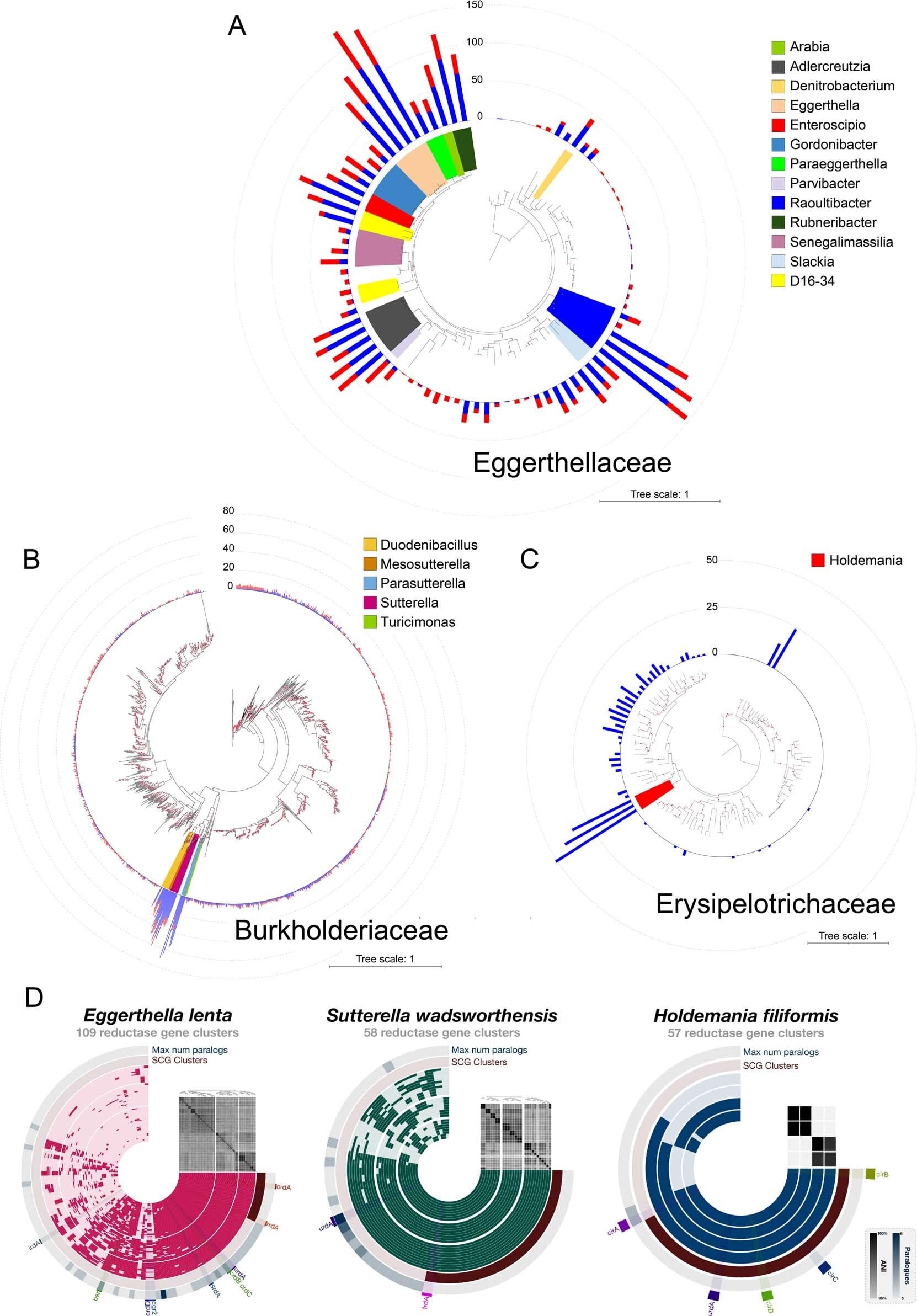
Harvard research uncovers gut-based strategies to combat obesity and diabetes
A Harvard-supported study identified gut-derived metabolites that influence liver function and insulin sensitivity, offering potential new strategies for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes by understanding how gut microbiome interactions affect metabolic health.