Cosmologists Pinpoint Hubble Constant to 1% Precision, Deepening the Cosmology Conundrum
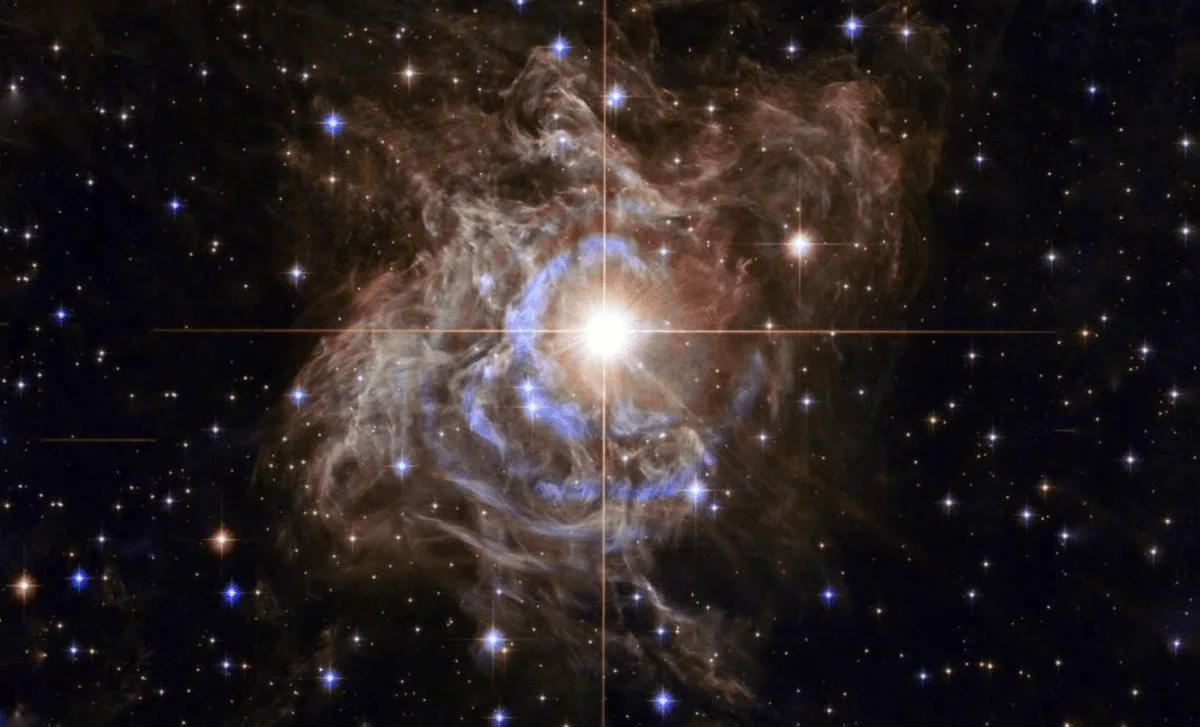
