Ancient DNA Upends the Beachy Head Woman’s Identity
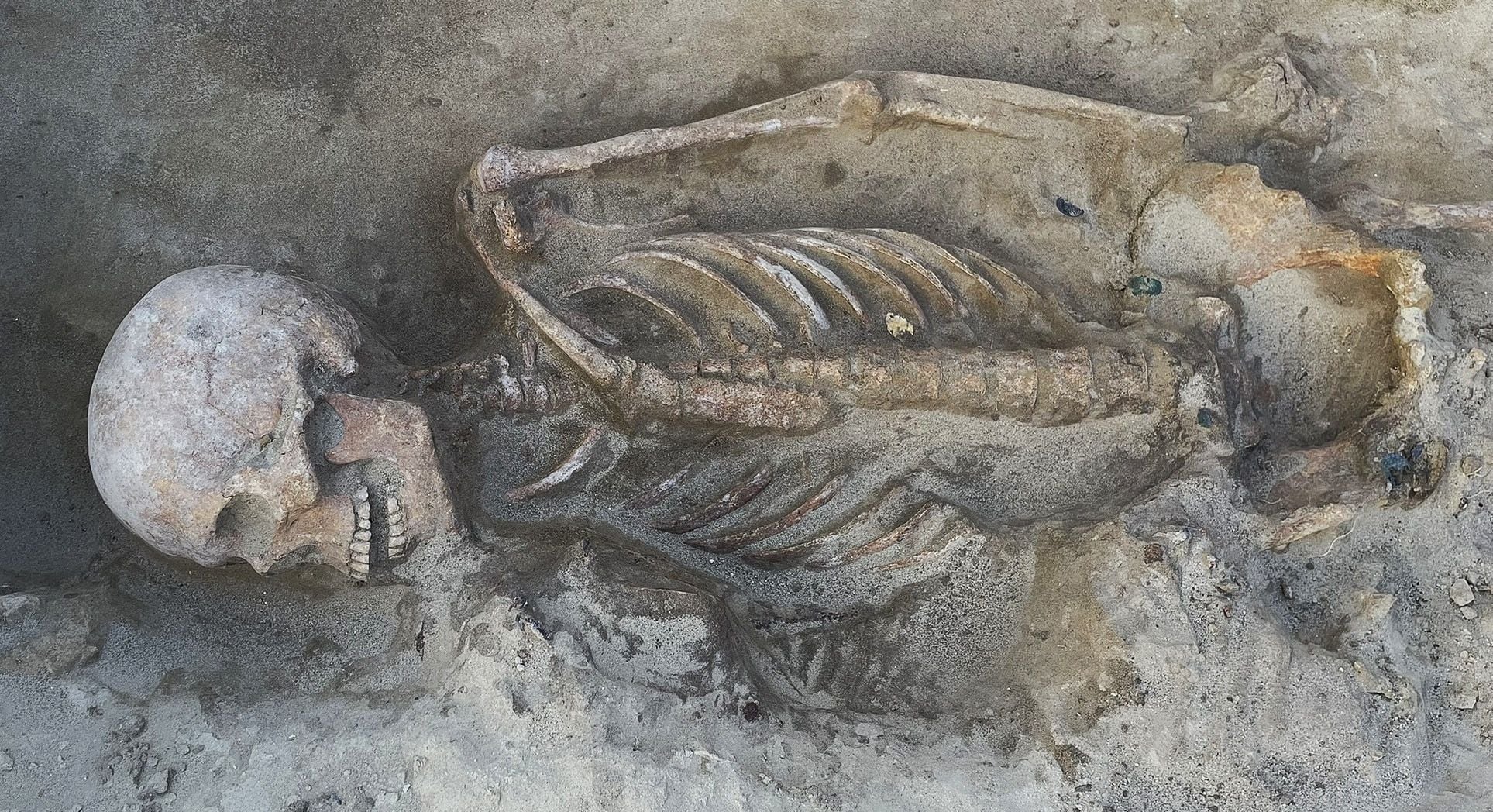
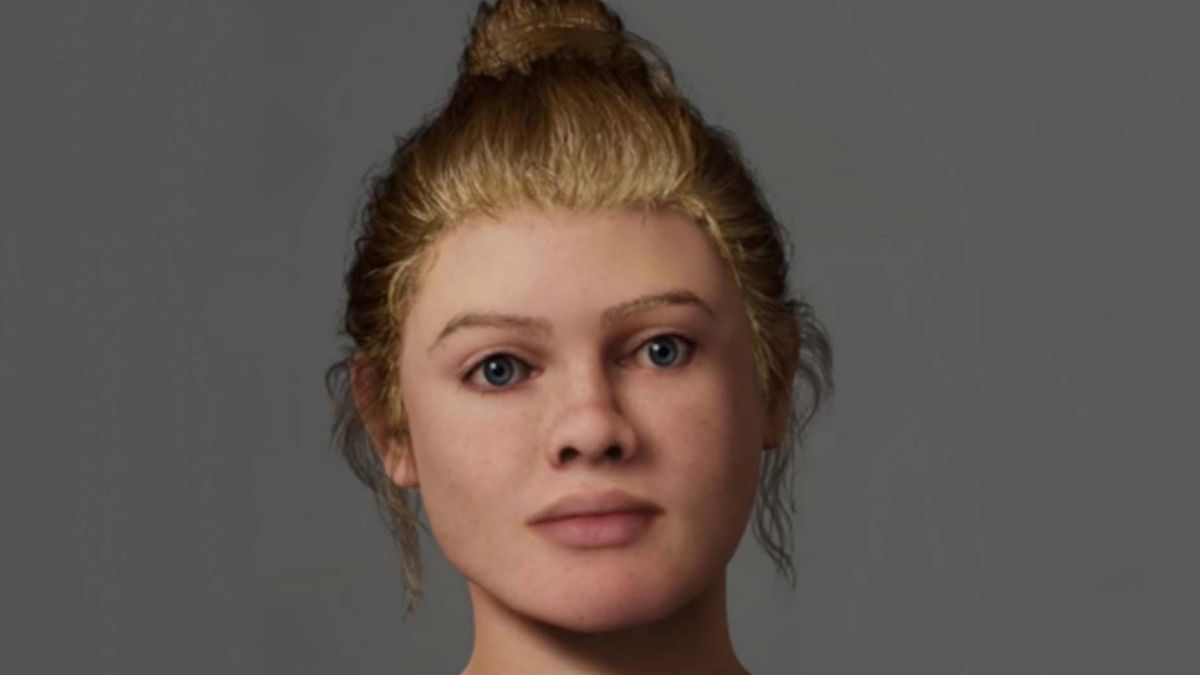
