AI-Driven Discovery of Two New MS Subtypes Sparks Hope for Improved Treatments
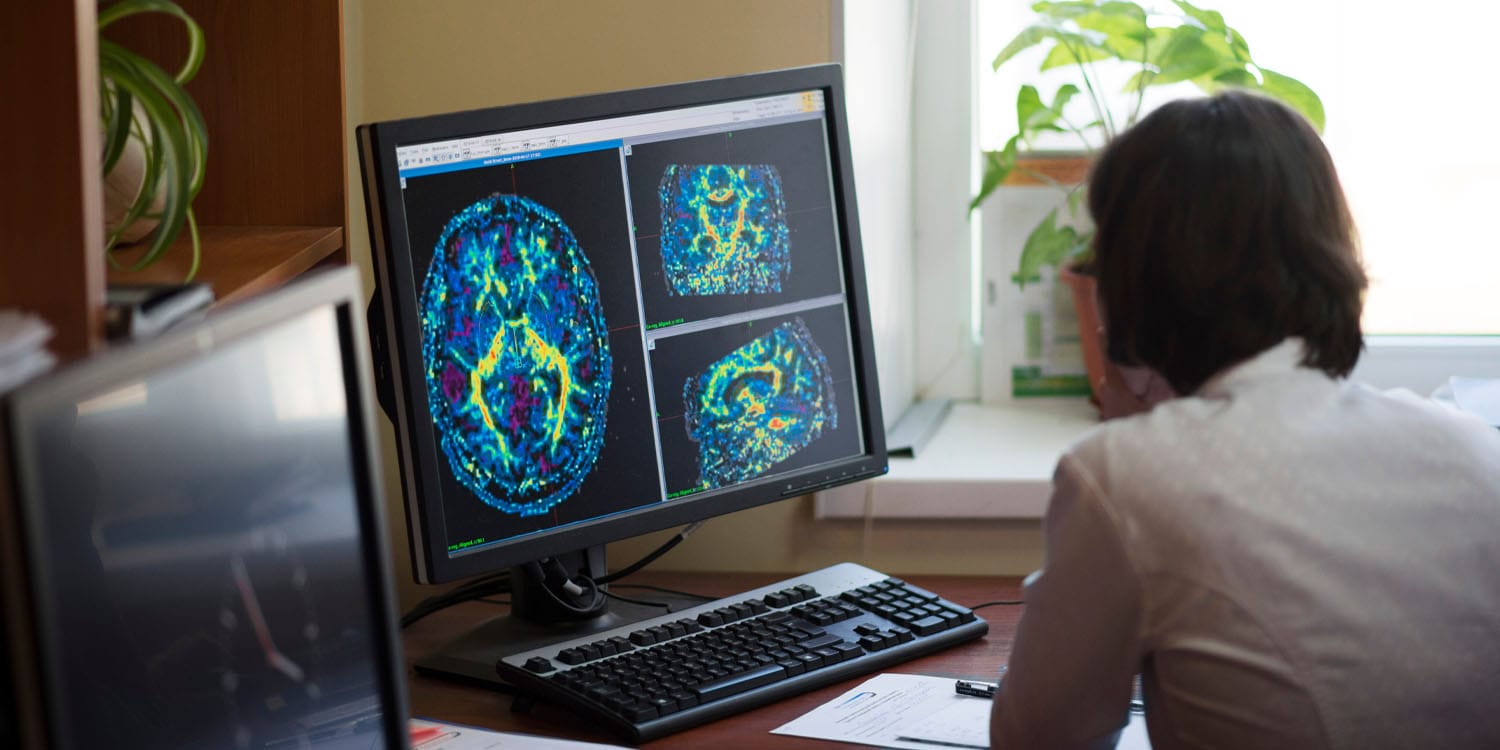
Scientists have identified two new biological subtypes of multiple sclerosis using AI, blood tests, and MRI scans, which could lead to more personalized and effective treatments for patients by better understanding disease progression and tailoring therapies accordingly.