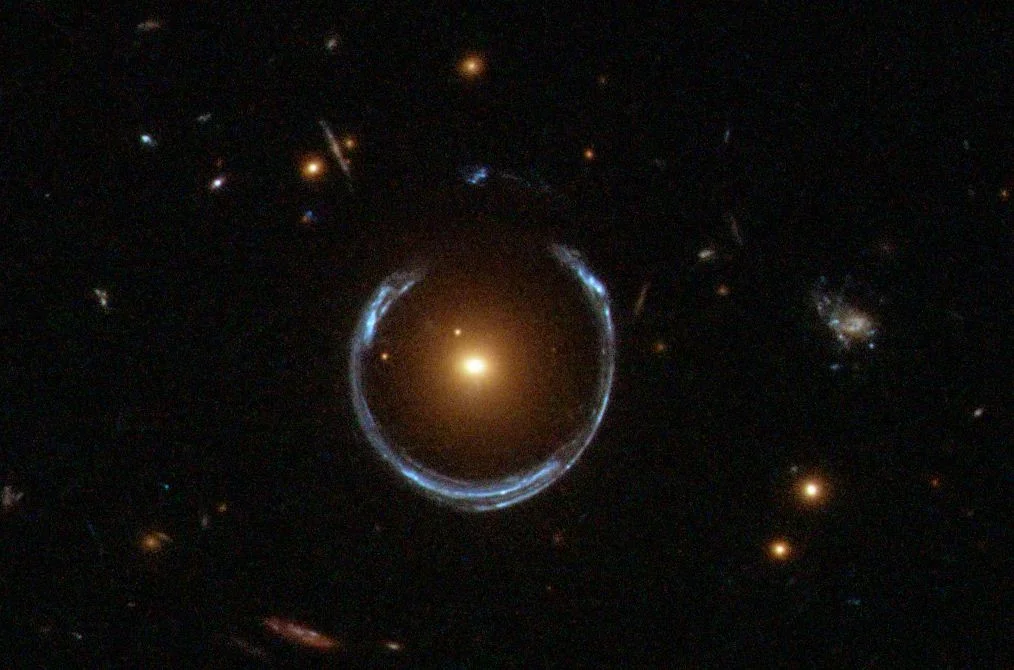
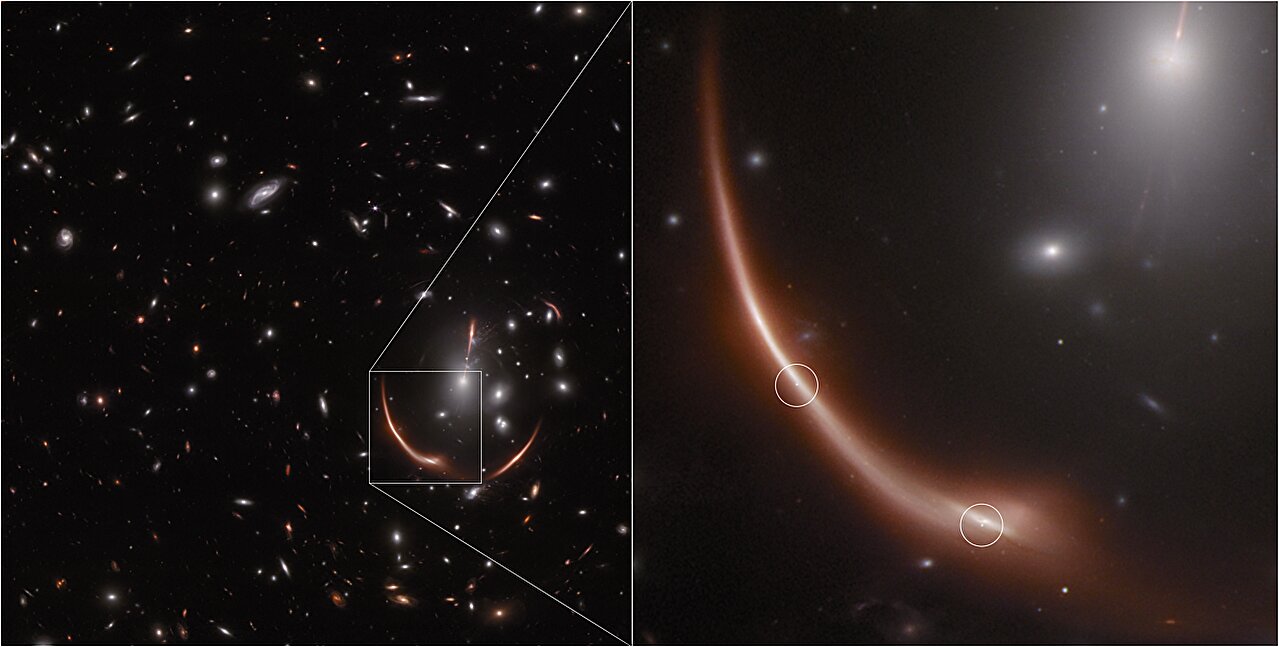
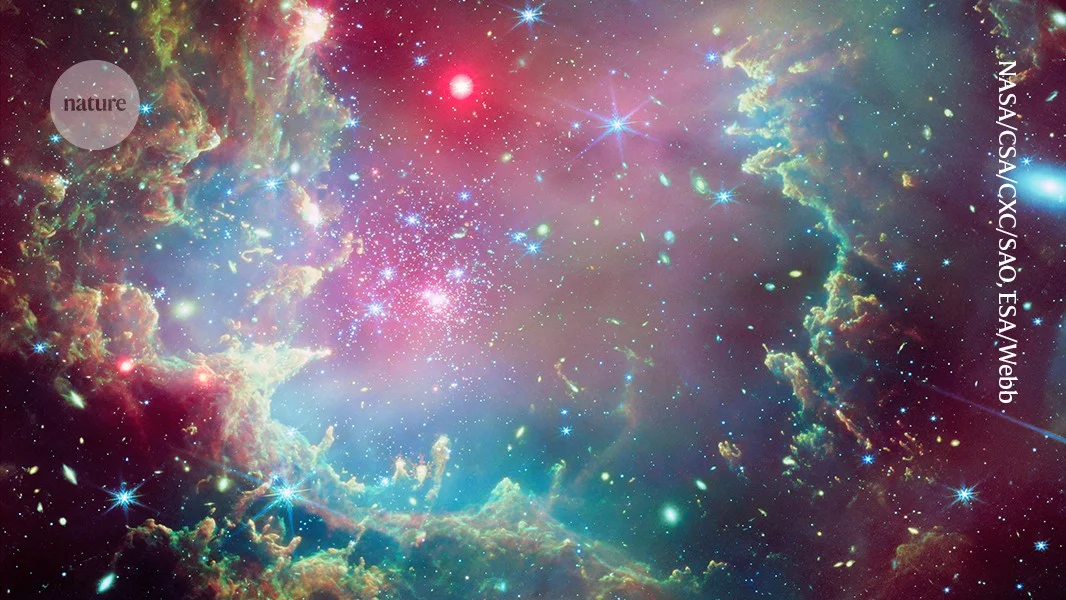
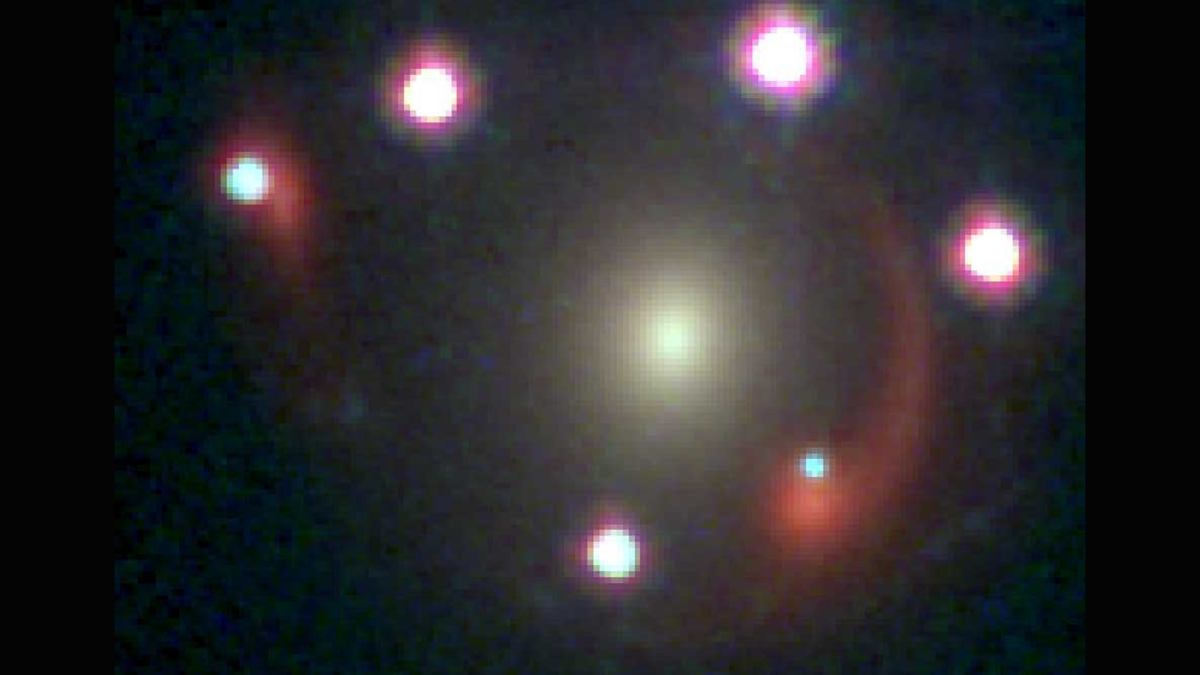
