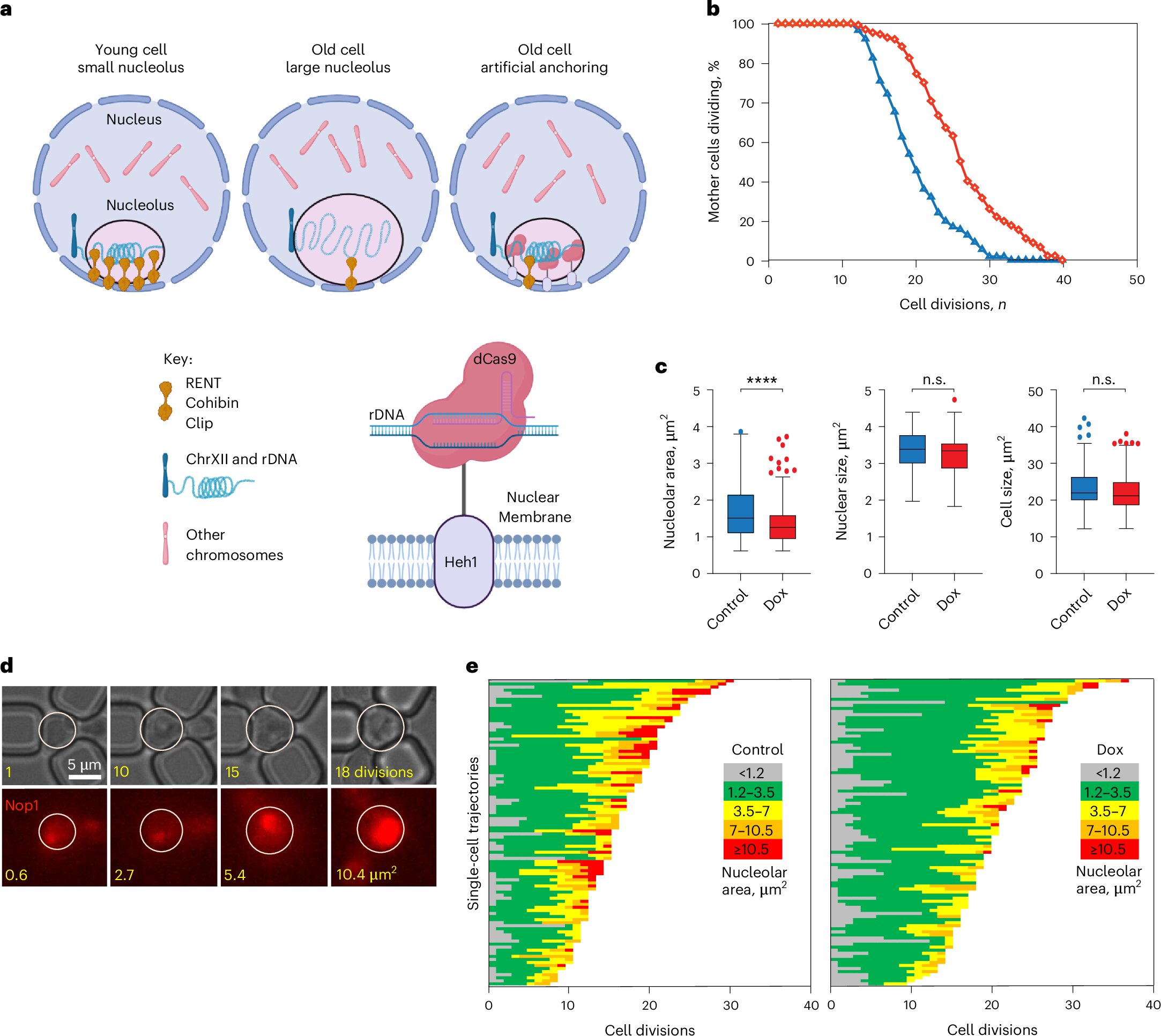
Compact Nucleolus: A Potential Key to Anti-Aging
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have discovered that maintaining a small nucleolus within cells may delay aging, as demonstrated in yeast. The study, published in Nature Aging, suggests that smaller nucleoli, achieved by tethering ribosomal DNA to the nuclear membrane, can extend lifespan similarly to calorie restriction. This finding could lead to new treatments for age-related diseases by preventing genomic instability associated with enlarged nucleoli. Future research will explore these effects in human stem cells.