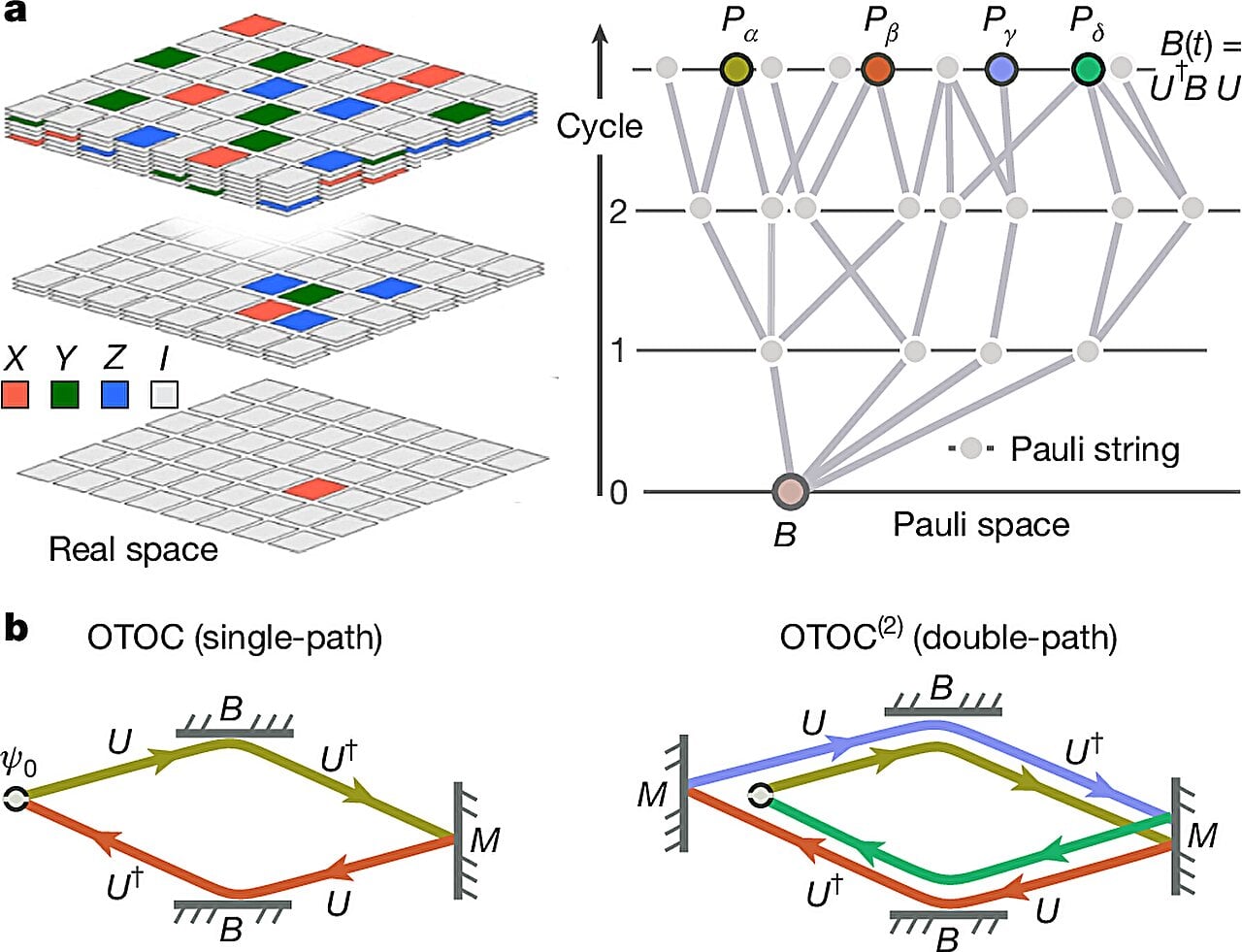
IBM Advances Quantum Technology with New Chips and Breakthroughs
IBM unveiled advanced quantum processors, including the Nighthawk with 120 qubits, aiming for quantum advantage by 2026 and fault tolerance by 2029, bringing quantum computing closer to practical, large-scale applications, though still far from threatening Bitcoin's cryptography.