CT Scans of Giant Hailstones Reveal Clues for Storm Prediction
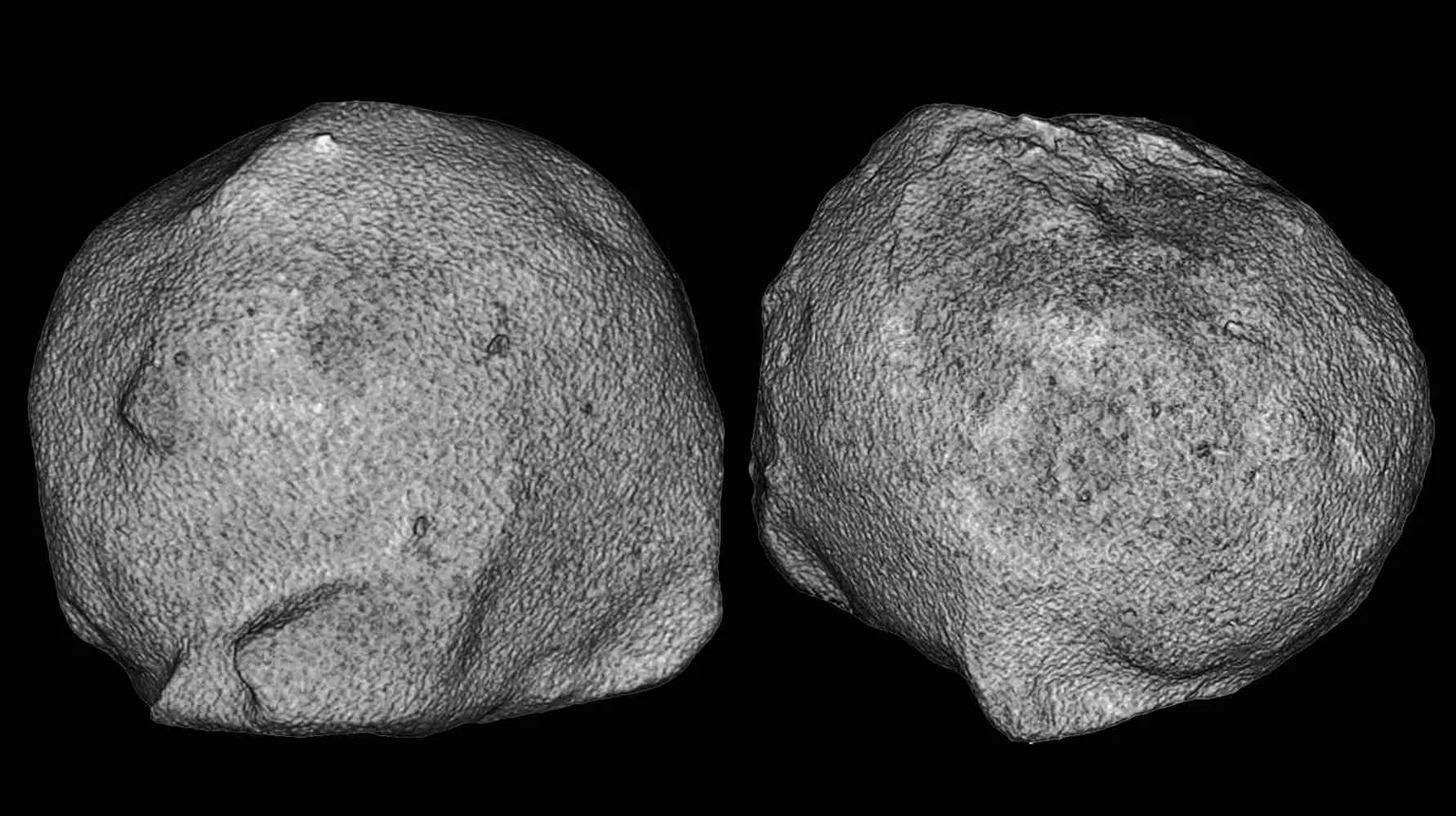
In August 2022, Catalonia experienced a severe hailstorm with giant hailstones causing injuries and damage. Researchers used CT scanning to study the internal structure of these hailstones without destroying them, revealing surprising insights into their formation. The study, published in Frontiers in Environmental Science, found irregular internal axes and uneven growth processes, challenging previous assumptions about hailstone shapes. Despite challenges like high costs, the findings could improve hail forecasting and help mitigate damage from extreme weather events.