Geometric Yellow Brick Road Discovered on the Deep Pacific Seafloor
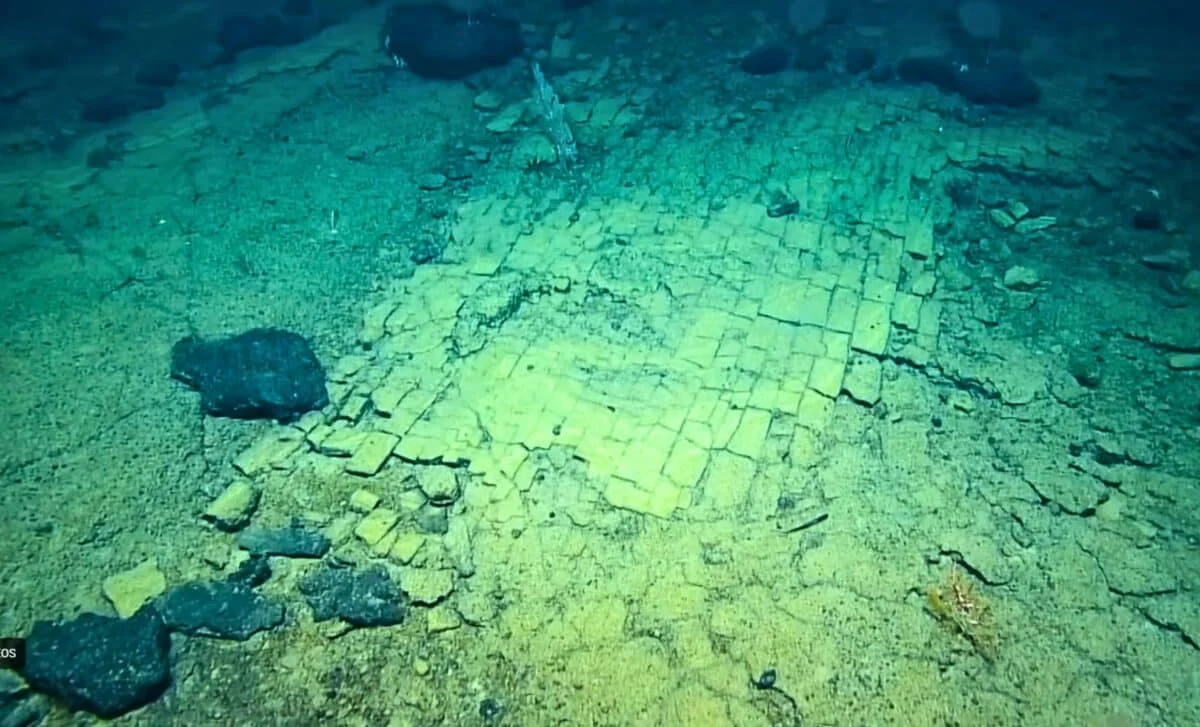
An Ocean Exploration Trust Nautilus dive at 3,000 meters depth near Nootka Seamount revealed a sharply geometric hyaloclastite formation dubbed a 'yellow brick road' due to 90-degree fractures likely from cooling during multiple eruptions. The find is part of the first visual survey of the Liliʻuokalani Seamounts within Papahānaumokuākea, with rock and microbial samples collected to date the formations and study deep-sea ecosystems, informing future monument management.