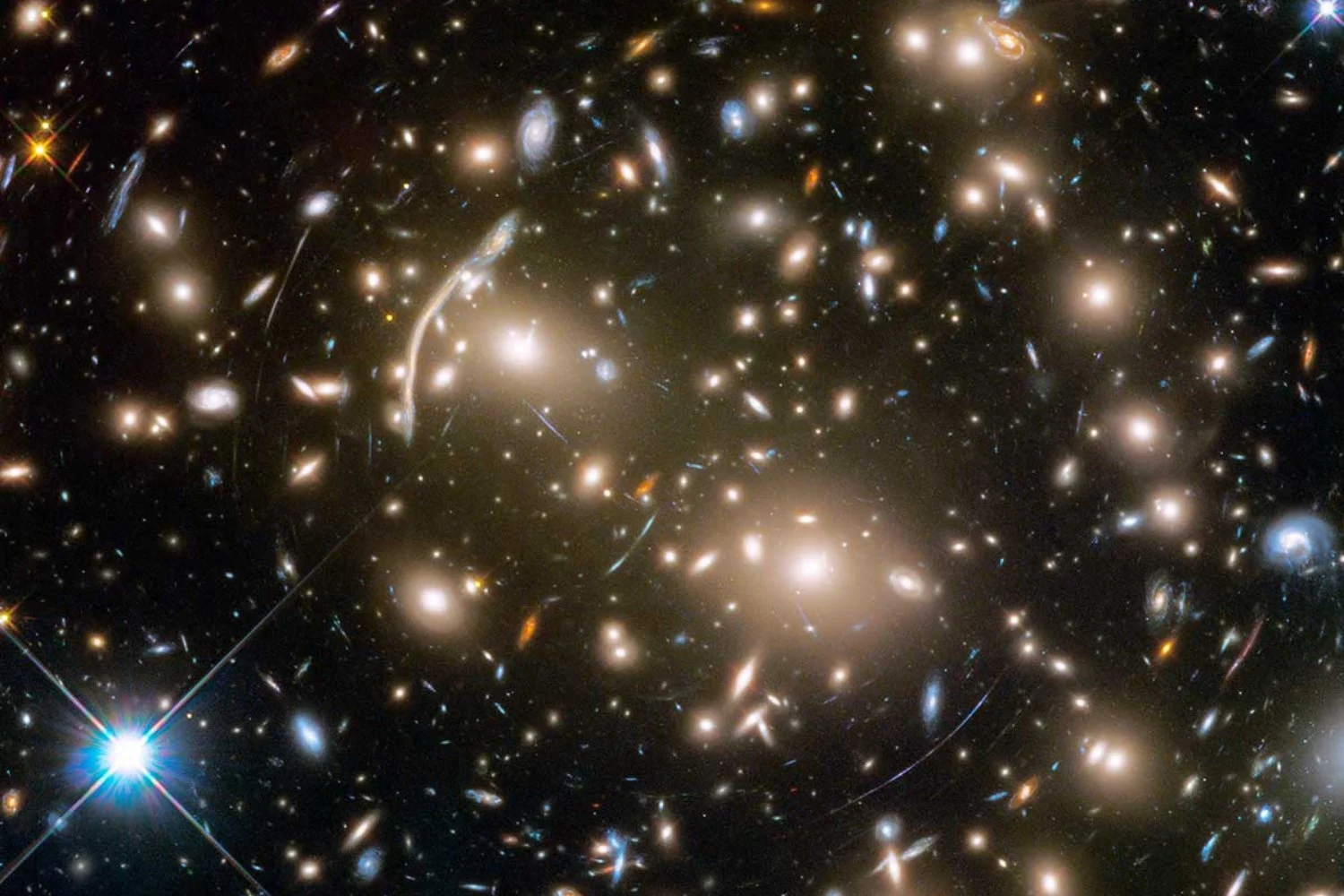
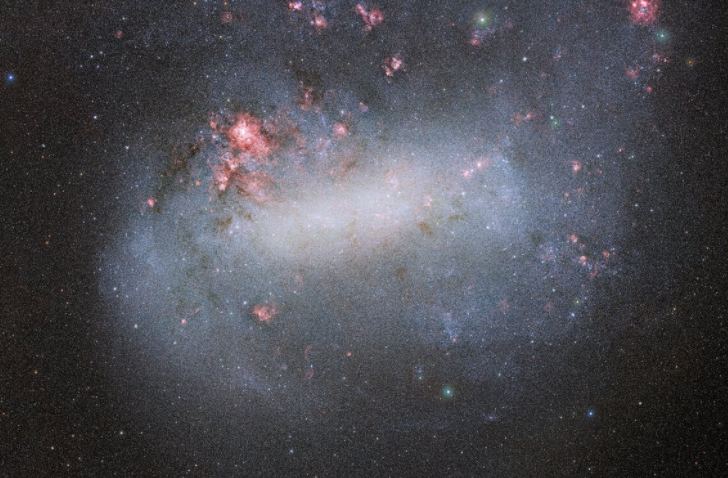
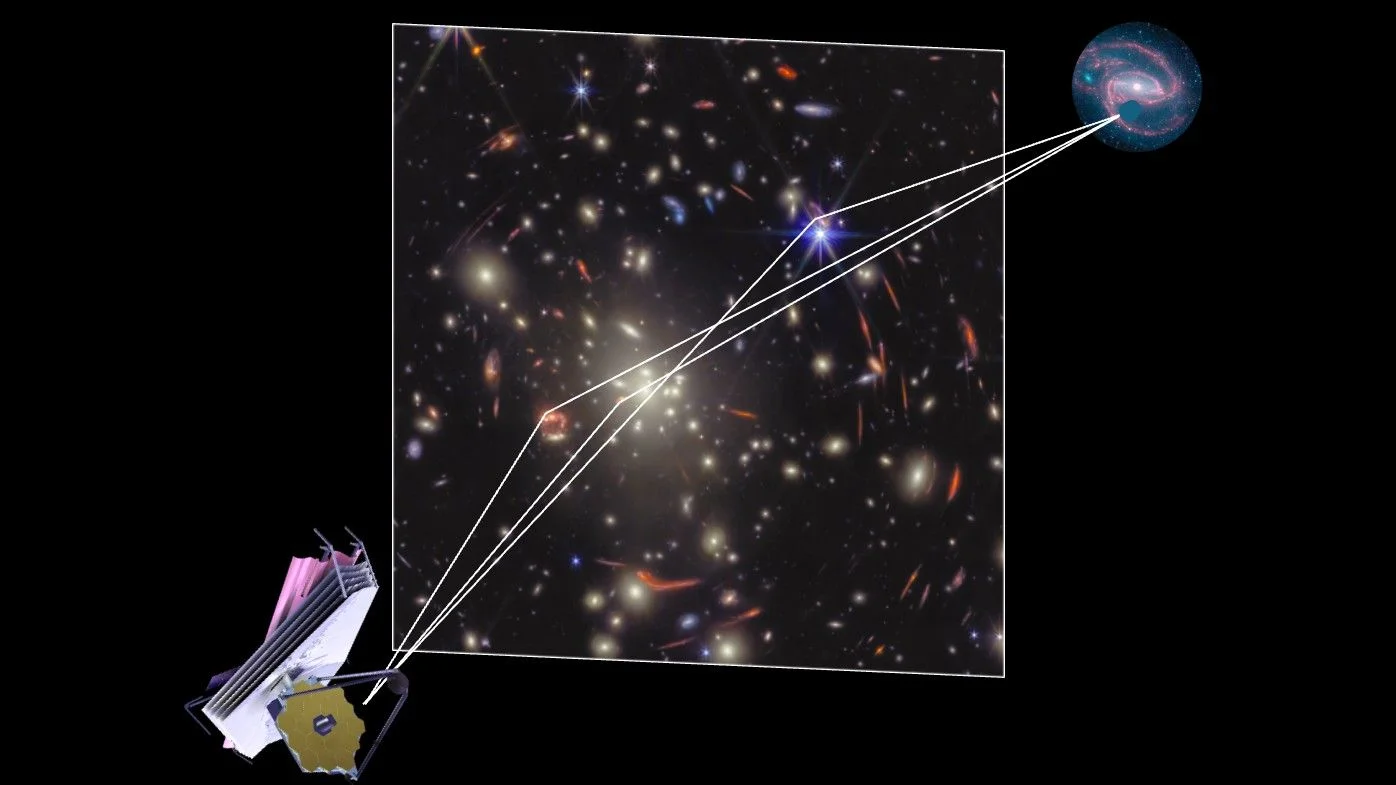
