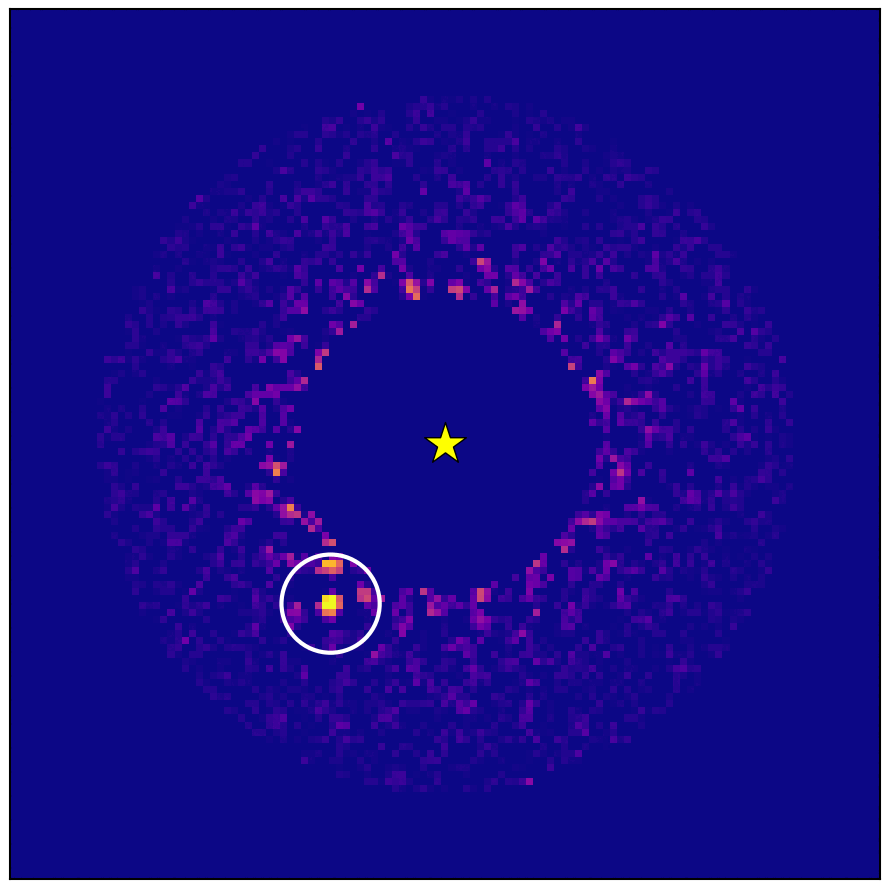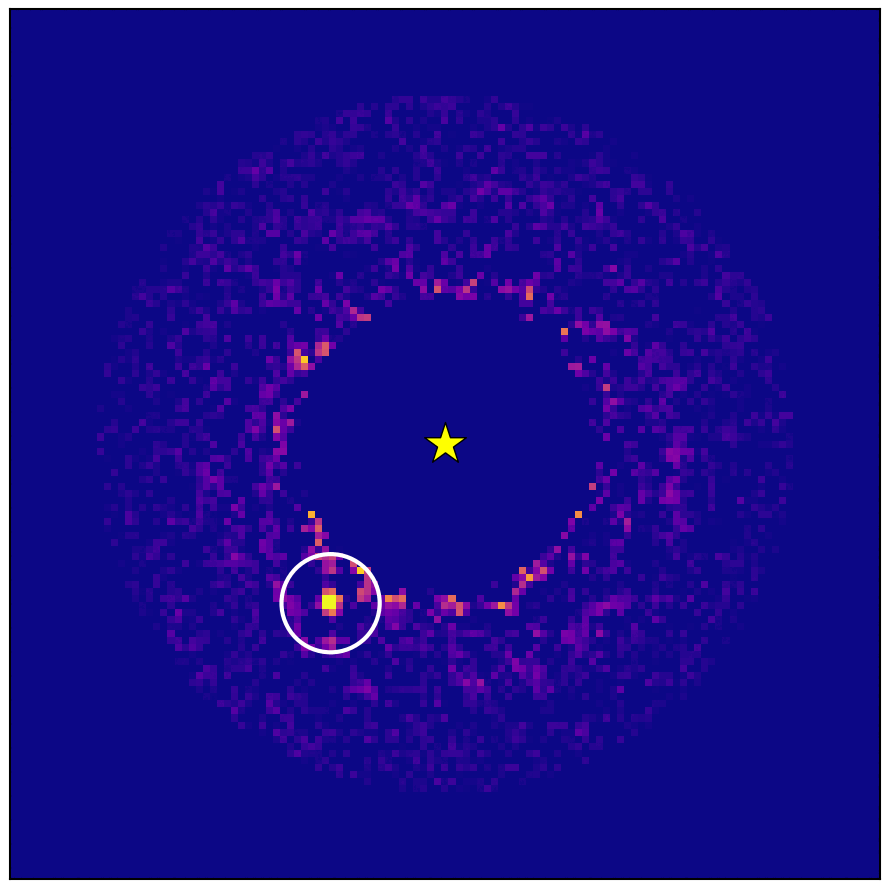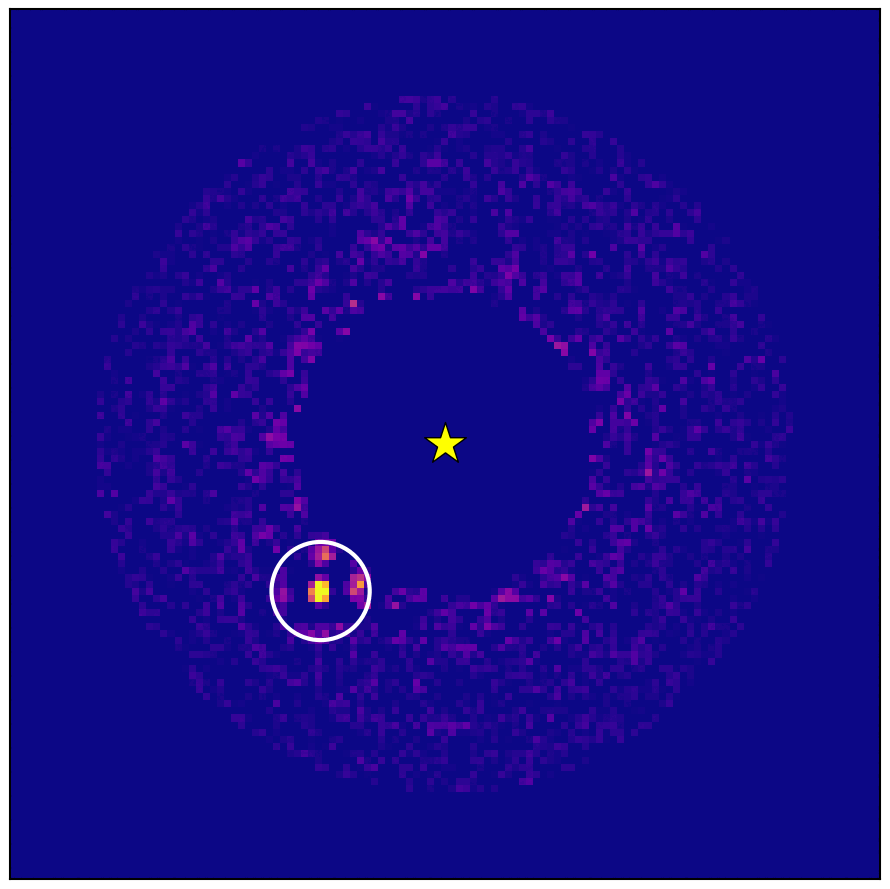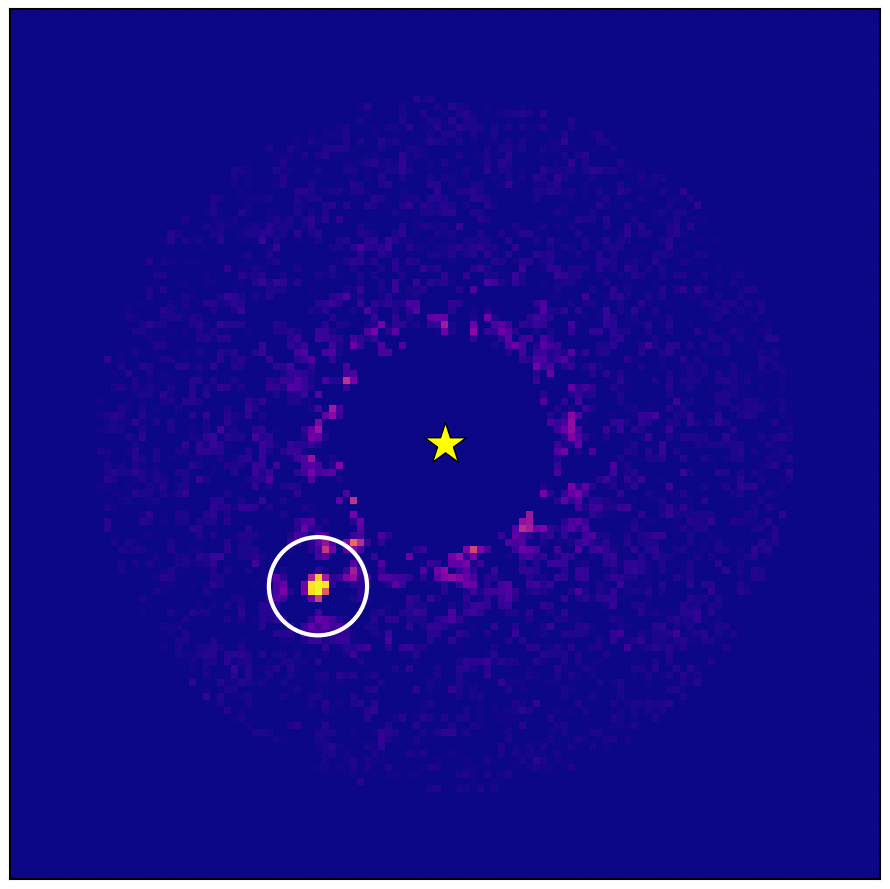
Exploring the Risks and Safety of Habitable Zones in Space
