Cancer Research News
The latest cancer research stories, summarized by AI
Featured Cancer Research Stories

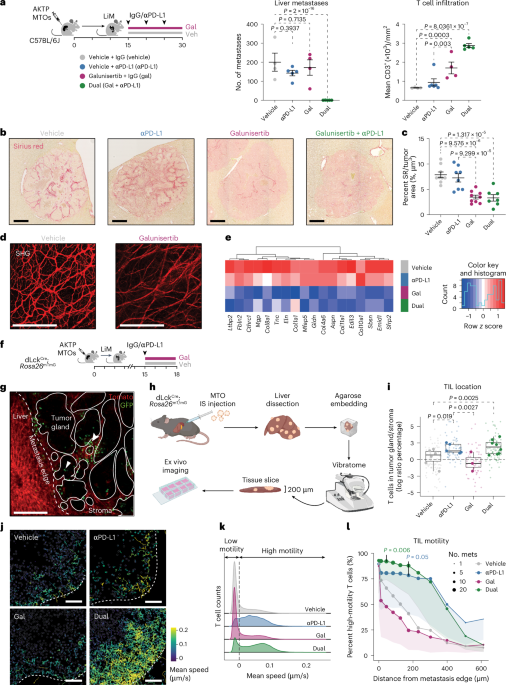
Unraveling the Immune Evasion and Genetic Drivers in Colorectal Cancer Progression
The study reveals that TGF-β creates a dual immune barrier in colorectal cancer by impairing T cell recruitment and instructing immunosuppressive SPP1+ macrophages, contributing to immune evasion and tumor progression.
More Top Stories
PTGES3 Identified as Key Regulator of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer
Nature•3 months ago
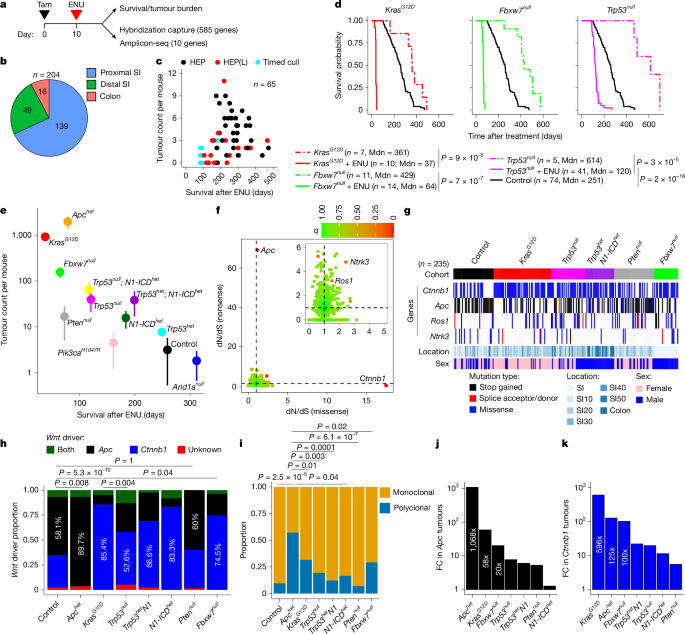
Key Genetic and Epigenetic Factors Drive Early Bowel Cancer Development
Nature•3 months ago
More Cancer Research Stories
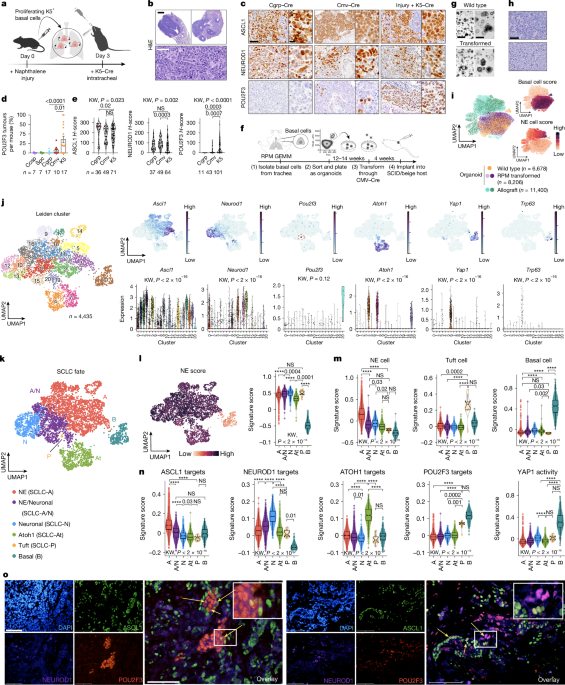
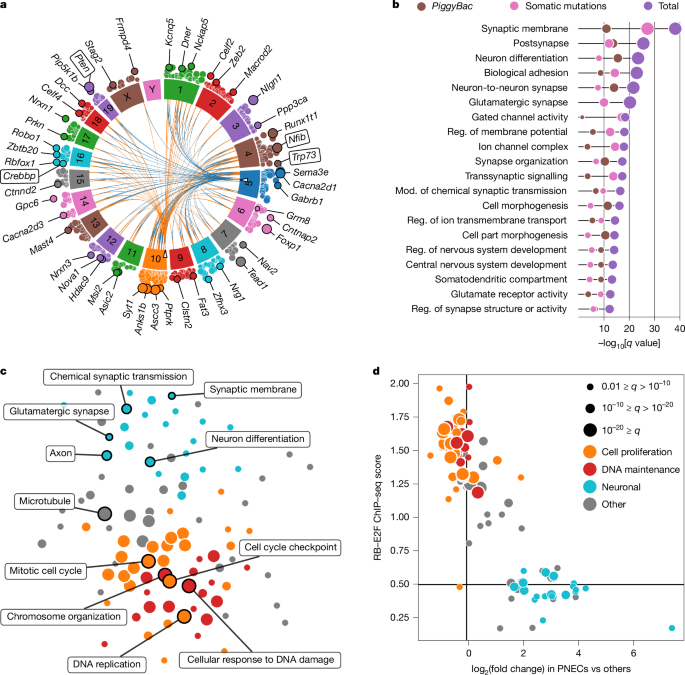
New Insights into Lung Cancer Origins and Lineage Plasticity