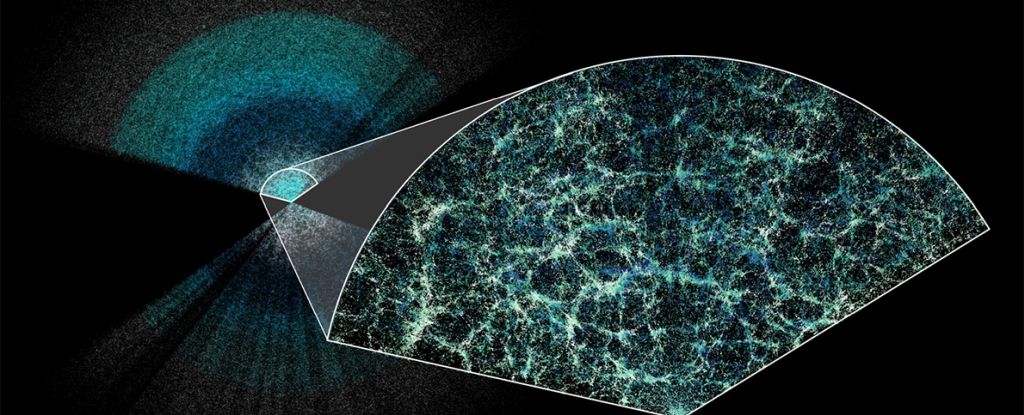
An international collaboration unified multiple distance-measurement methods into a single statistical framework, achieving a 1% precise measurement of the Hubble constant—the most accurate value to date. While the improved precision narrows uncertainties, it does not resolve the ongoing tension with early-universe predictions, underscoring the need for new physics or modifications to current cosmological models.