Understanding 'Gravitationally Bound' in an Expanding Universe
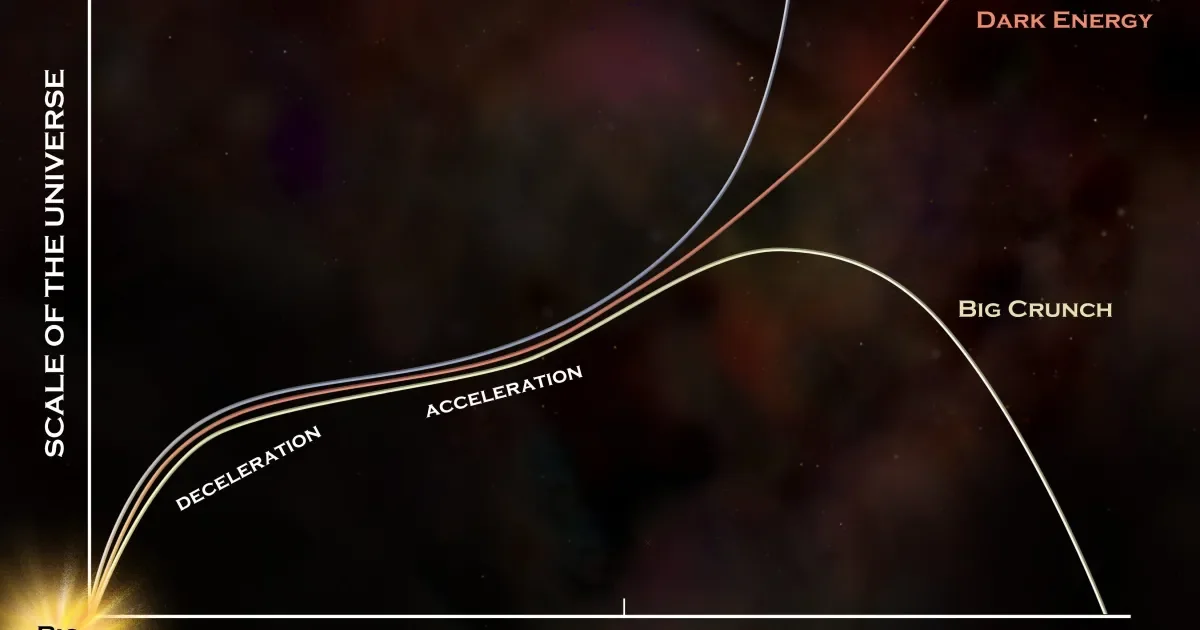
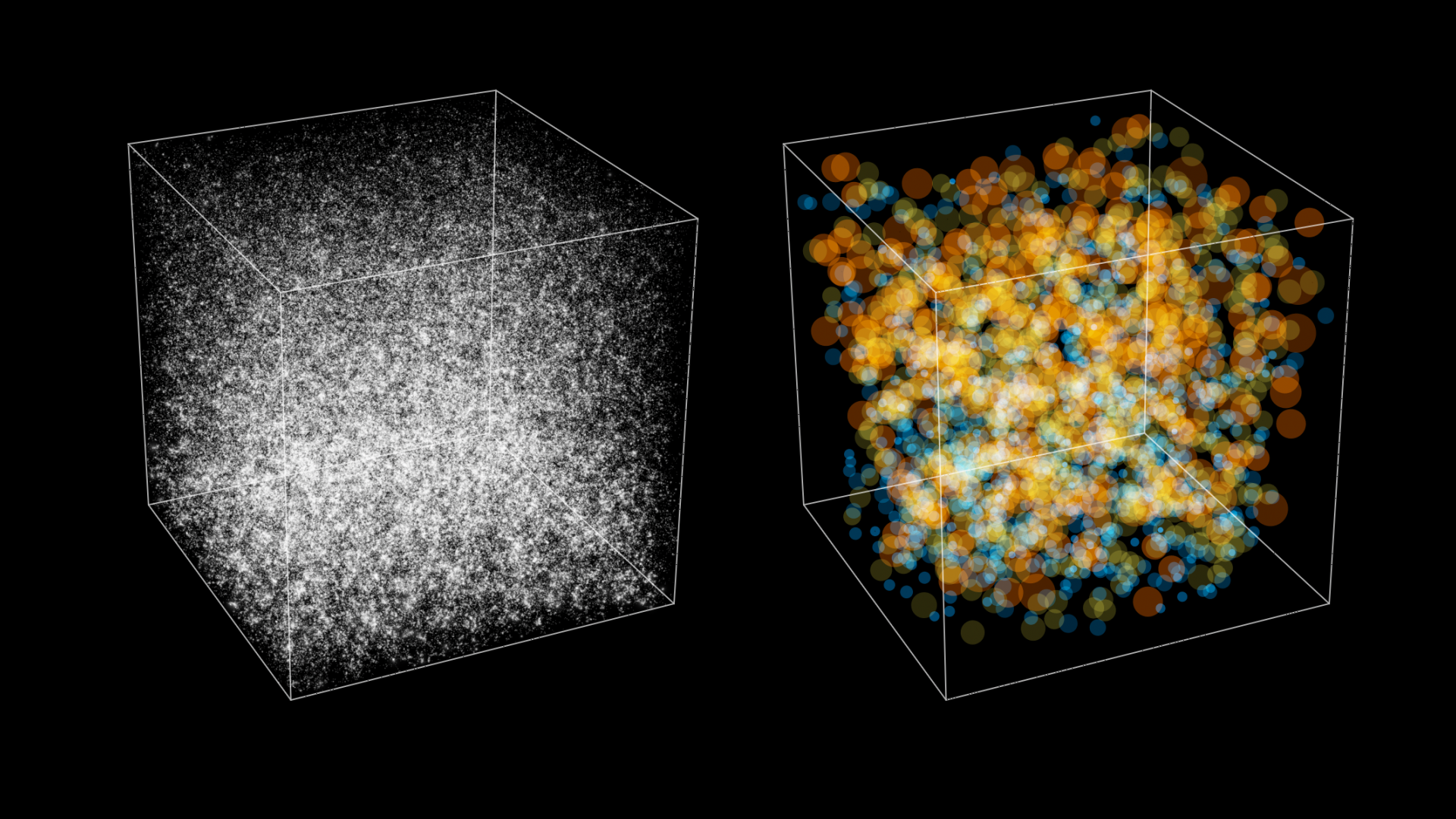
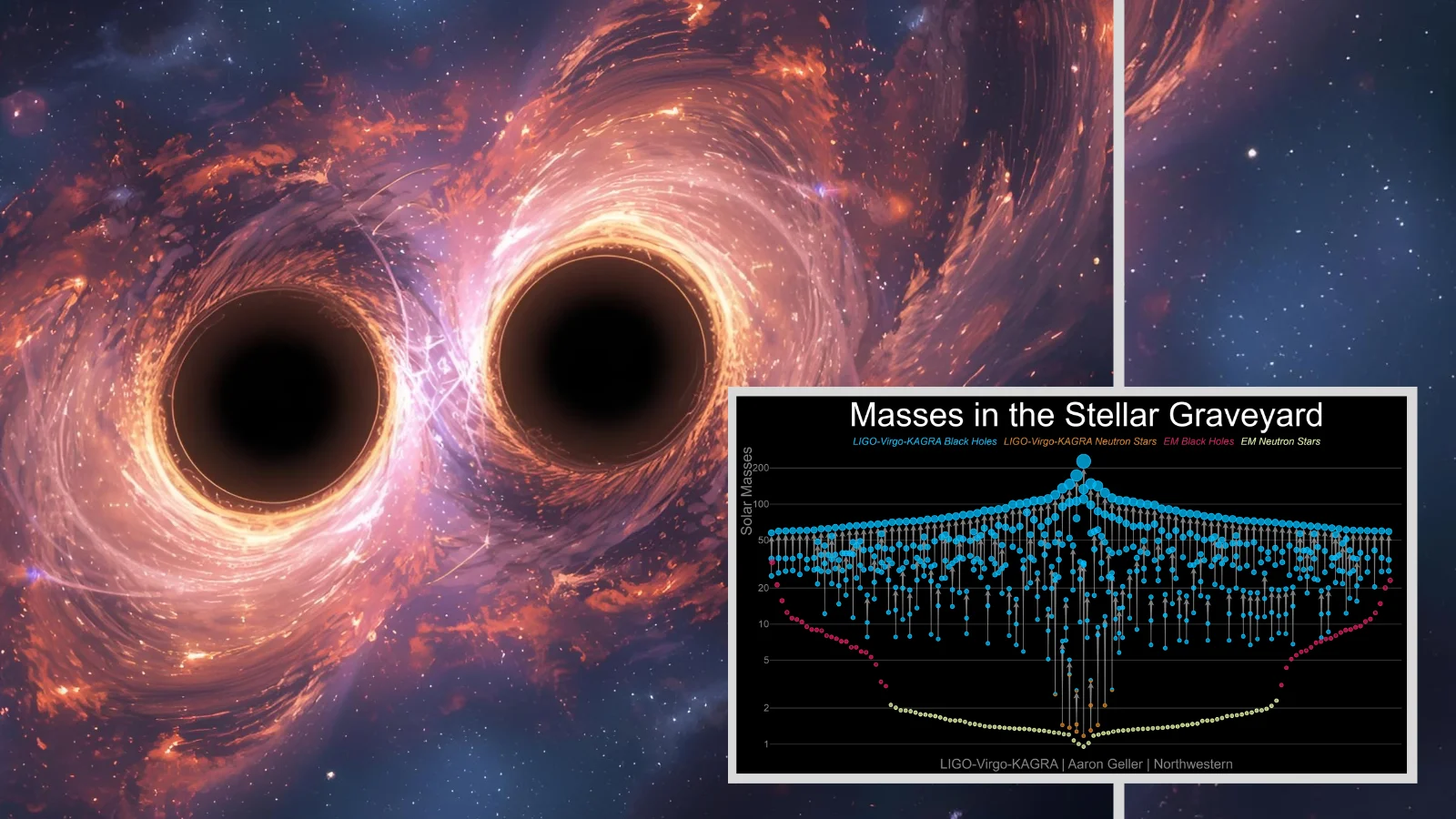