The study reveals that basal lung epithelial cells can give rise to diverse subtypes of small cell lung cancer (SCLC), including neuroendocrine and tuft-like states, with lineage plasticity driven by genetic factors like MYC and PTEN loss. Loss of ASCL1 promotes tuft-like POU2F3+ SCLC, and lineage tracing confirms transitions between subtypes, highlighting the role of cell of origin and genetic alterations in SCLC heterogeneity and plasticity.
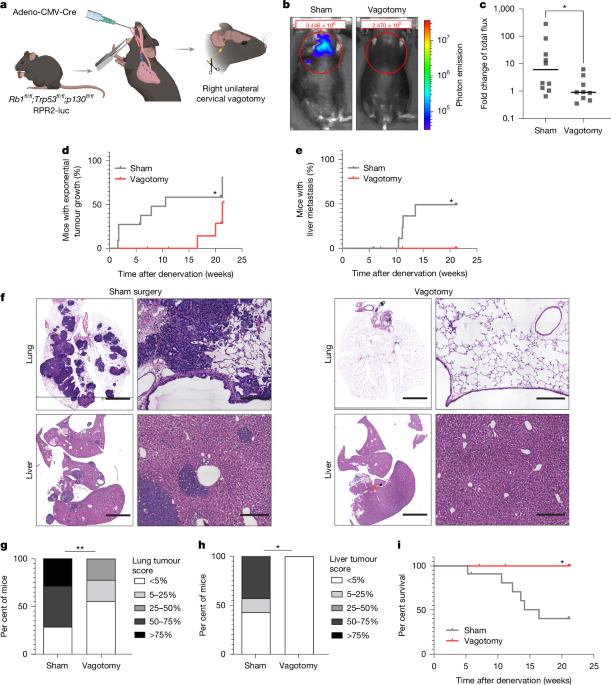
Small Cell Lung Cancer Exploits Brain Neuronal Synapses to Promote Growth
The article explores how neuronal activity and innervation, particularly via the vagus nerve, influence the initiation, progression, and metastasis of small cell lung cancer (SCLC), highlighting the role of neuron-tumor interactions, synaptic communication, and membrane depolarization in tumor growth within the lung and brain.
