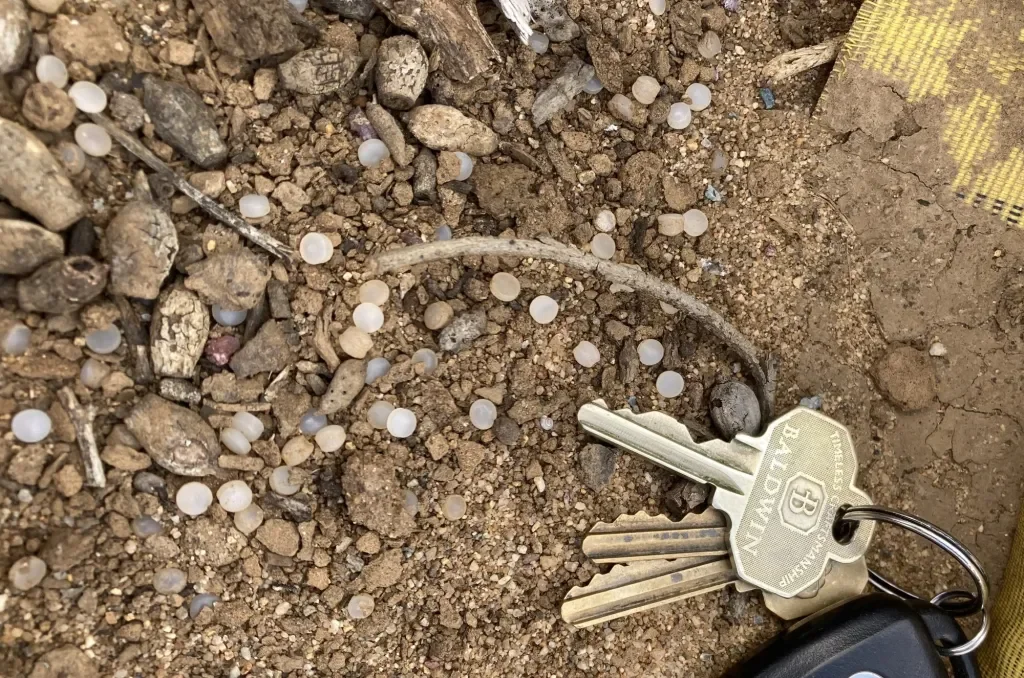
San Diego rail nurdle settlement tightens transport rules for plastic pellets
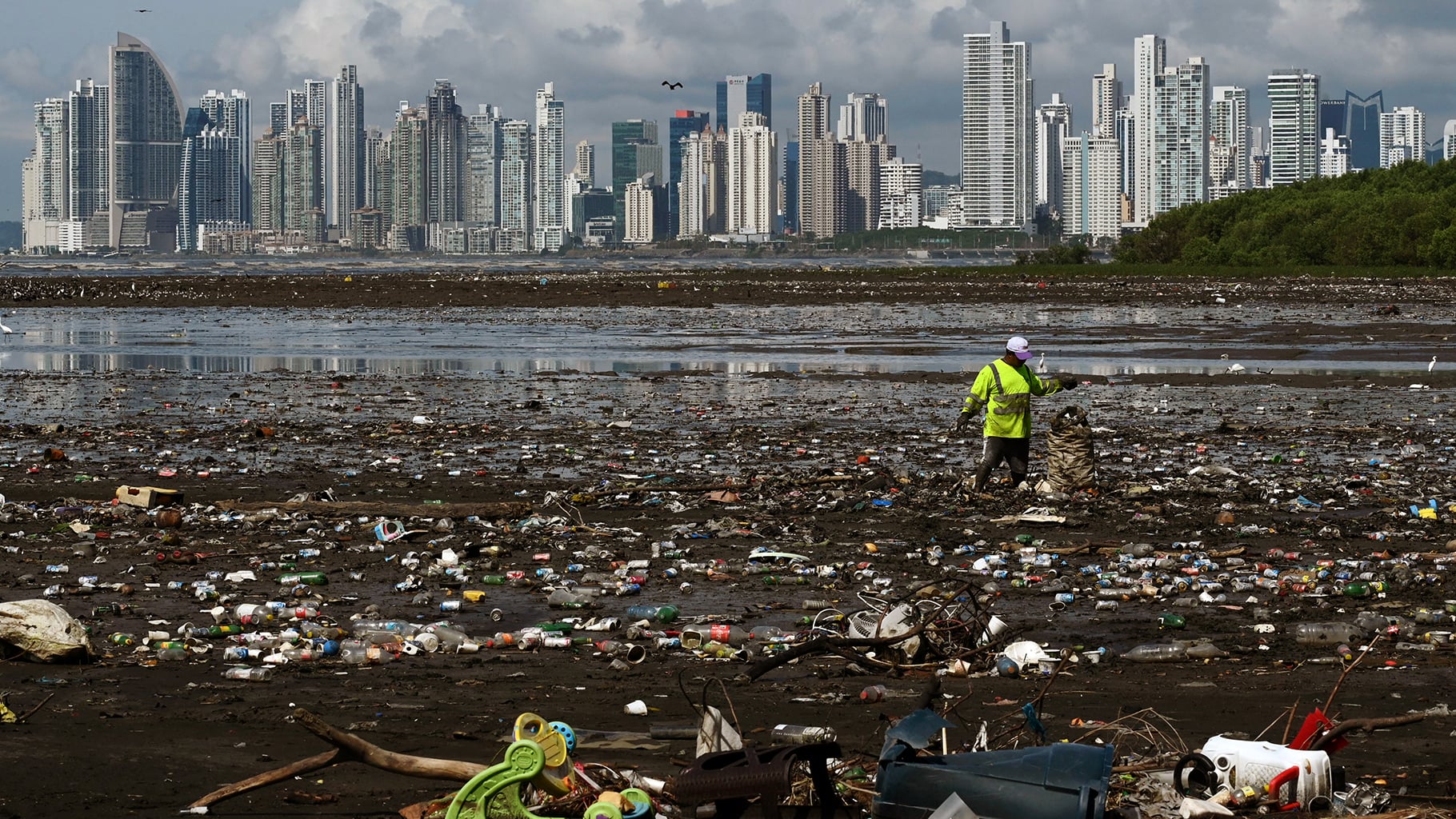
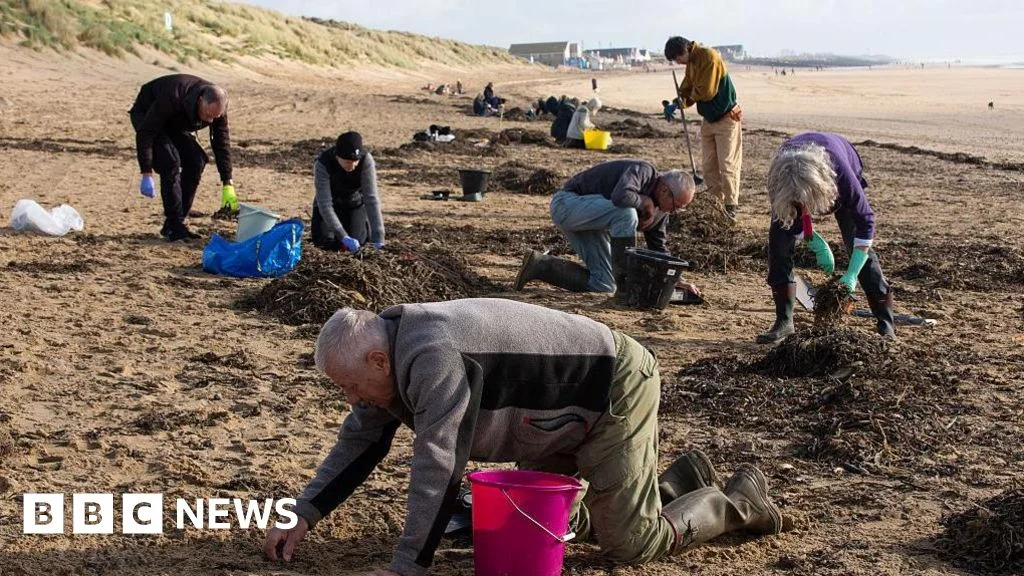
A settlement over nurdle spills along San Diego-area rail lines leads BNSF Railway, the Coastal Environmental Rights Foundation, San Diego Coastkeeper, and the North County Transit District to adopt nationwide policies requiring sealed plastic-pellet rail cars, penalties for non-compliance, and a donation to local cleanup efforts, in an effort to curb plastic-pellet pollution.