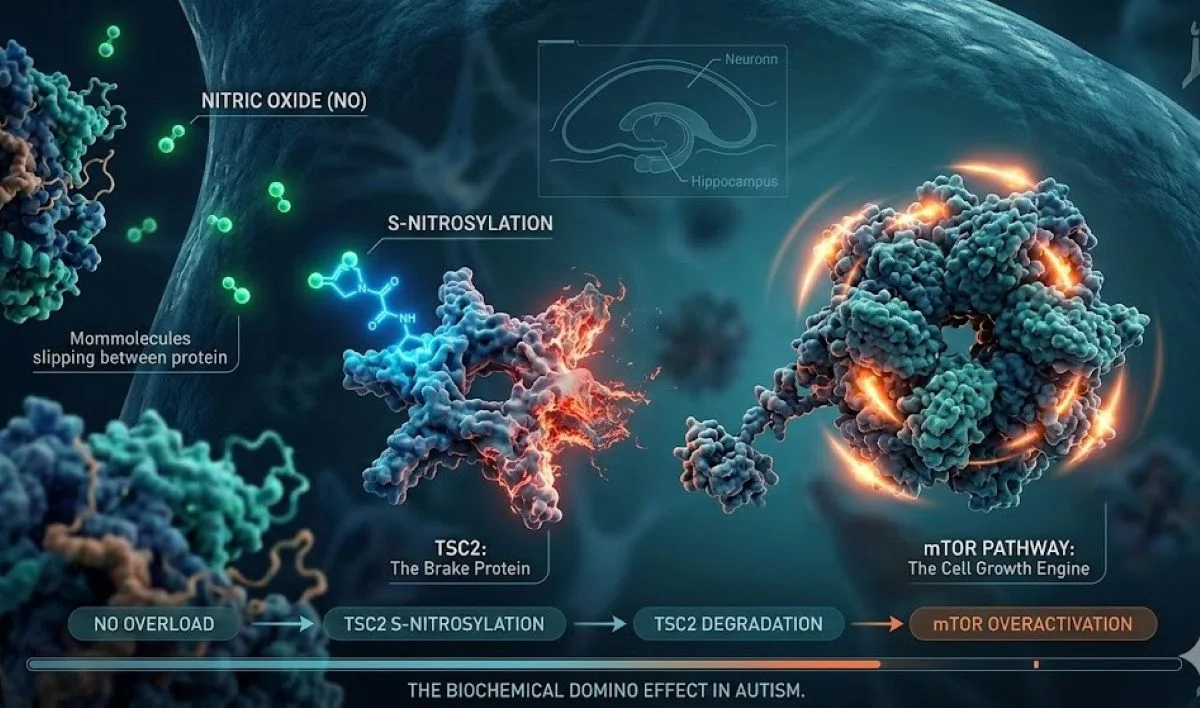
Nitric Oxide Triggers TSC2 Loss, Overactivates mTOR in Autism
Excess nitric oxide can modify TSC2 via S-nitrosylation, marking it for destruction and removing the mTOR 'brake.' With TSC2 diminished, mTOR activity surges, disrupting neuronal signaling in autism models. Blocking NO signaling or engineering a NO-resistant TSC2 normalized mTOR and improved related cellular readouts in SHANK3 and CNTNAP2 mouse models, and clinical samples from children with SHANK3 mutations and idiopathic ASD showed reduced TSC2 and elevated mTOR, supporting a NO–TSC2–mTOR mechanism and suggesting nitric oxide inhibitors as a potential ASD therapy and biomarker target.