Hidden Lava Tubes Hint at a Subsurface Network Beneath Venus
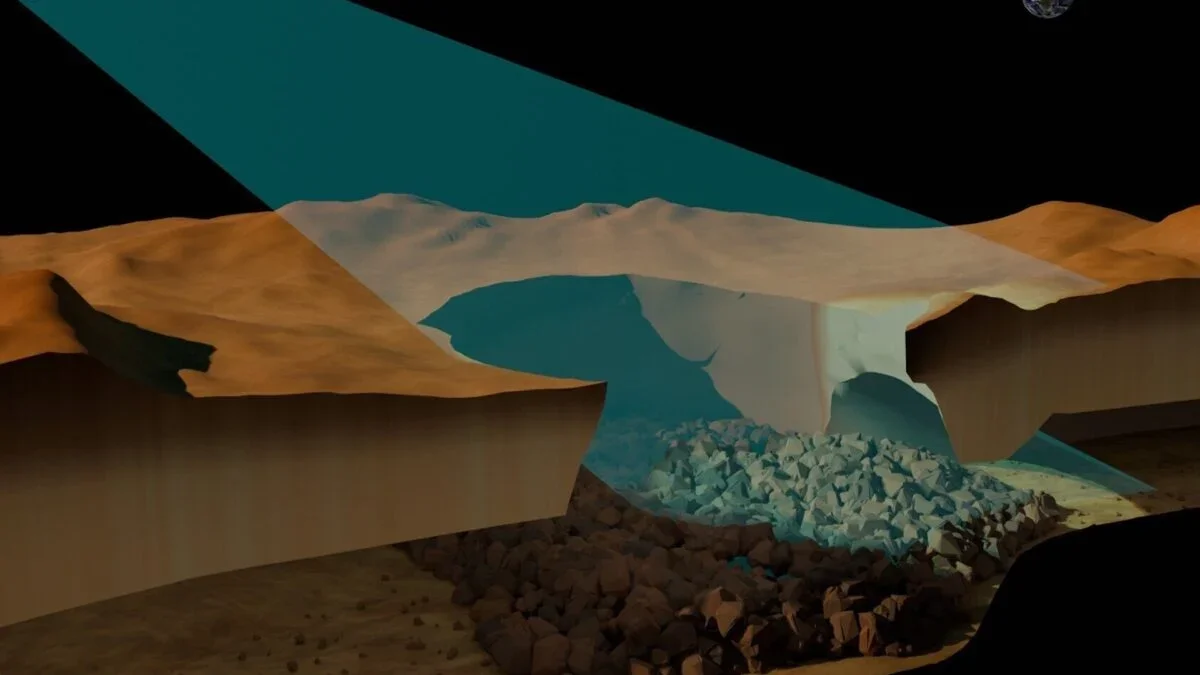
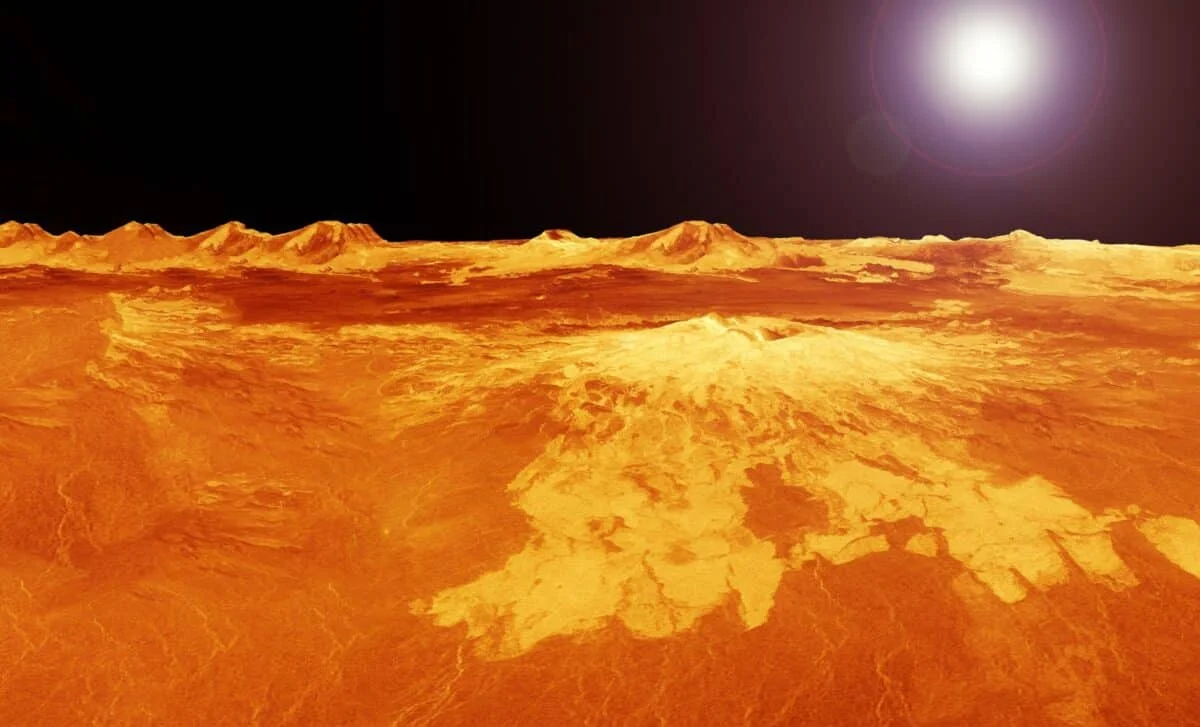
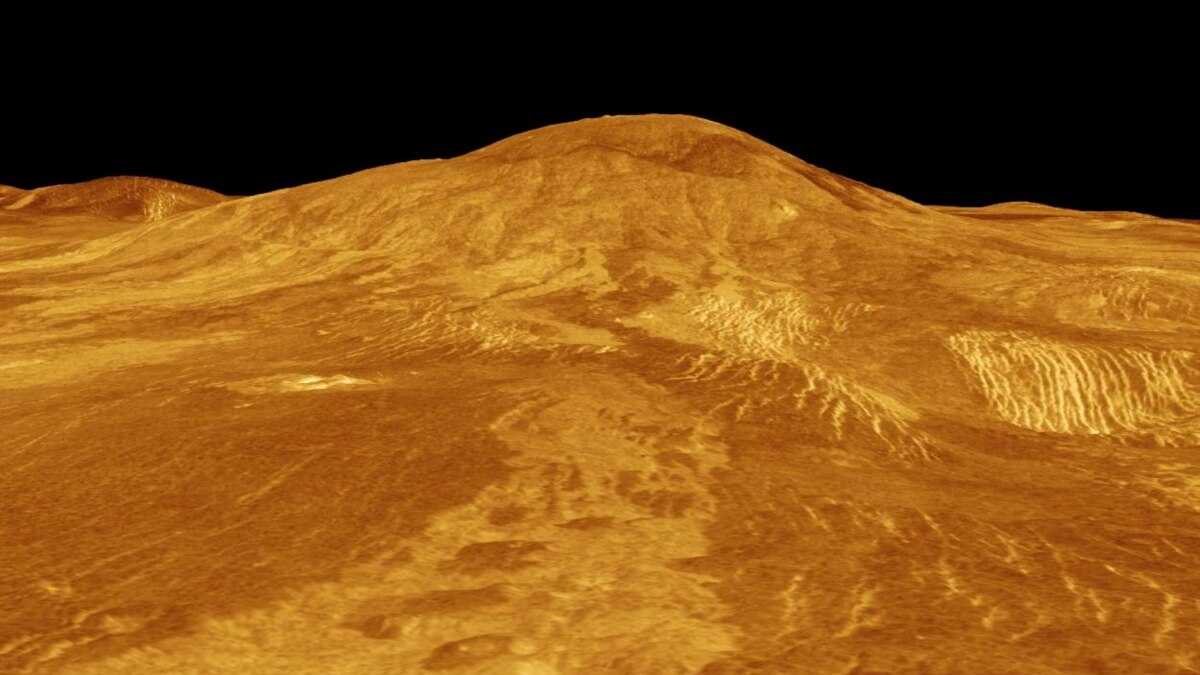
Researchers analyzing radar data from the Magellan mission detected what appears to be a large underground lava tube beneath Venus, near the Nux Mons region. The tube is about 1 kilometer wide, with a roof around 150 meters thick and a hollow cavity at least 375 meters high, marking the first confirmed subsurface feature on Venus and supporting long-held ideas about the planet’s volcanic activity. If confirmed, there may be more tubes beneath Venus’ surface, a task for upcoming radar-focused missions VERITAS and EnVision, planned to launch around 2031.