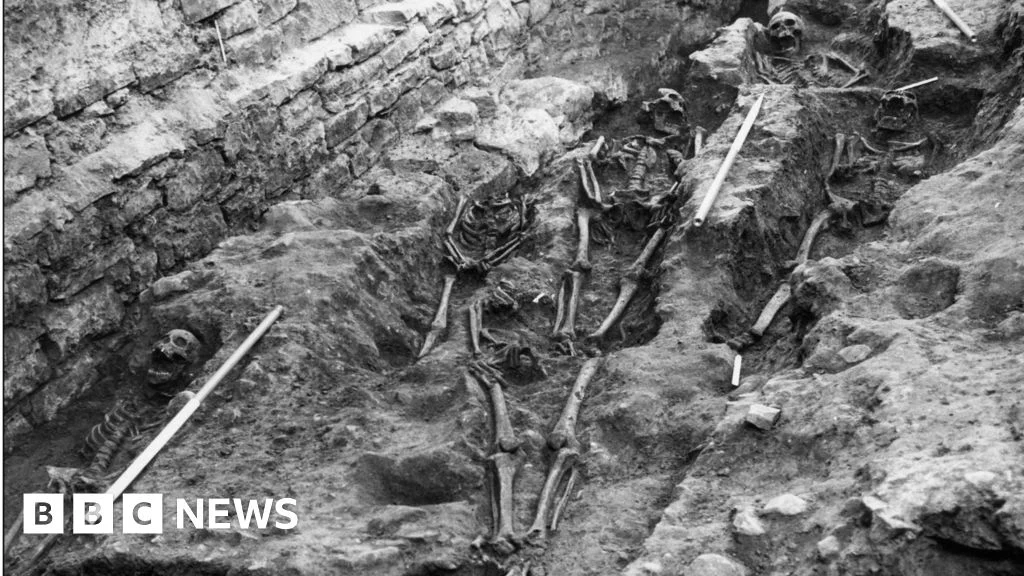
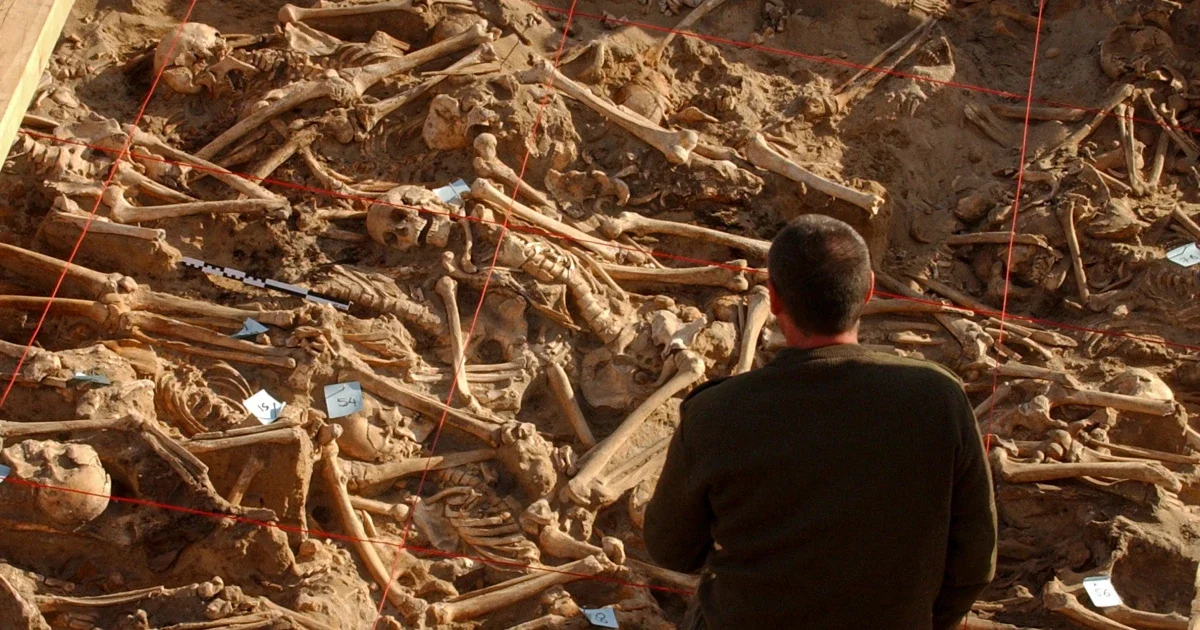
