Falcon 9 reentry leaves upper-atmosphere lithium plume, raising space-pollution concerns
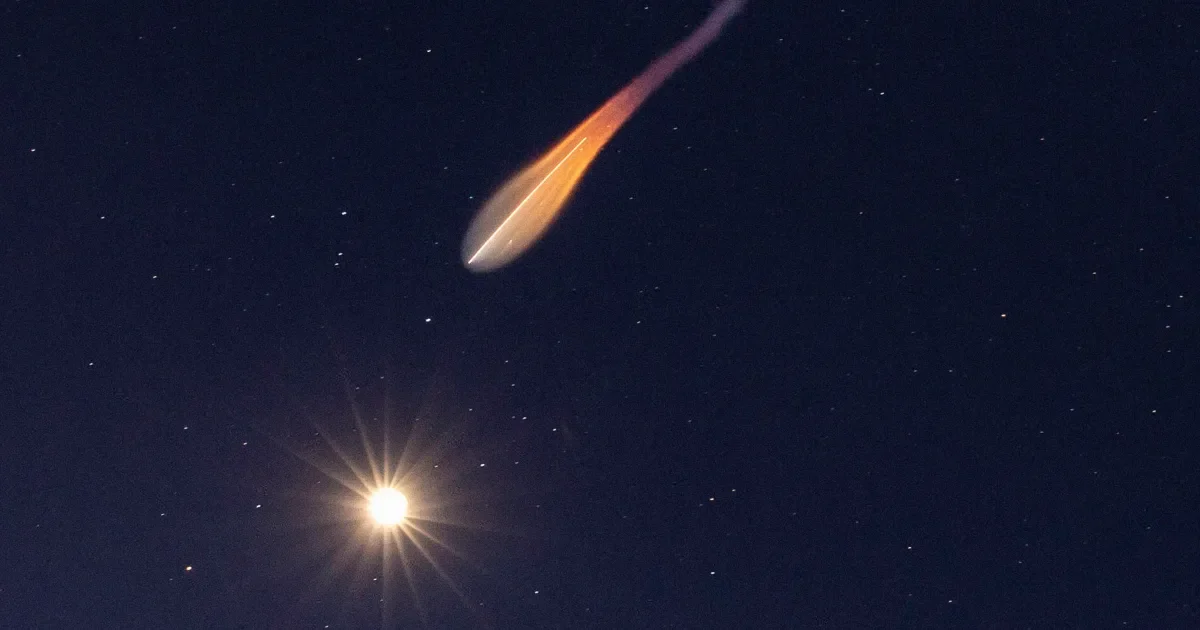
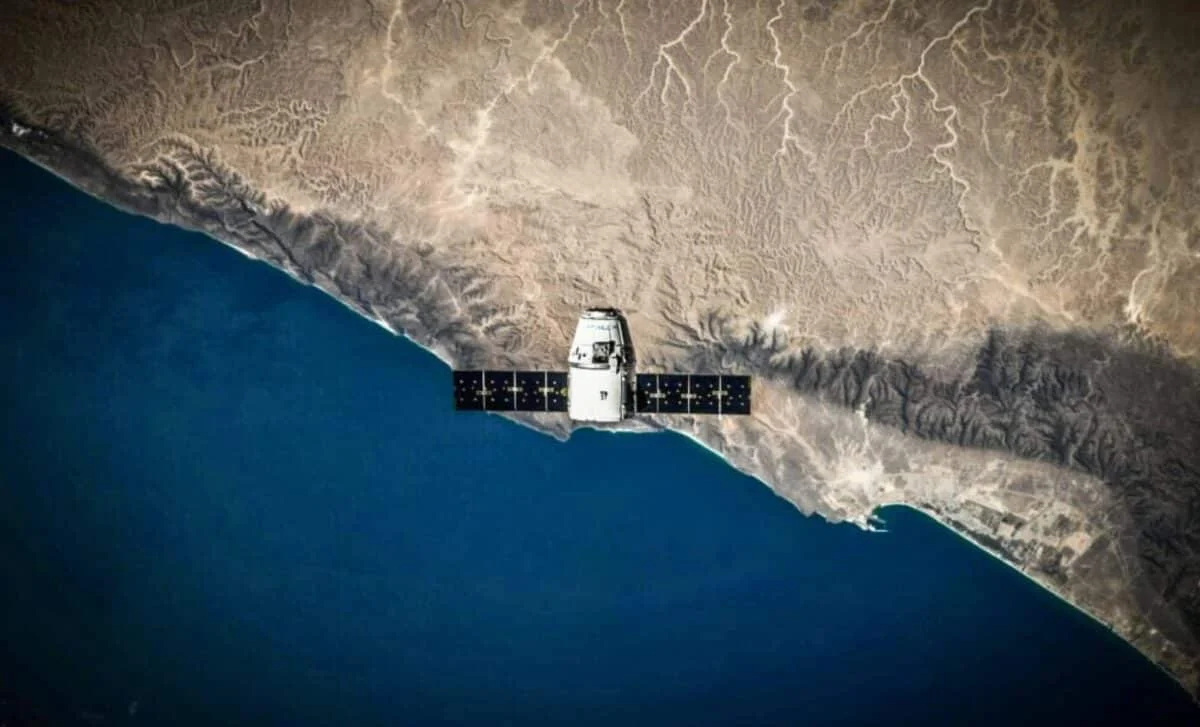
Researchers using ground-based lidar detected a large lithium plume from SpaceX’s Falcon 9 upper-stage reentry ~62 miles up over Europe, marking the first observed upper-atmosphere pollution from space debris. As satellite constellations grow, such reentries could alter atmospheric composition and potentially impact the ozone layer, though the long-term climate effects remain unknown.