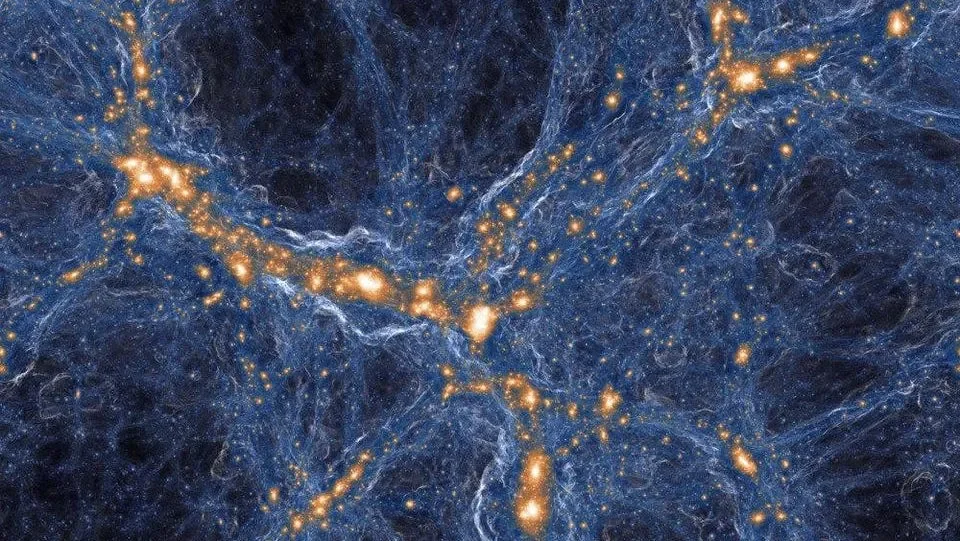
The article explains what it means for objects to be gravitationally bound in an expanding universe, discussing how structures like stars, galaxies, and clusters are held together by gravity despite the universe's overall expansion, and explores how dark energy influences the future of these structures.