
Plant-based diets linked to lower risk of five cancers, study finds
A new study finds vegetarians have a lower risk of five cancers, suggesting plant-based diets may offer cancer-preventive benefits, though details are behind the paywall.
All articles tagged with #study

A new study finds vegetarians have a lower risk of five cancers, suggesting plant-based diets may offer cancer-preventive benefits, though details are behind the paywall.
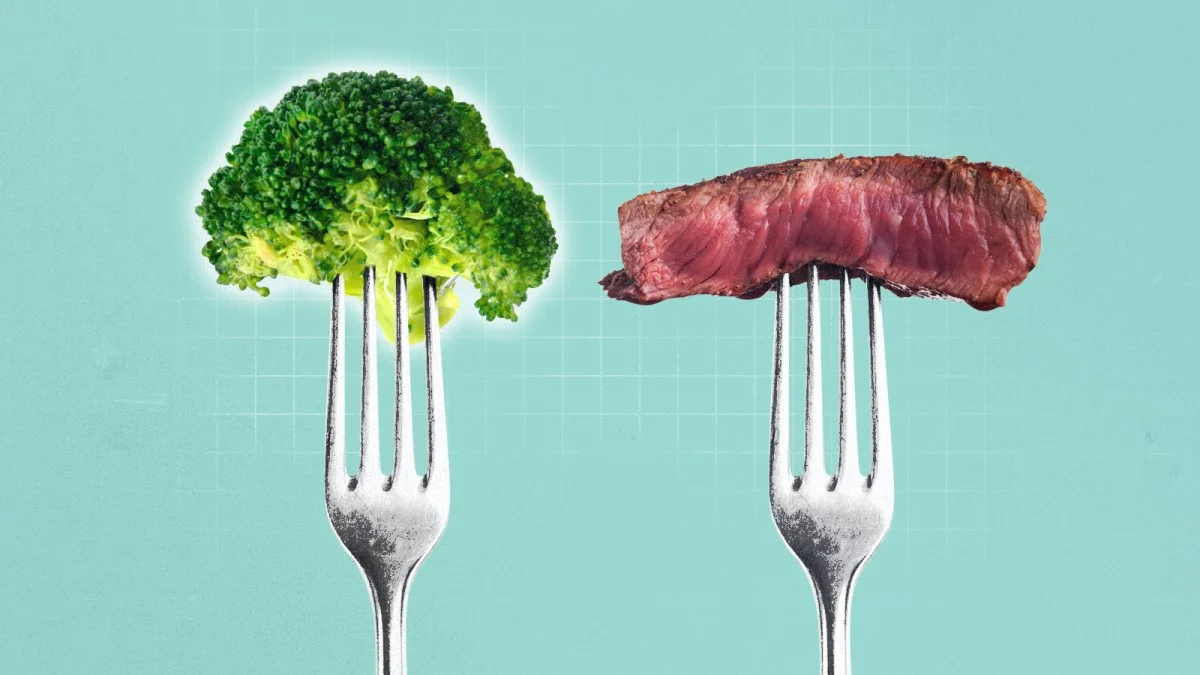

