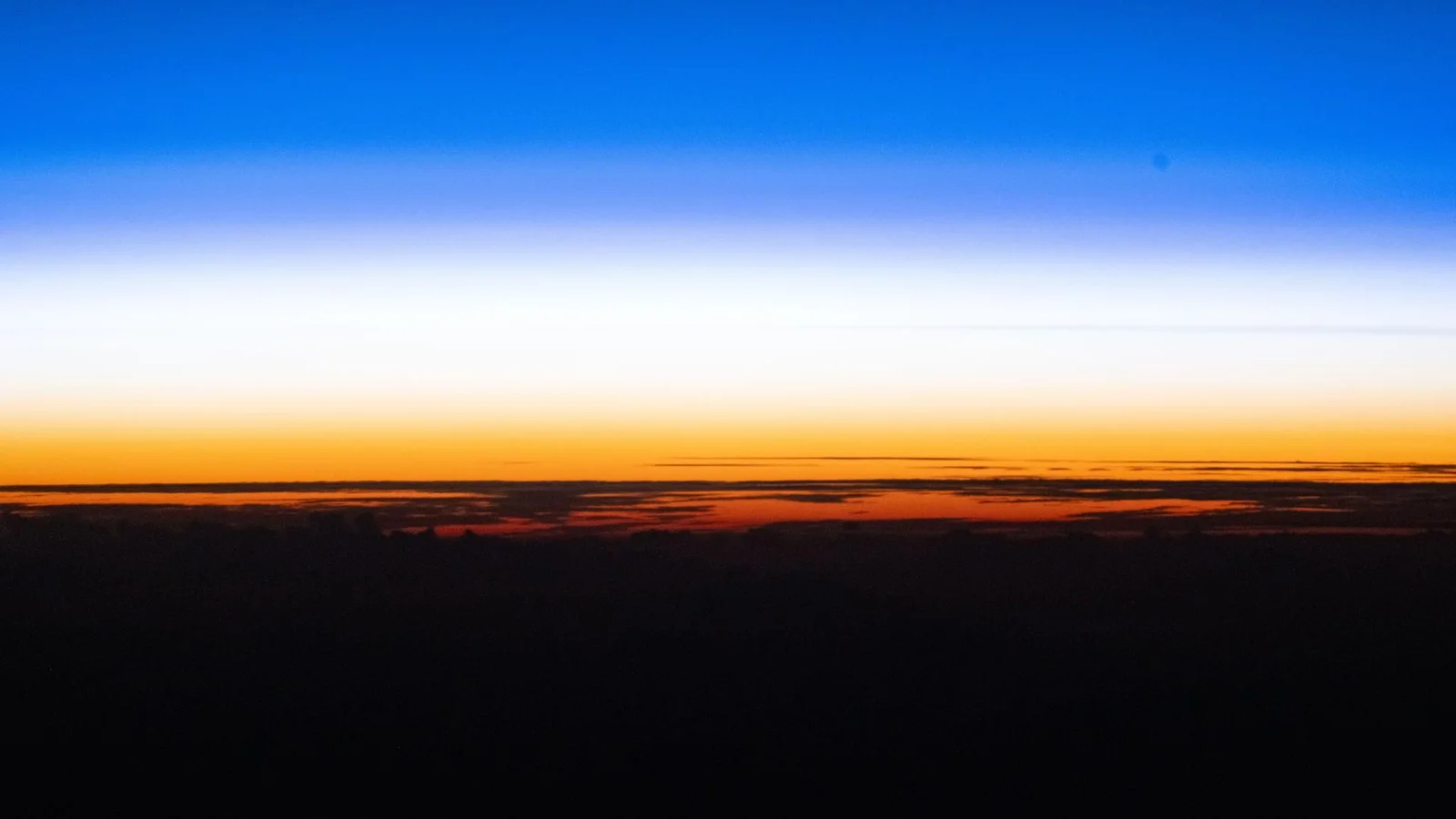
Golden Hour Over Earth: ISS Captures Sunset from Space
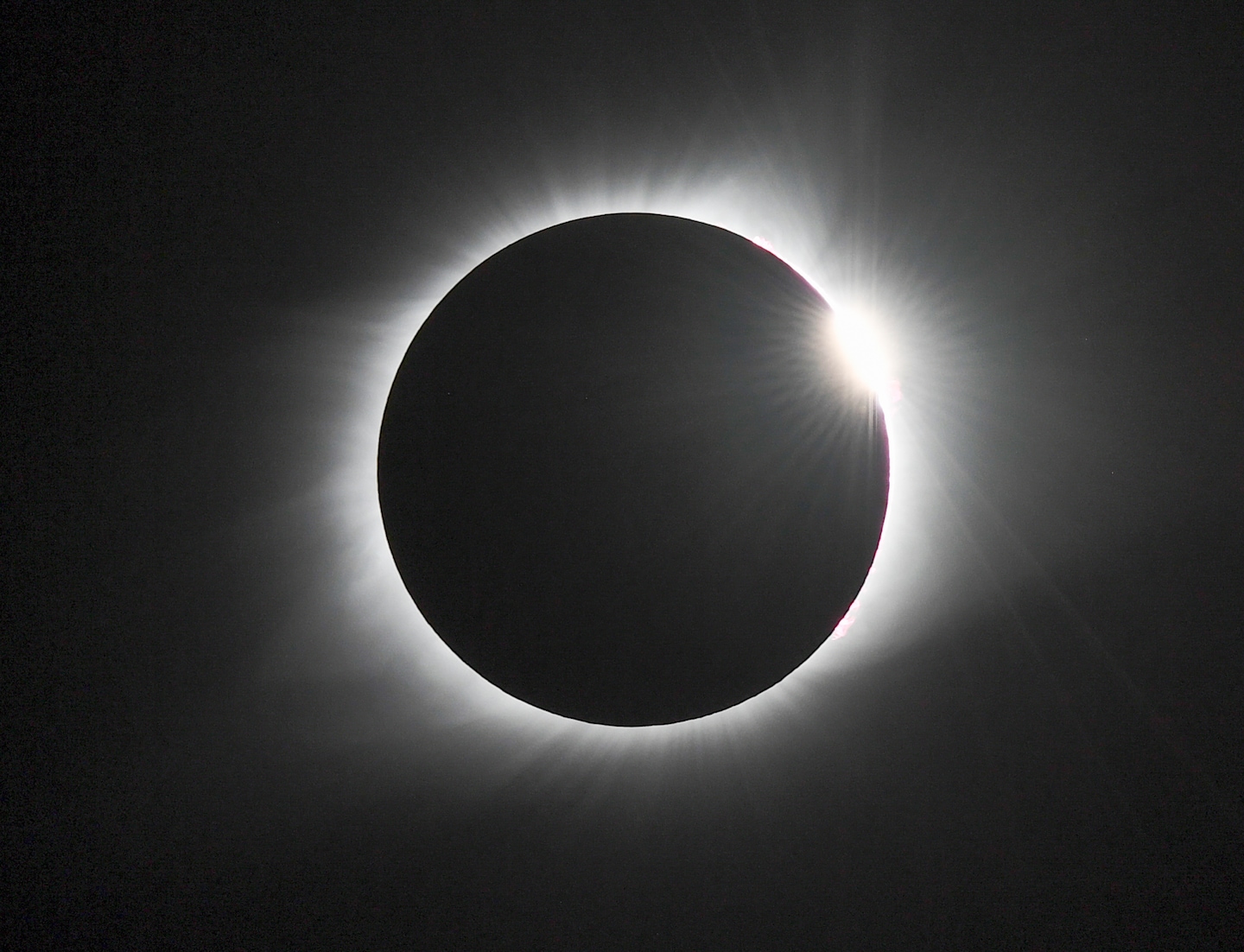
A sunset over the Pacific is captured by astronauts aboard the International Space Station, which orbits roughly 250 miles above Earth and experiences about 15–16 sunrises and sunsets each day. The image highlights Earth's curved silhouette and the vivid colors produced as sunlight passes through the atmosphere at a different angle, offering a unique perspective on our planet and the ongoing work aboard the ISS.