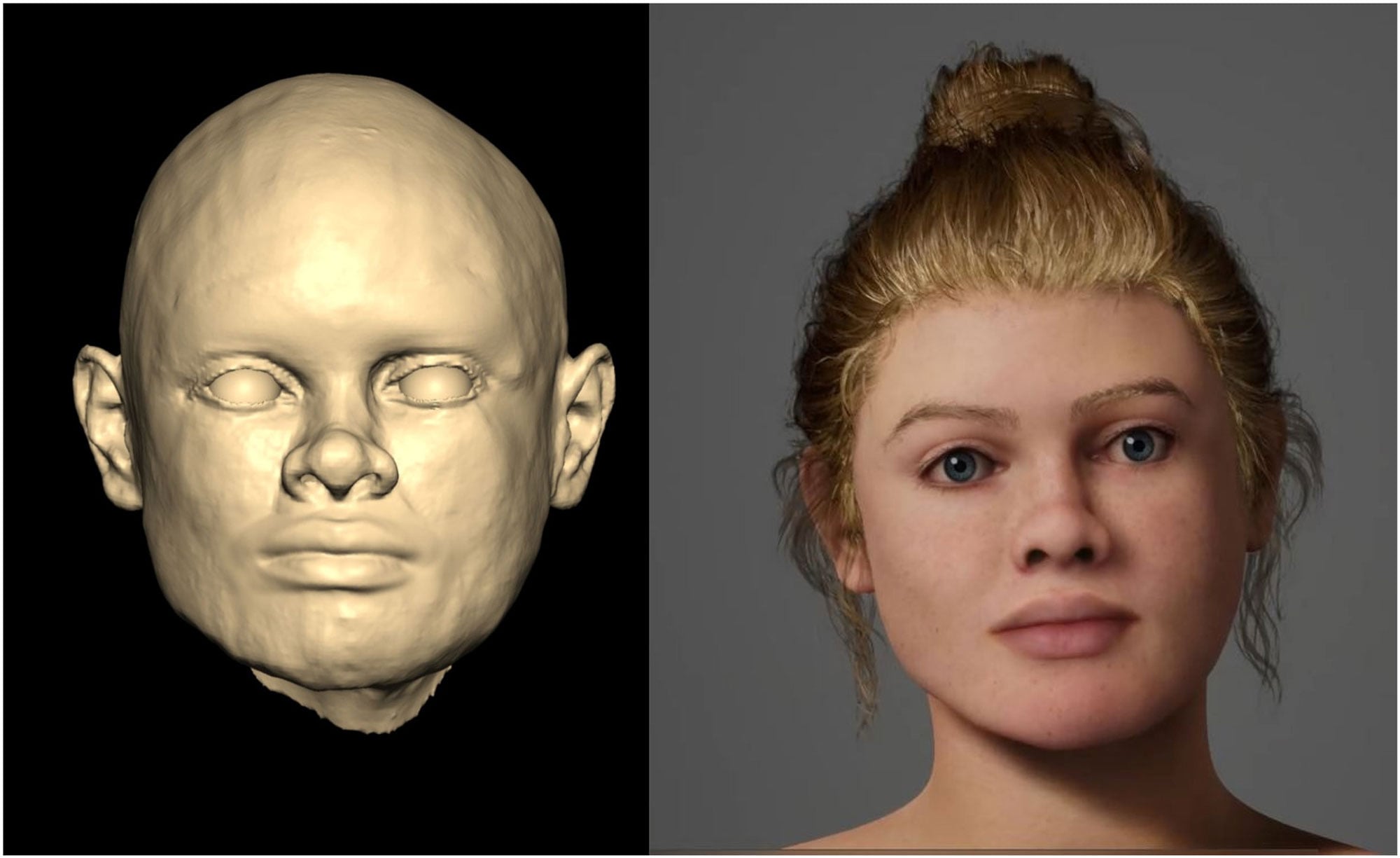
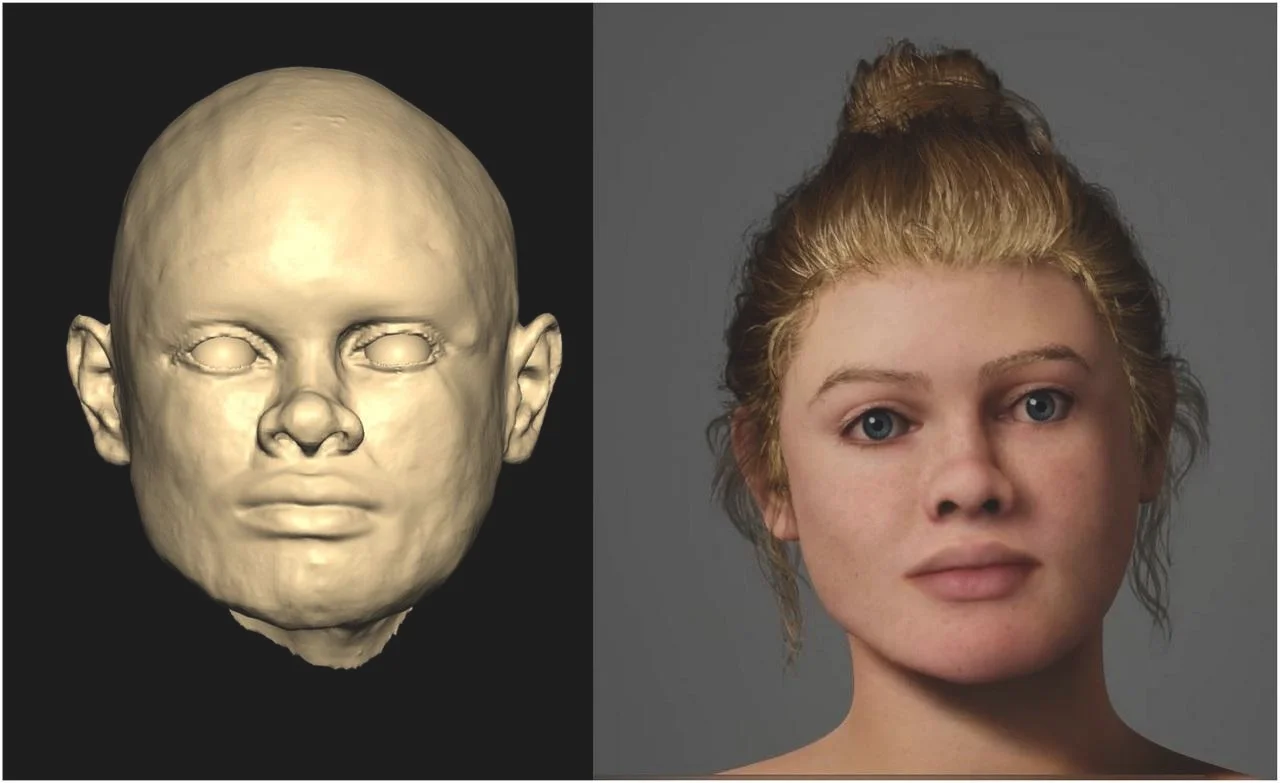
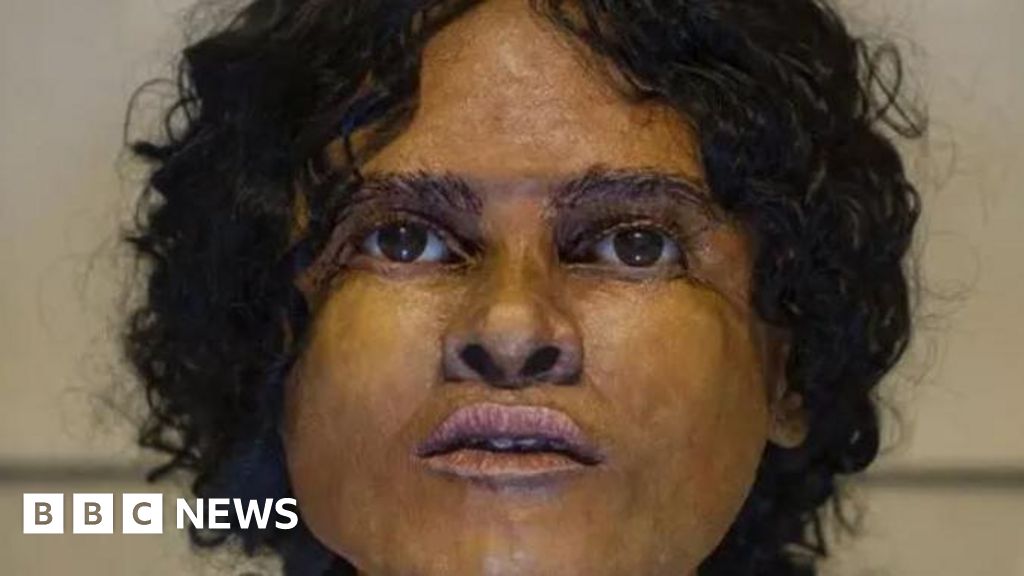