Small Cell Lung Cancer Exploits Neuronal Synapses to Promote Tumor Growth
The study reveals that small cell lung cancer (SCLC) forms functional synapses with neurons, particularly glutamatergic ones, which promote tumor growth. These synaptic interactions are characterized by structural and functional evidence of bona fide synapses, including electrophysiological activity and ultrastructural features. Targeting glutamate signaling with drugs like riluzole and DCPG shows promise in reducing tumor growth and improving survival in preclinical models, highlighting a novel neuro-oncological mechanism and potential therapeutic avenue.
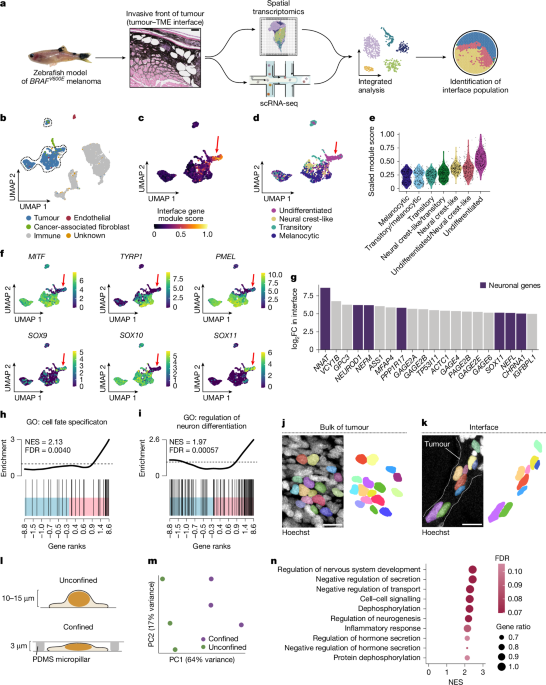
Mechanical Confinement Influences Melanoma Cell Plasticity
The study reveals that mechanical confinement in the tumor microenvironment induces stable chromatin and cytoskeletal changes in melanoma cells, promoting a neuronal, invasive phenotype characterized by HMGB2 upregulation, nuclear stiffening, and phenotype switching, which enhances tumor invasion and drug resistance.
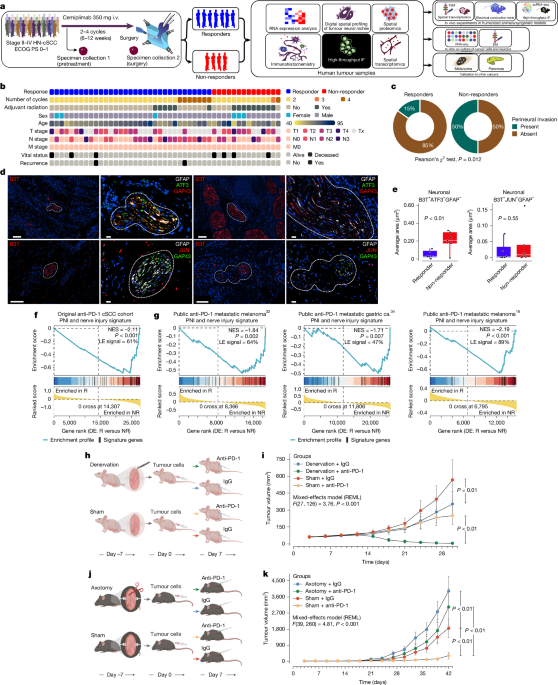
Cancer-Induced Nerve Damage and Inflammation Drive Immunotherapy Resistance
Cancer-induced nerve injury (CINI) promotes resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy by causing myelin degradation and chronic inflammation, which leads to immune exhaustion. The study shows that nerve injury within tumors correlates with immunosuppressive activity and therapy resistance across multiple cancer types, and that blocking nerve injury signaling can improve immune response and treatment efficacy.