An Oxford-led study of 1.8 million people finds vegetarians are up to a third less likely to develop five cancers than meat eaters, with 21% lower risk of pancreatic cancer, 9% lower risk of breast cancer, 12% lower risk of prostate cancer, 28% lower risk of kidney cancer and 31% lower risk of multiple myeloma; however vegetarians and vegans show higher risks for oesophageal and bowel cancers, potentially due to nutrient gaps. The researchers suggest meat itself may be the trigger and advocate diets focused on whole grains, pulses, fruit and vegetables while avoiding processed meat; the study, published in the British Journal of Cancer, analyzed UK/US data over two decades and was funded by the World Cancer Research Fund.
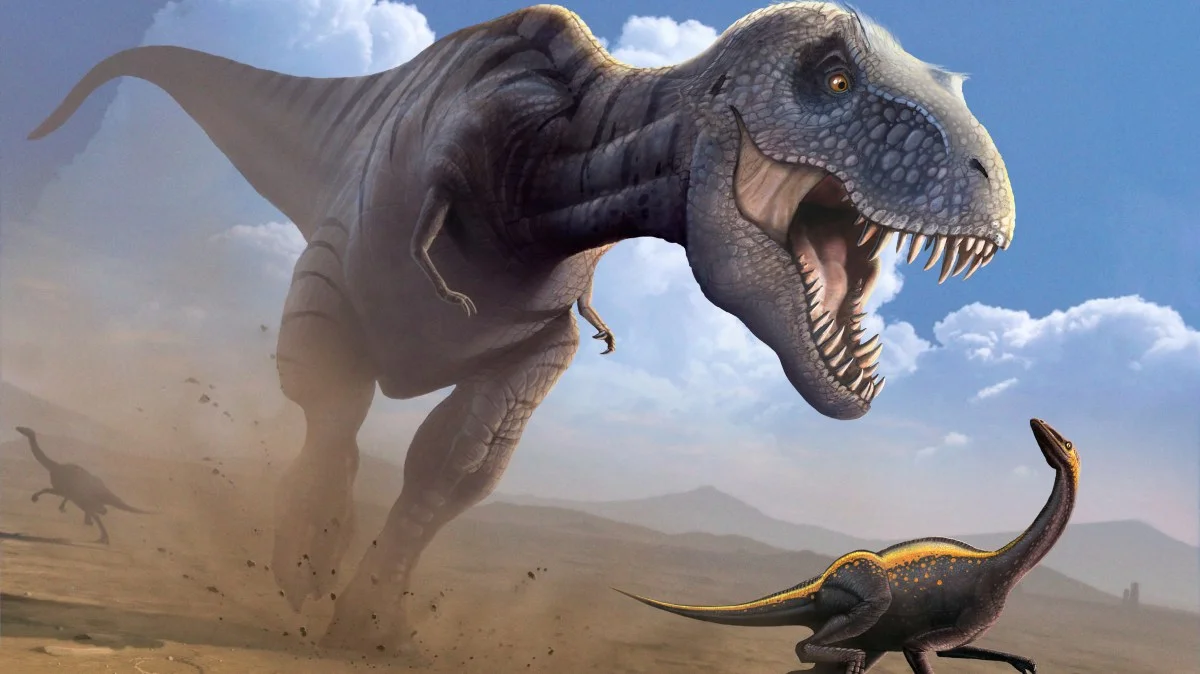

A biomechanical analysis finds T. rex likely moved toe-first, similar to birds, enabling up to 20% faster speeds; a light 1.4-tonne T. rex could cover 100m in about 8.77 seconds, faster than Usain Bolt’s world record, with larger individuals still near 10.5 seconds.

A Minnesota-led study with 107 adults found that alcohol at a driving-penalty level increases local brain connectivity and clustering while reducing global connectivity, making brain regions more insular. These network changes measured by MRI after rest predict subjective intoxication and may explain common alcohol effects like visual and motor impairment; effects vary by individual and health status, with broader implications for understanding alcohol's impact on brain communication.

A University of Kent survey of about 4,000 people found that using AI to craft personal messages such as love letters, apologies, or wedding vows leads to harsher judgments, with people viewing the sender as less caring, less authentic, less trustworthy and lazier—even when the AI text is high quality—highlighting the value of genuine effort in relationships.

A BMJ Medicine study analyzing data from over 111,000 adults across 30 years found that those who varied their exercise types had about a 19% lower mortality risk than those with less variety, with higher total activity offering benefits up to a plateau around 20 hours per week. The results show association, not causation, and note limitations like self-reported activity and limited demographic diversity.

A new study finds that spending by wealthy households is rising while spending by middle- and lower-income Americans remains largely flat, signaling a widening gap in consumer behavior.

A BMJ Medicine study tracking about 110,000 US adults over 30 years found that people who engaged in a broader mix of activities were 19% less likely to die than those who stuck to a single exercise. Variety provided added protection beyond any one sport, with six hours of moderate activity or three hours of vigorous activity per week appearing optimal; combining workouts with complementary benefits (like resistance plus cardio) was particularly beneficial. The study notes that while results are robust, it cannot prove causation and other lifestyle factors were accounted for in the analysis.

A recent study questions the benefits of time-restricted intermittent fasting on metabolic and cardiovascular health, suggesting that calorie reduction, rather than timing, may be the key factor in health improvements. The study found no significant changes in health markers despite weight loss, highlighting the importance of calorie intake over fasting schedules.

