Strength Without Age: Why Lifting Heavy Pays Off as We Grow Older
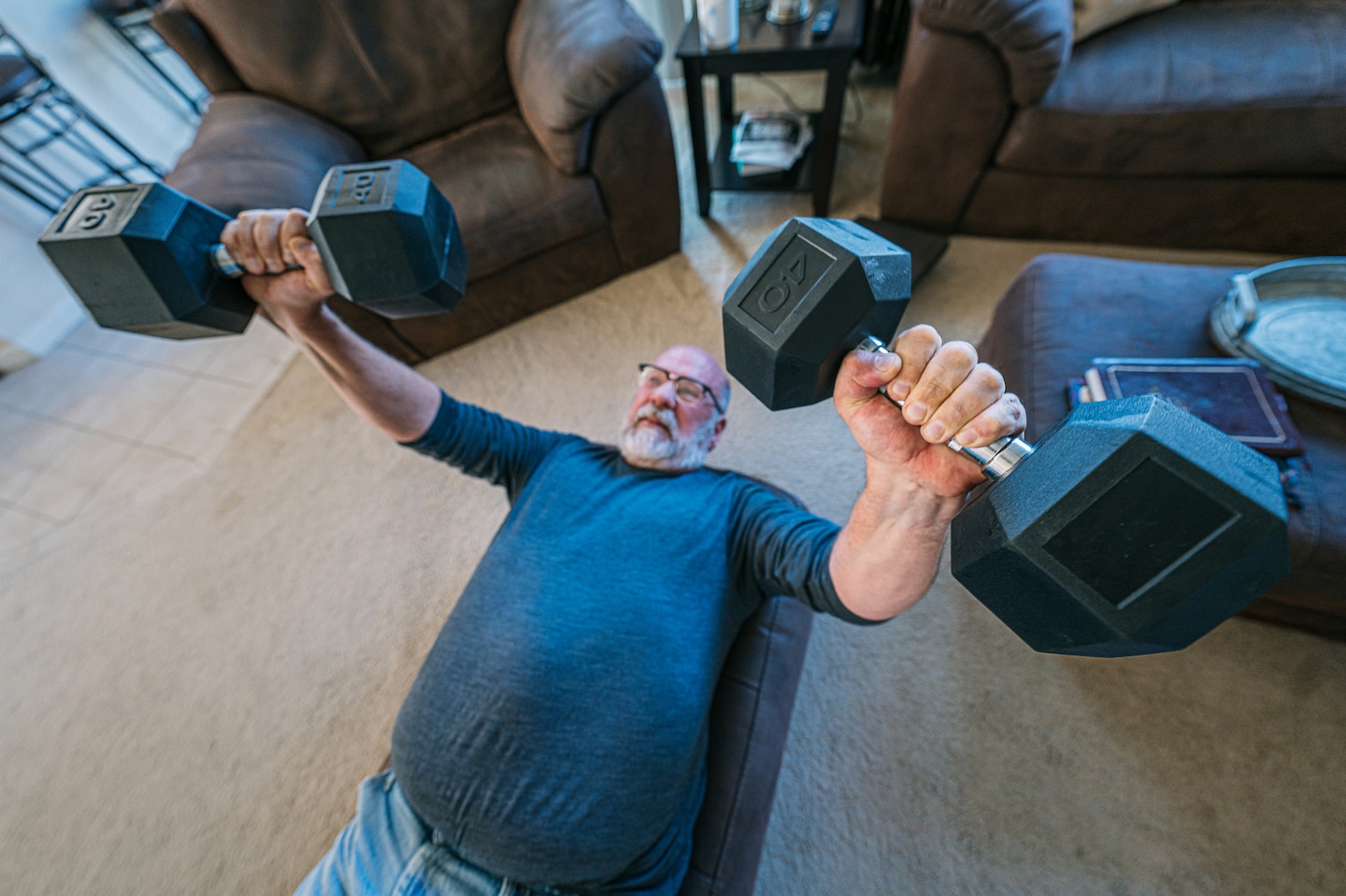
Regular heavy lifting offers aging adults multiple benefits: increased muscle, better insulin sensitivity, stronger bones, improved cardiovascular health, and enhanced cognitive function and sleep. A quiet revolution in strength-training is challenging the “old and frail” stereotype, with stories of older lifters and compelling mental-health gains. Safety hinges on coaching, proper technique, and gradual progression, including a three-month plan to move from 6–8 reps to 2–4 reps as strength increases, focusing on push, pull, hinge, squat, lunge, and carry movements.