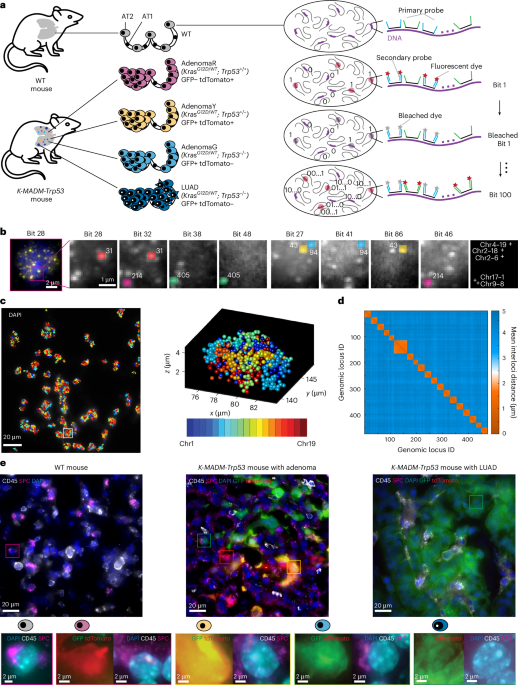
Evolution of Single-Cell 3D Genomes in Kras-Driven Cancers
This study uses in situ single-cell chromatin tracing to map 3D genome changes during Kras-driven lung and pancreatic cancers, revealing stage-specific conformational alterations that can distinguish cancer states, identify prognostic genes, and uncover regulators like Rnf2 that influence genome architecture and tumor progression.
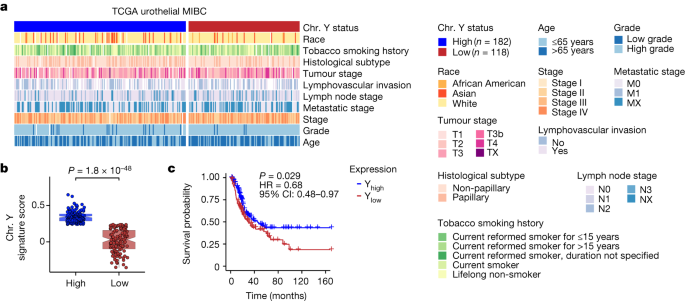
The Role of Y Chromosome Loss in Cancer Growth and Aggressiveness.
Loss of the Y chromosome in cancer cells allows them to evade the body's adaptive immune response, leading to increased cancer growth. This finding could explain why men are more susceptible to certain types of cancer. The study also suggests that targeting the Y chromosome could be a potential strategy for improving immunotherapy treatments for bladder cancer.
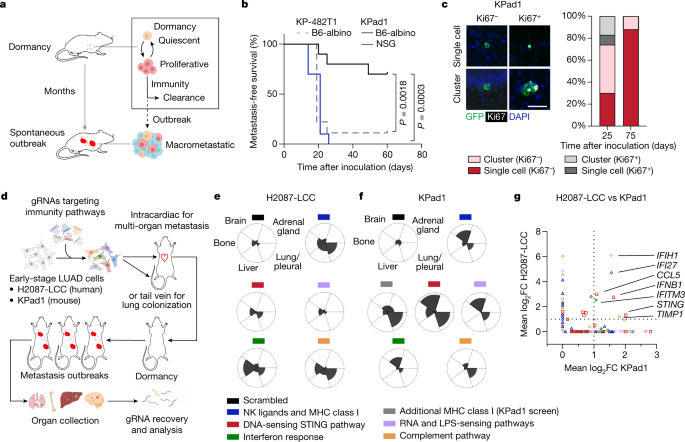
"STING Pathway Targeted for Antitumor Activity in Lung Adenocarcinoma"
A new study has found that STING, a protein that plays a role in the immune system's response to cancer, can inhibit the reactivation of dormant metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Dormant tumor cells can remain inactive for years before reactivating and causing cancer to spread. The study suggests that STING could be a potential target for preventing the reactivation of dormant metastasis and improving cancer treatment outcomes.
Transposable elements and ganglioside GD2 play key roles in cancer progression.
A pan-cancer analysis has identified tumor-specific antigens derived from transposable elements (TEs), which are DNA sequences that can move around the genome. The study found that TEs are frequently expressed in cancer cells and can produce novel proteins that are recognized by the immune system as foreign, making them potential targets for immunotherapy. The researchers also found that DNA methylation, an epigenetic modification that can silence genes, plays a role in regulating TE expression in cancer cells.