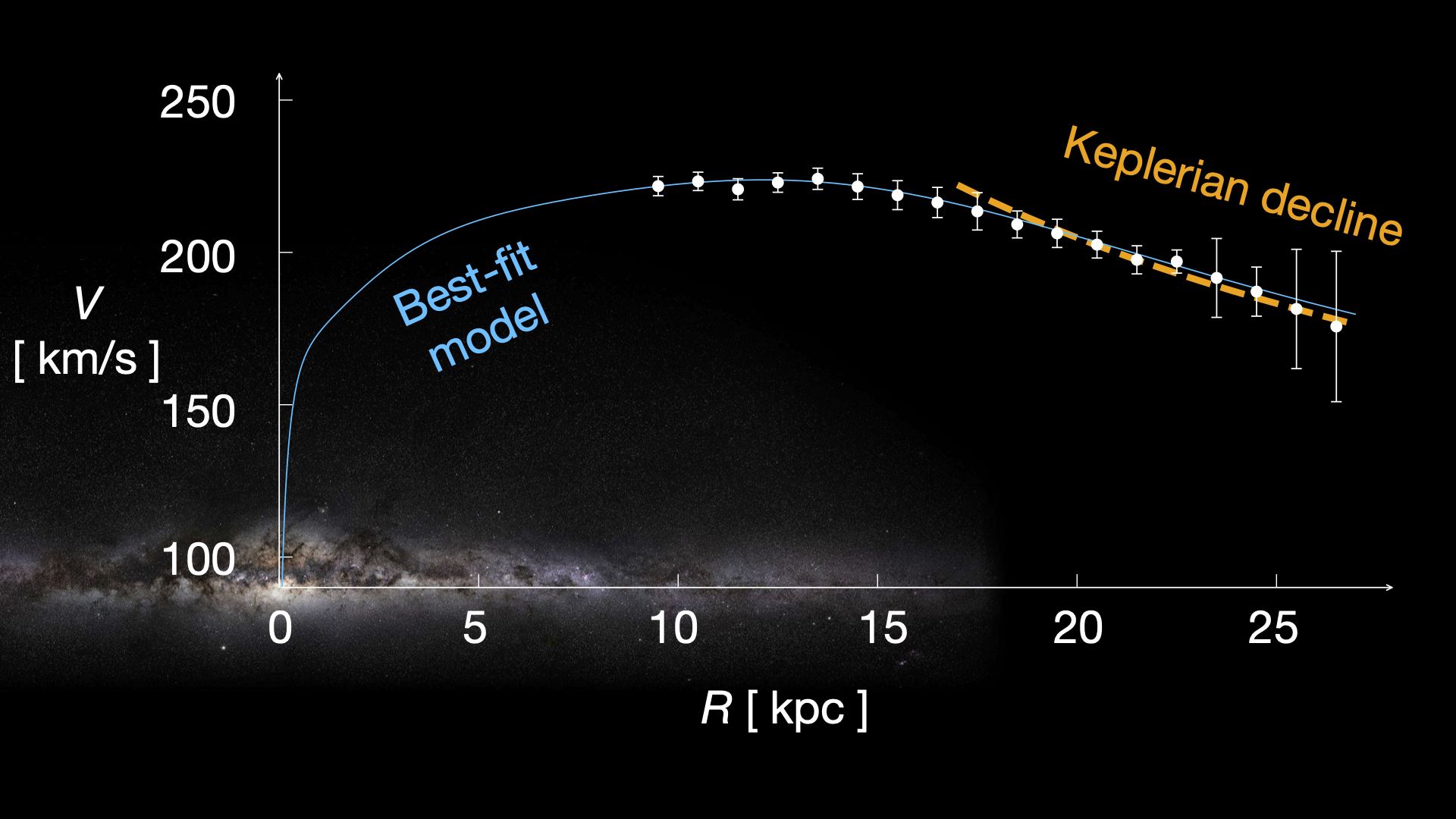
New research highlights that exoplanets in the habitable zone face significant threats from their stellar environments, such as supernovae and stellar flybys, which can strip atmospheres or eject planets from their orbits. The study, using data from the Gaia spacecraft, suggests that the stability required for life may be more precarious than previously thought, raising questions about the rarity of Earth's stable environment in the galaxy.