Giant mimivirus commandeers host ribosomes to turbocharge replication
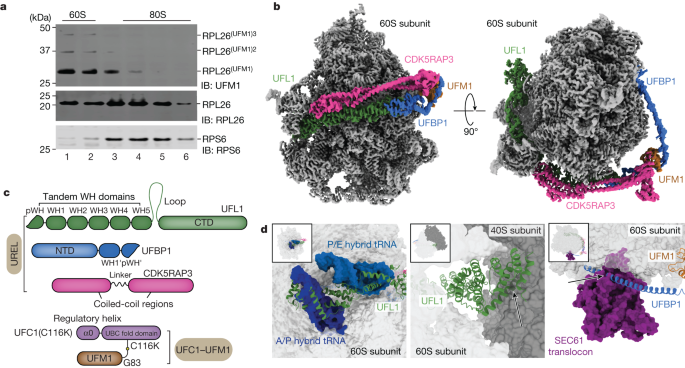
Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus, a giant virus visible under a light microscope, multiplies by hijacking the host’s ribosome‑based protein production. The study identifies three viral proteins that form a complex with host ribosomes to drive viral protein synthesis; deleting any one of these proteins slows replication by 1,000–100,000 times, providing the first clear experimental evidence that giant viruses can co-opt cellular machinery.