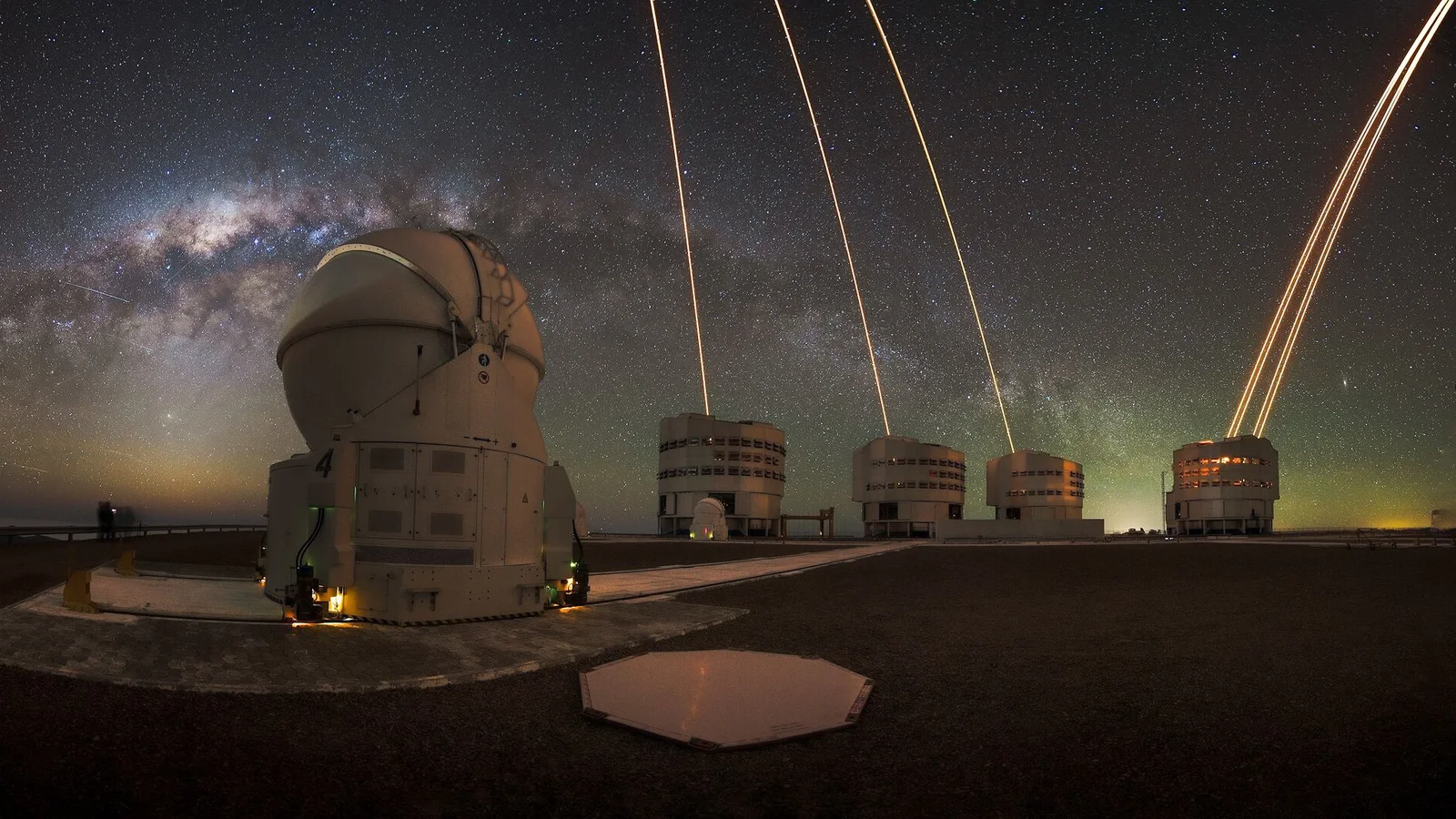
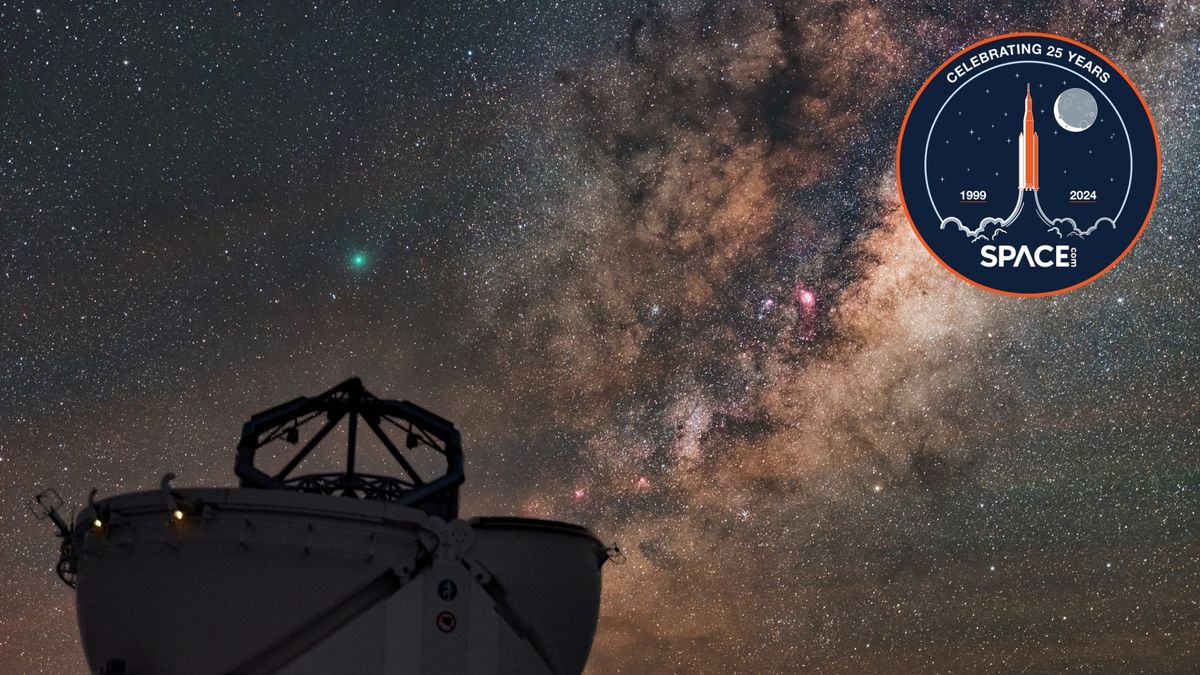
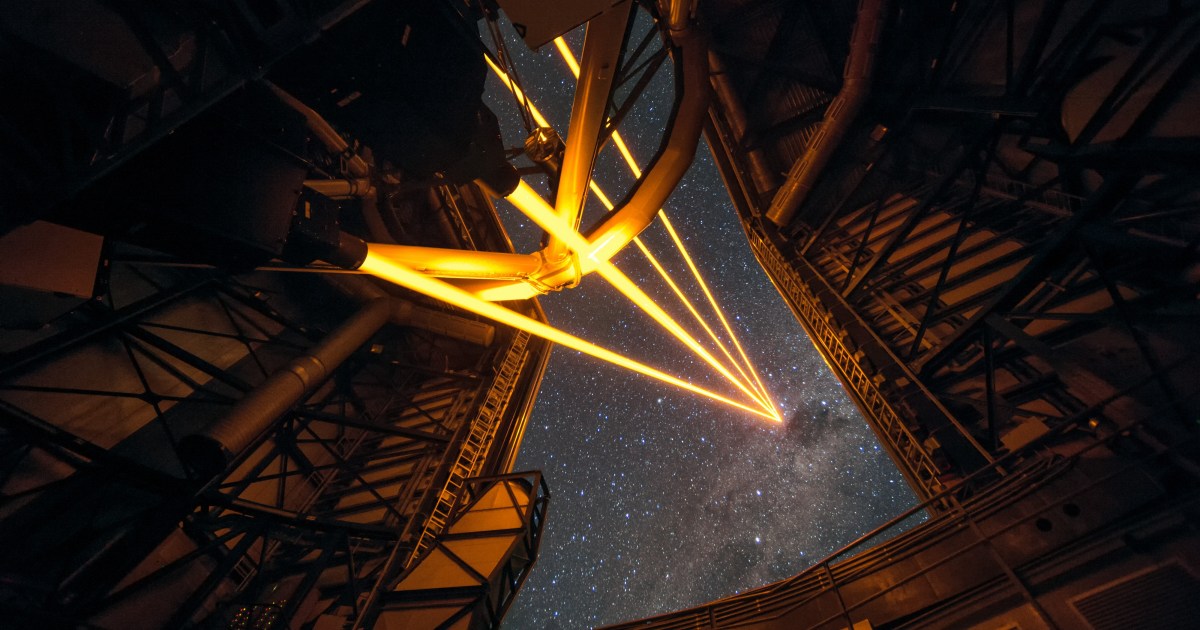
Artificial stars rise over Chile as VLT lasers power adaptive optics
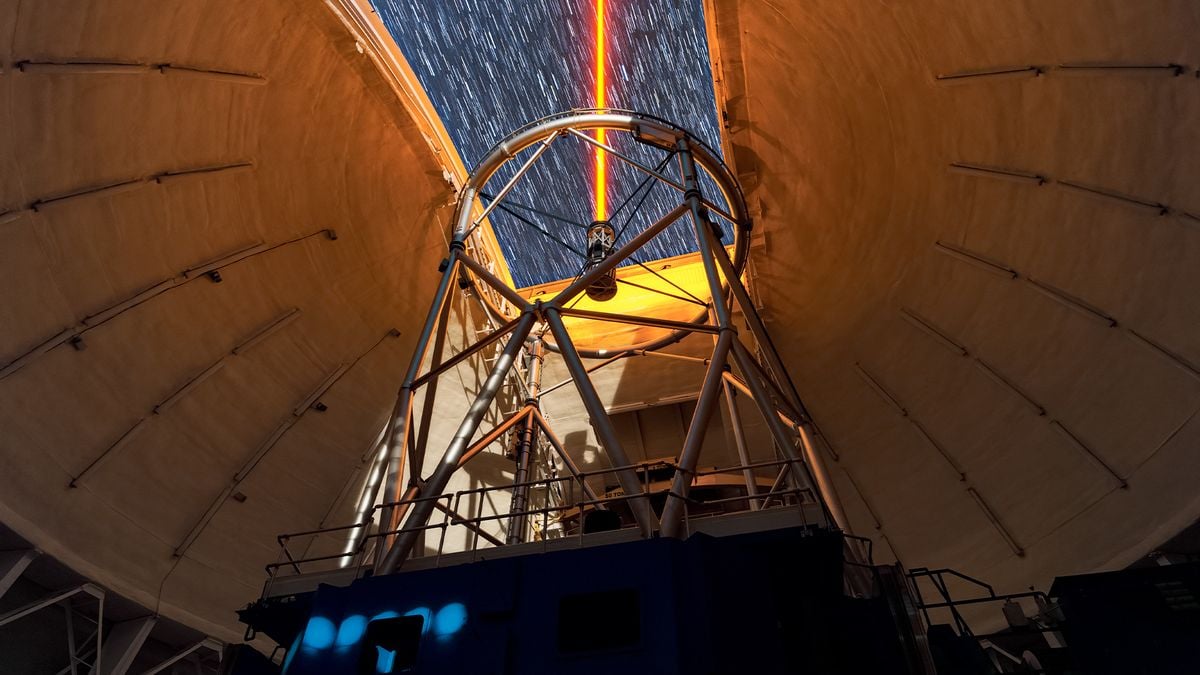
Space.com highlights a European Southern Observatory photo showing the Milky Way over Chile’s Paranal Observatory while four Unit Telescopes of the Very Large Telescope fire lasers high in the atmosphere to create artificial guide stars. These glow-displays let adaptive optics systems correct for Earth’s atmospheric blur in real time, sharpening observations. The UTs Antu, Kueyen, Yepun and Melipal work together (Melipal’s laser use dates to 2016; the other three were added in December 2025 to support VLTI and GRAVITY+), showcasing the VLT’s capability to peer deeper into the universe as lasers illuminate the sky above Chile.