A 50-year Swedish study reveals that our bodies start to decline in strength, endurance, and fitness as early as age 35, but staying active can slow this deterioration, emphasizing the importance of regular movement for healthy aging.

An experiment with experienced software developers using AI tools found that, contrary to expectations, their tasks took 20% longer, highlighting that AI may currently hinder productivity for skilled workers due to the need for extensive debugging and integration of AI outputs. The study emphasizes caution in AI deployment and suggests that organizational adjustments are necessary to realize potential productivity gains.
A study published in European Urology suggests that men who ejaculate around 21 times a month may have a lower risk of developing prostate cancer, possibly due to flushing out harmful chemicals or healthier lifestyle habits, with orgasms also providing mental health benefits.

A new study suggests that using waist-based measurements alongside BMI could nearly double the estimated prevalence of obesity among U.S. adults, highlighting potential underestimation by BMI alone and emphasizing the need for revised diagnostic criteria.
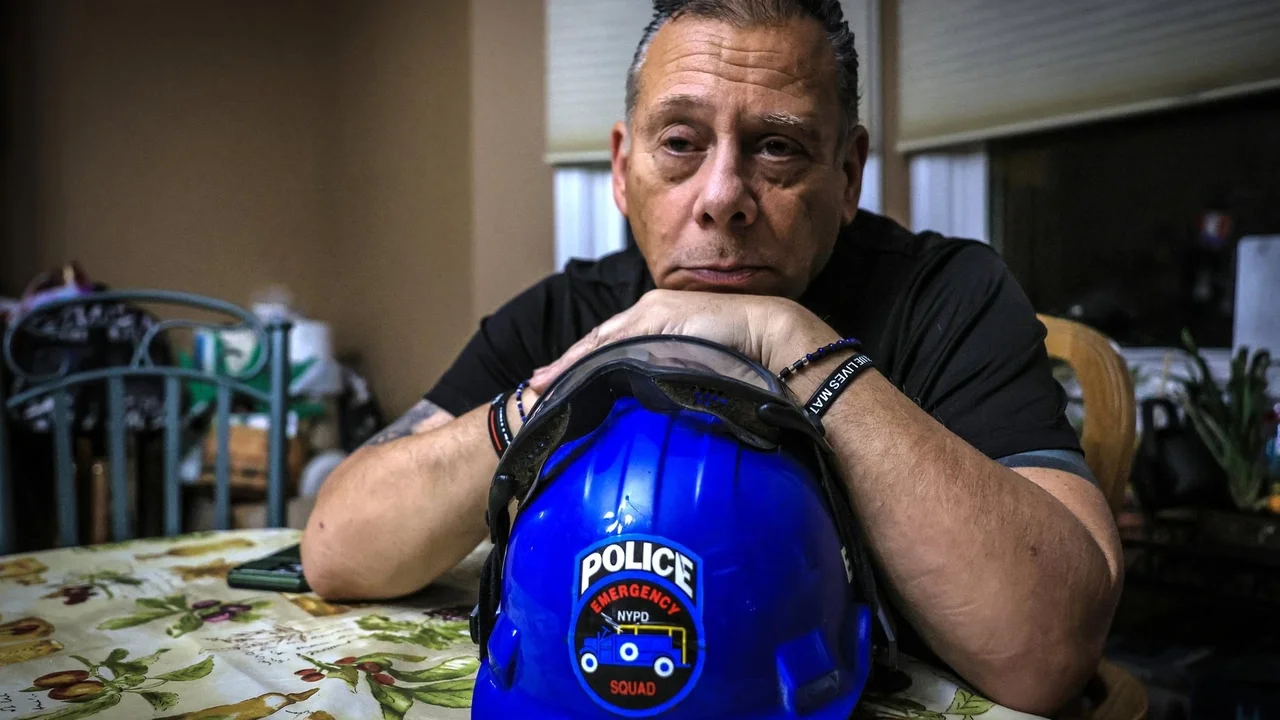

A study on 9/11 first responders found that many suffer from PTSD, with over 6,000 cases identified, highlighting the long-term mental health impact of the disaster and the importance of addressing stigma around seeking help.
A recent study published in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine found that tramadol, a commonly prescribed opioid for chronic pain, offers minimal pain relief and poses significant health risks, including serious cardiovascular events, leading experts to question its use for long-term pain management.