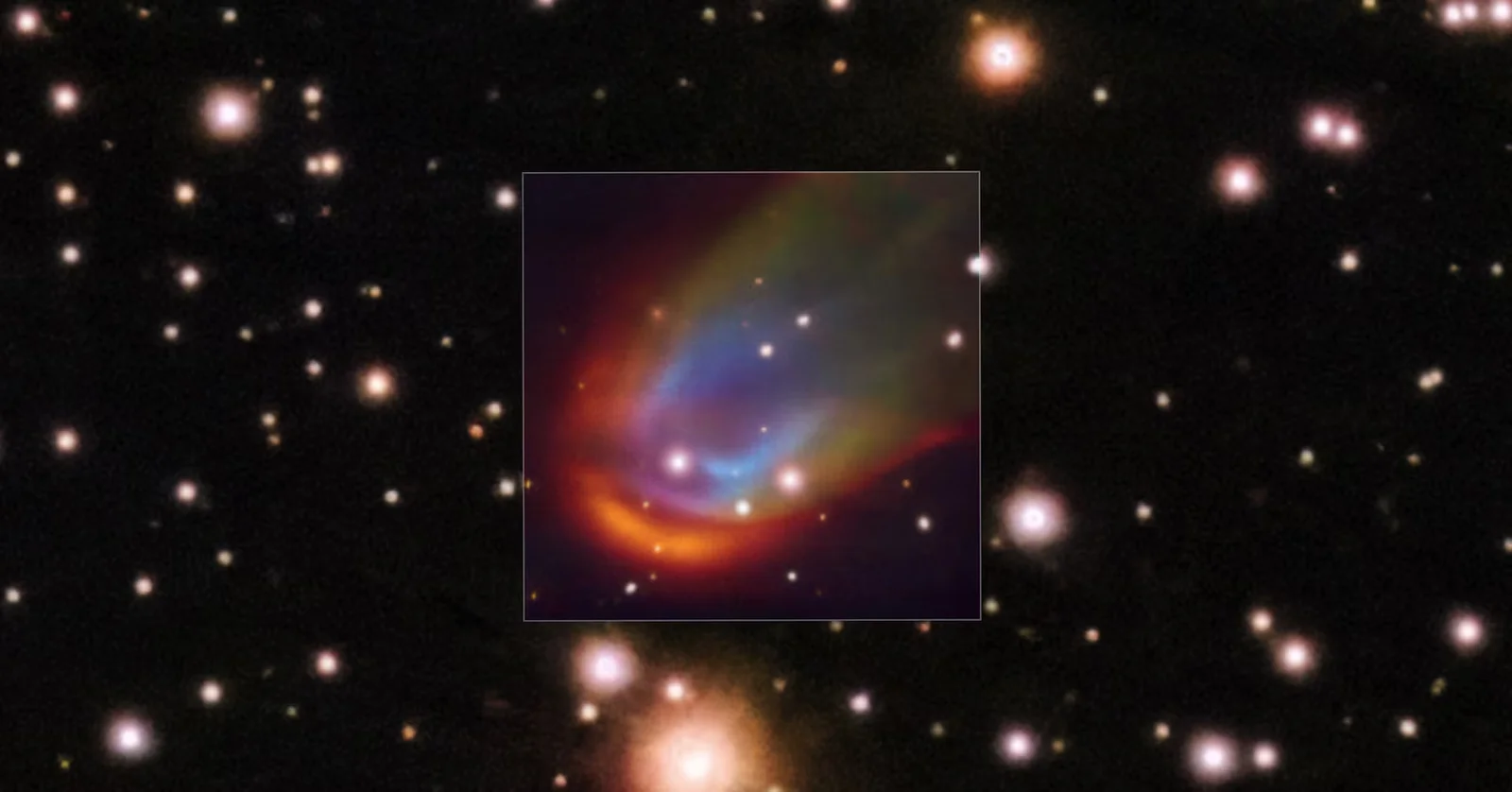
Record-breaking four-star system packs inner trio inside Mercury’s orbit
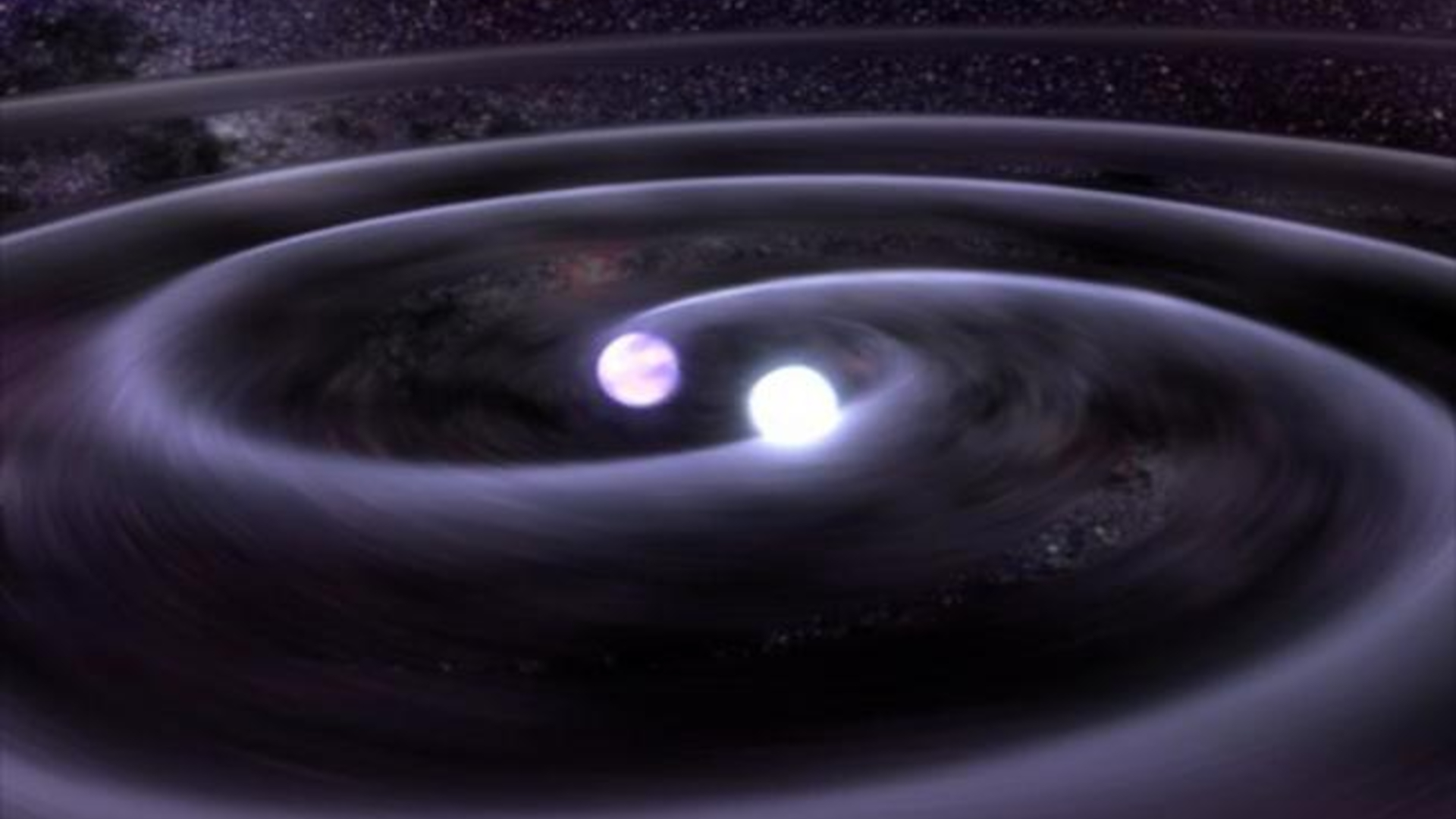
Astronomers using NASA’s TESS have found TIC 120362137, the most compact known 3+1 quadruple star system: a tightly bound inner triple is orbited by a distant fourth star, with the outer companion about the distance of Jupiter from the Sun, while the inner trio would fit inside Mercury’s orbit. This rare architecture helps scientists study how such systems form and stay stable, and simulations predict the system will eventually merge into two white dwarfs in a ~44-day orbit, a scenario described in Nature.