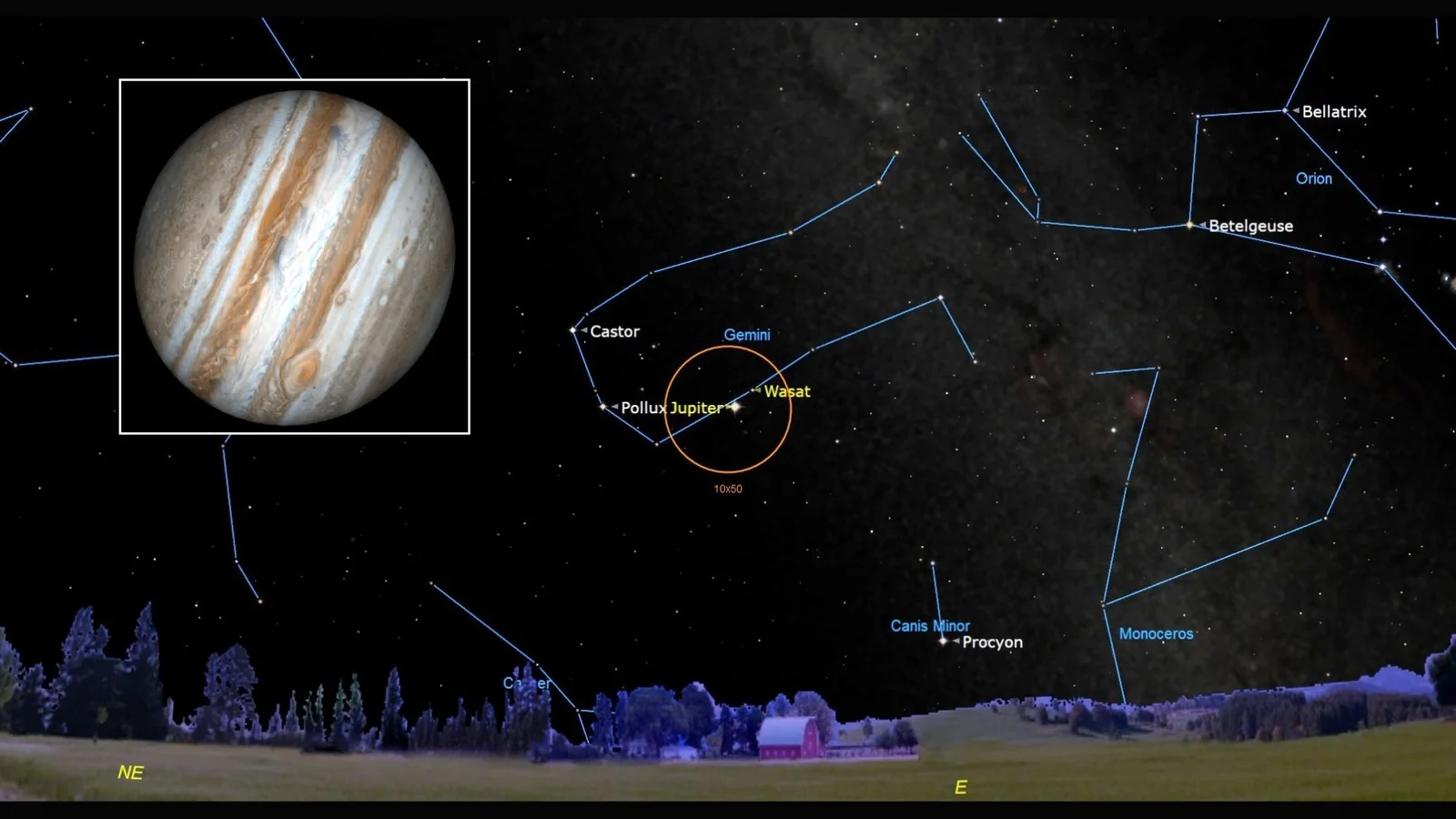
Elite skywatching gear for 2026: smart telescopes, stabilized binos, and AI-powered mounts
Space.com’s premium skywatching gear guide for 2026 highlights high-end, automation-rich equipment—from image-stabilized binoculars (Canon 18x50 IS UD; Fujifilm TS-L 16x40; Canon 10x42 L IS WP) to smart telescopes (Unistellar Envision, eVscope 2, Odyssey Pro, Vaonis Vespera Pro, Celestron Origin Mark II) and GoTo mounts (Celestron StarSense DX 130AZ, Sky-Watcher Star Adventurer GTi, Benro Polaris Astro)—emphasizing how better optics and software let you find, capture, and share celestial targets, albeit at premium prices.