Deep mantle shift links rivers as Green River climbs 100 miles
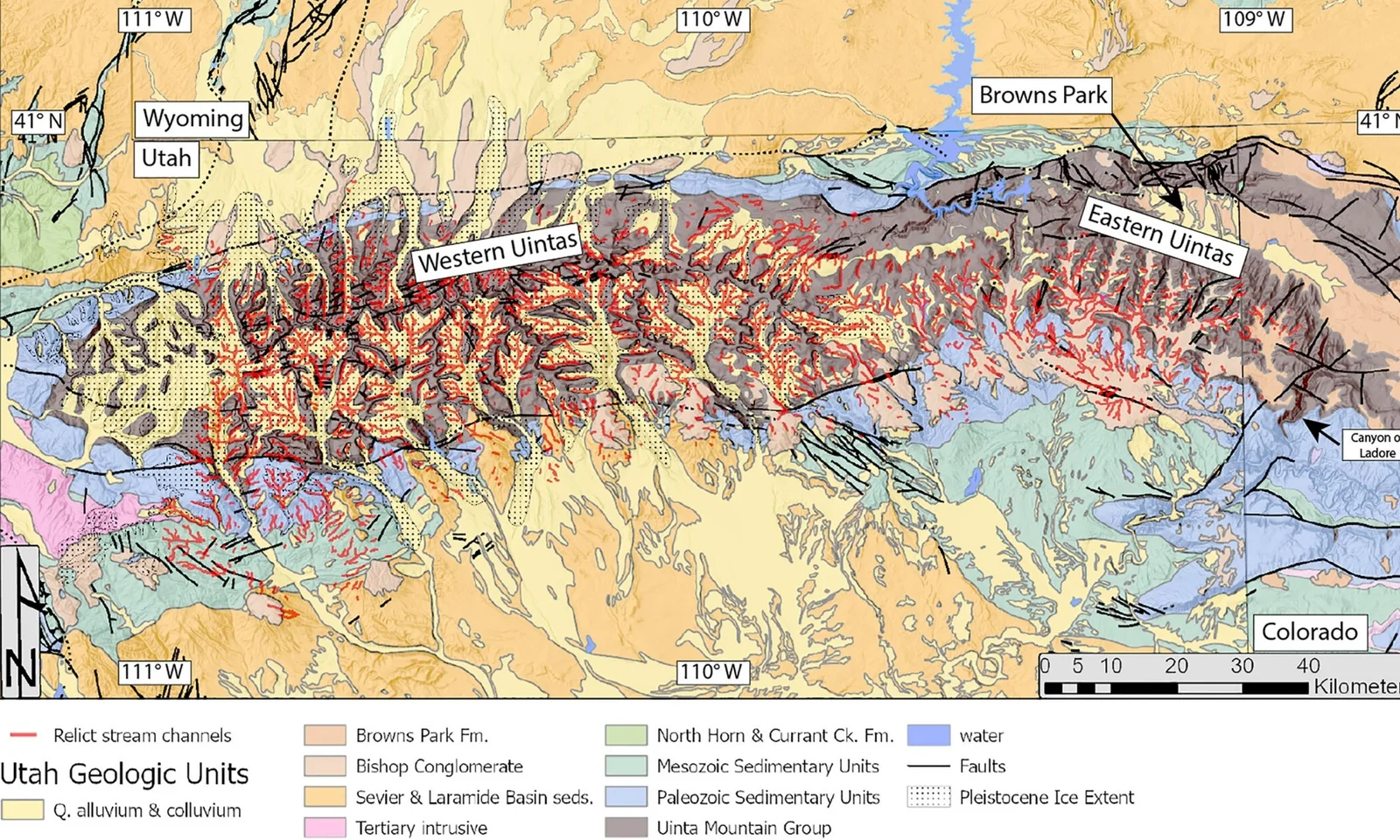
Geologists say a deep lithospheric drip beneath the Uintas briefly lowered a barrier, allowing the Green River to cut uphill and merge with the Colorado River for about 99–100 miles in northeastern Utah. The event is dated to roughly 2.3–4.7 million years ago and is supported by sediment records and seismic imaging showing a mantle root beneath the mountains. This deep-earth movement helped shift the continental drainage divide, enabled fish to mix between basins, and helped carve the Canyon of Lodore, illustrating how subterranean processes shape surface rivers.