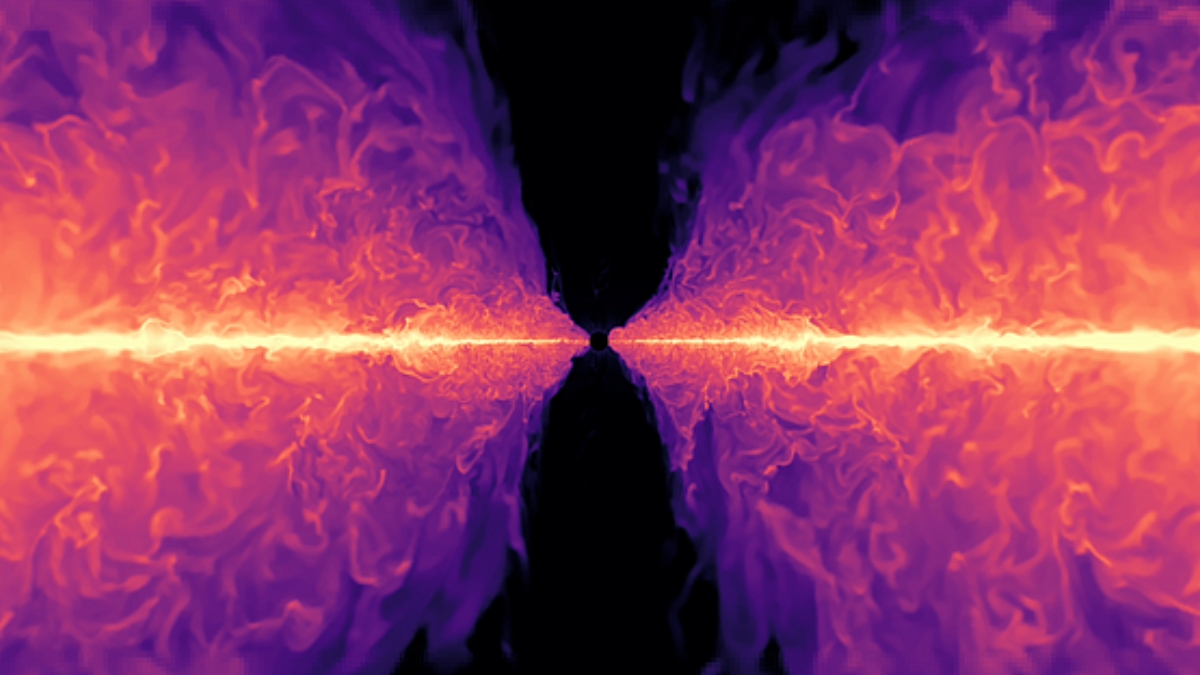
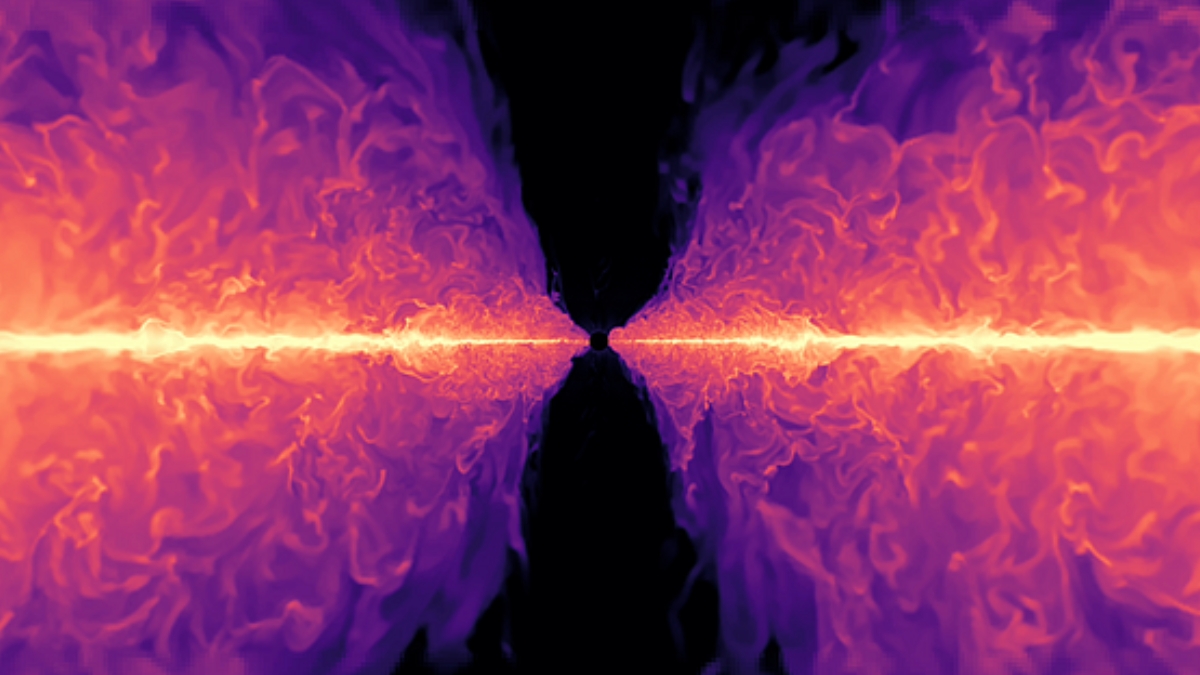
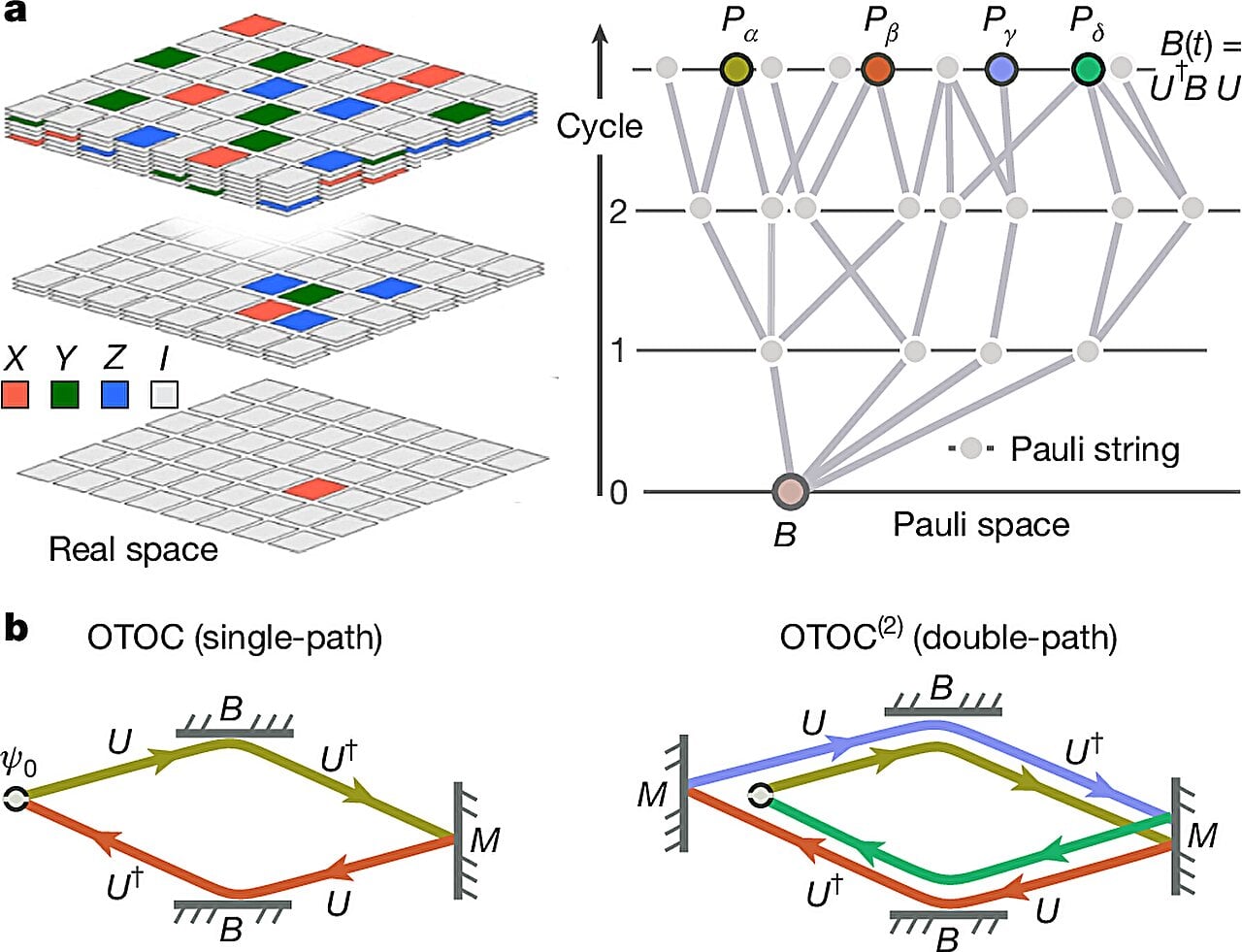
The Spin Factor: Rotation Drives Element Mixing in Red Giants
Researchers using high-resolution 3D simulations on powerful supercomputers found that stellar rotation greatly enhances the mixing of elements from a star’s core to its surface, explaining observed chemical changes in red giants; rotating stars mix materials over 100 times faster than non-rotating ones, revealing rotation as a key driver of stellar evolution and informing predictions for the Sun’s future.