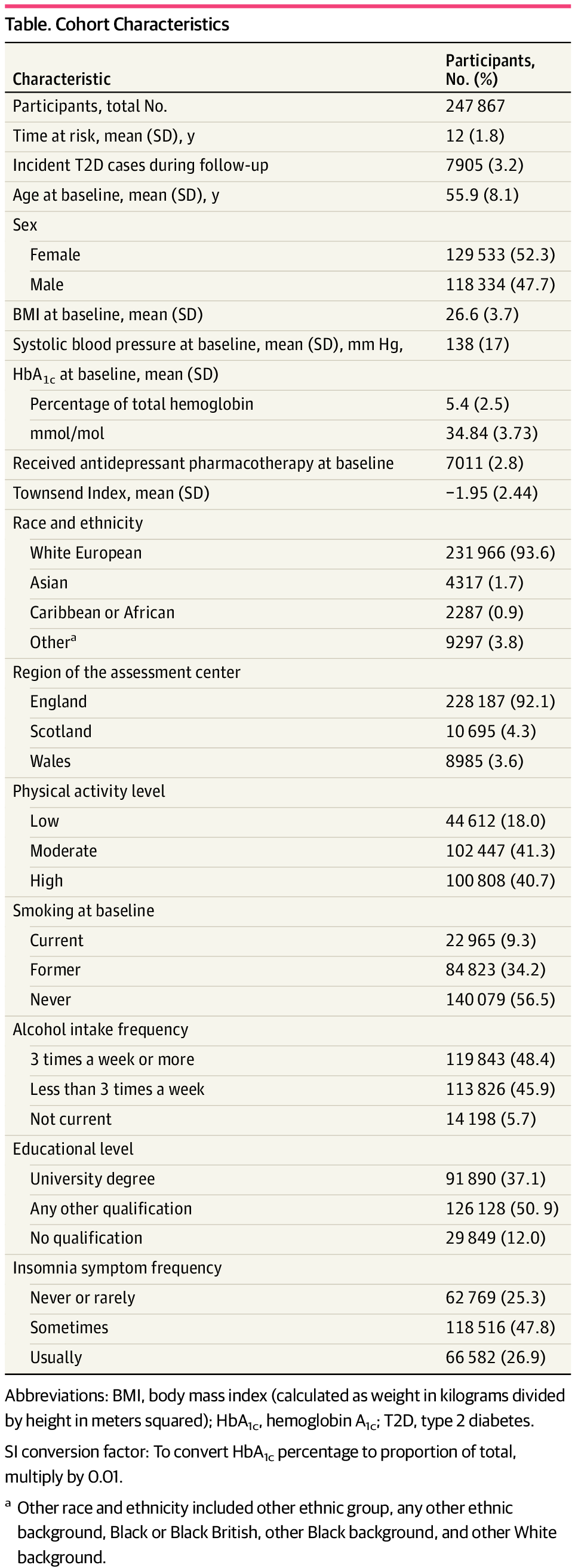
Global study links diet type to varied cancer risks across 1.8 million participants
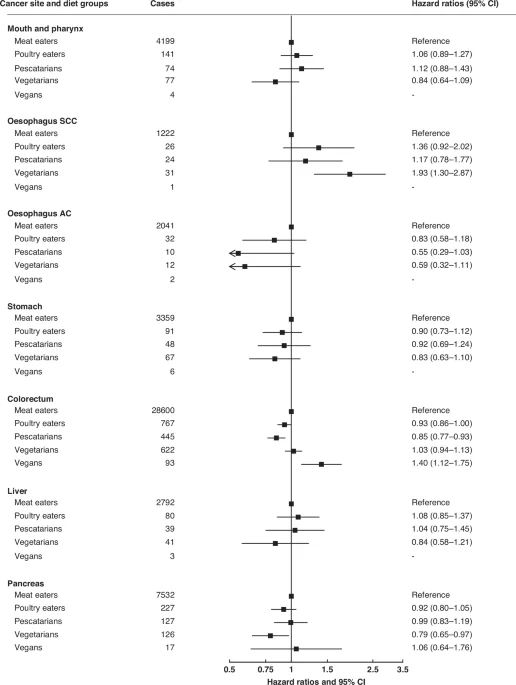
A pooled analysis of 1.8 million adults from nine prospective cohorts across the UK, US, Taiwan, and India found diet‑related differences in cancer risk. Compared with meat eaters, poultry eaters had a lower prostate cancer risk; pescatarians had lower colorectal, breast, and kidney cancer risks; vegetarians had lower risks of pancreatic, breast, prostate, kidney cancers and multiple myeloma but a higher risk of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma; vegans had a higher risk of colorectal cancer. The authors caution that results may not generalize and could be influenced by residual confounding and misclassification in diet groups.