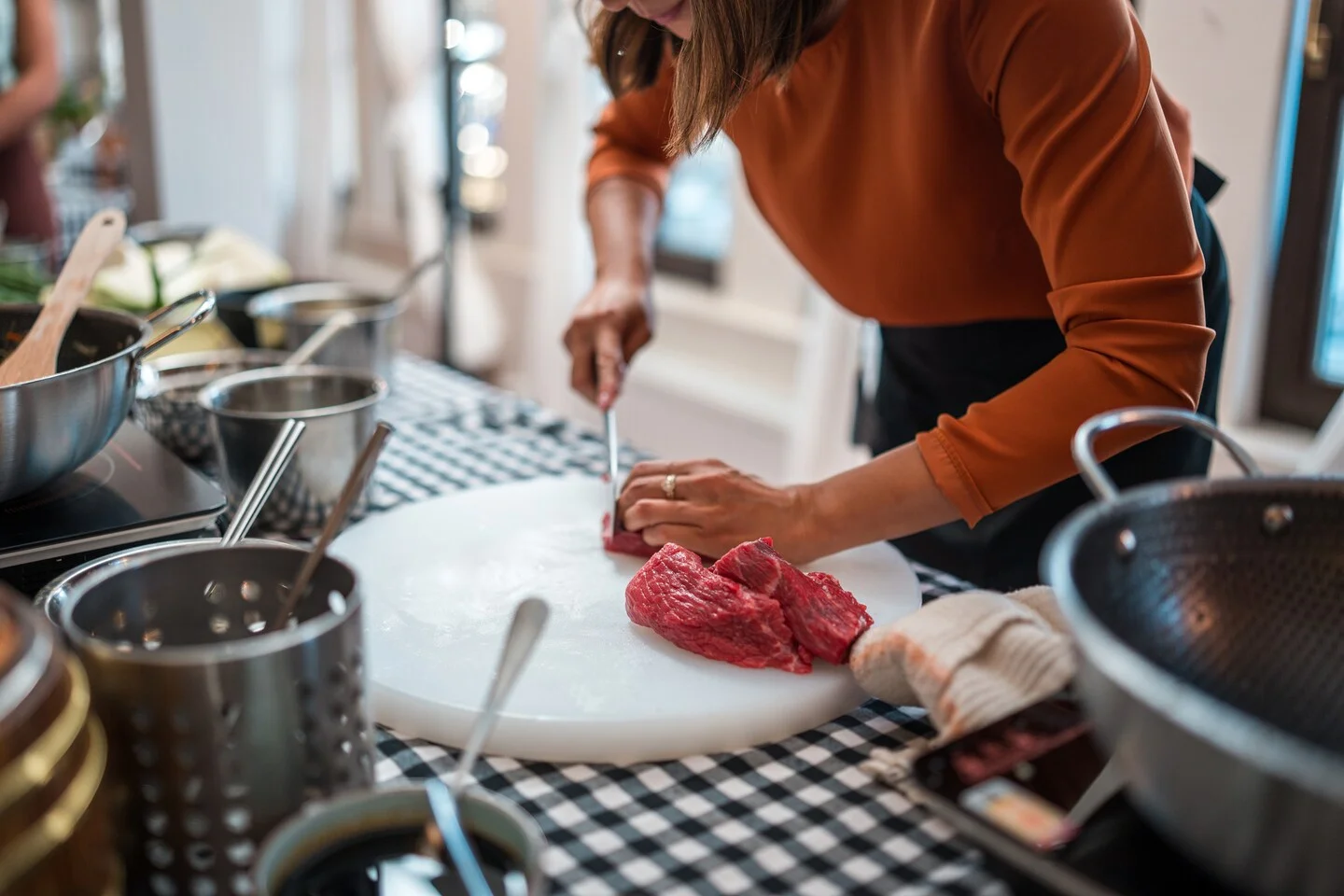
Meat and UTIs: Can what you eat affect infection risk?
A Washington Post Well+Being article explains that urinary tract infections are usually caused by bacteria, most often E. coli, and that research suggests these bacteria may originate from meat in some cases. The piece emphasizes food-safety practices and proper meat handling/cooking as potential ways to reduce risk, noting that this link may influence those with recurrent UTIs.