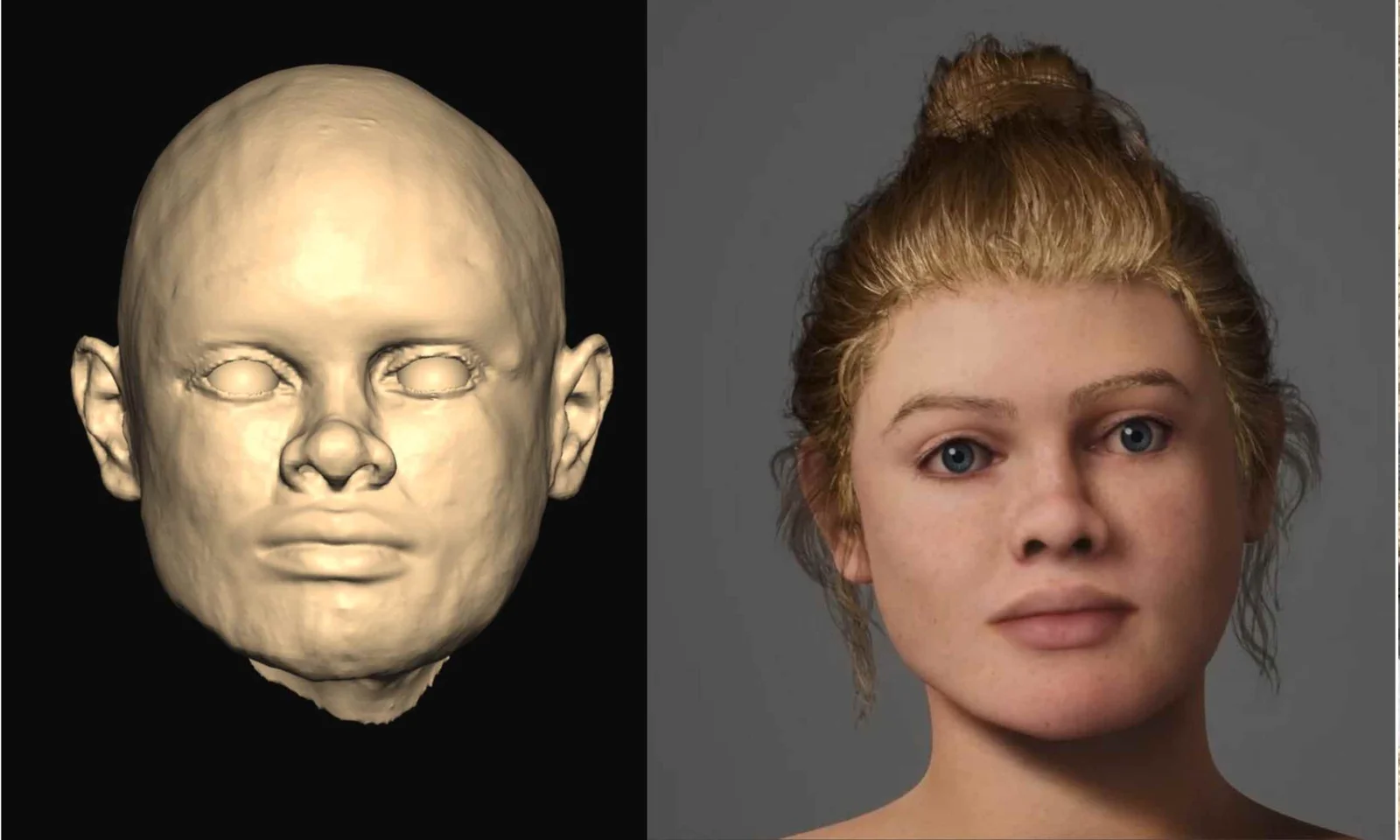
Genetic and isotopic data from the Beachy Head Woman, a 2,000-year-old skeleton, show she grew up locally in southern Britain during Roman Britain, contradicting earlier skull-based theories of African or eastern Mediterranean ancestry and highlighting the value of multi-method approaches over cranial traits alone.