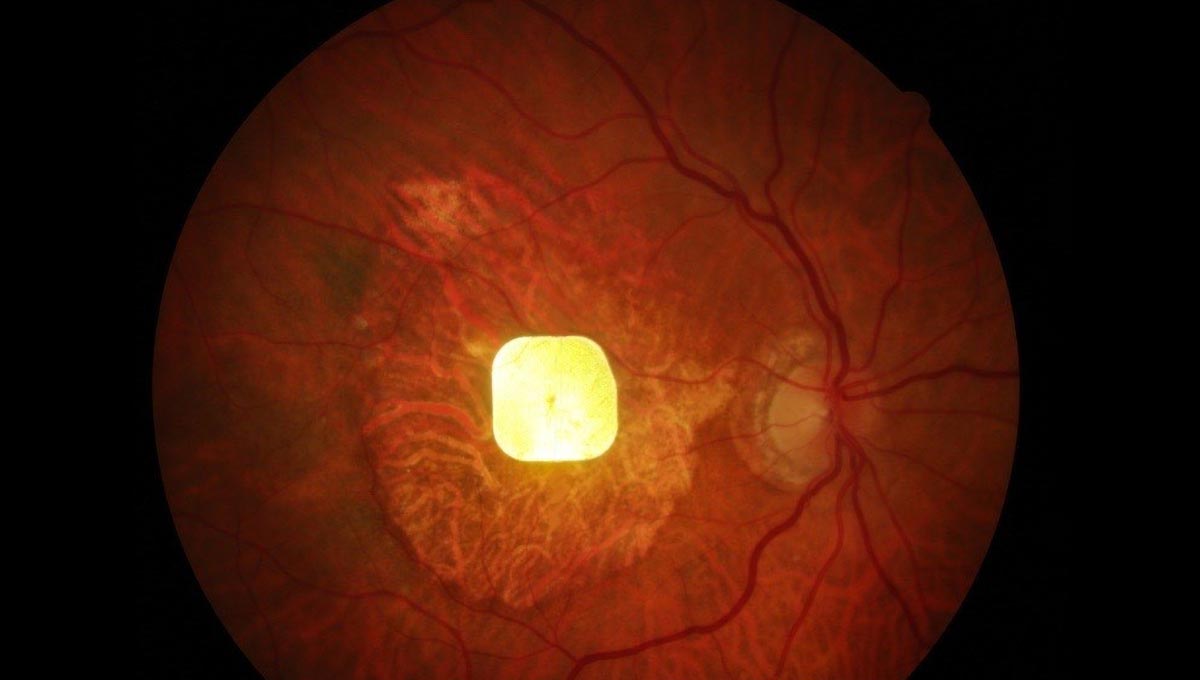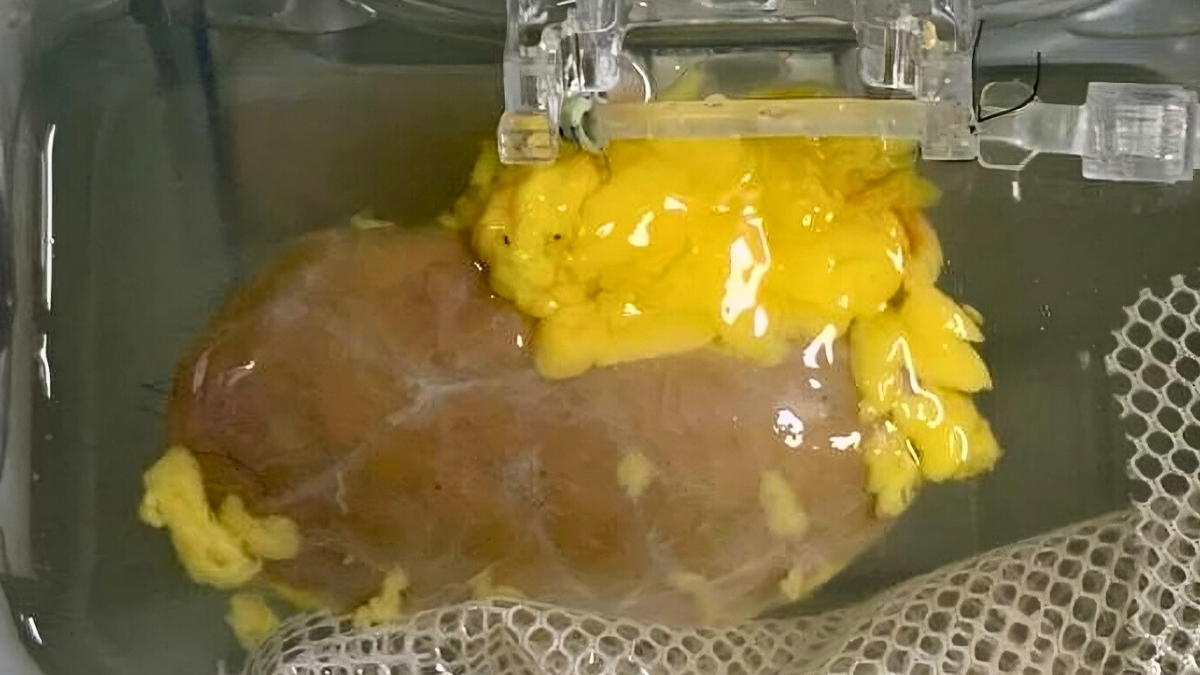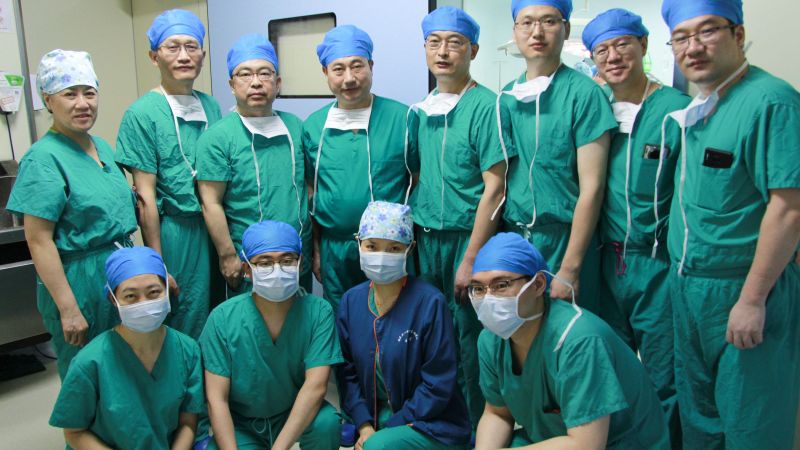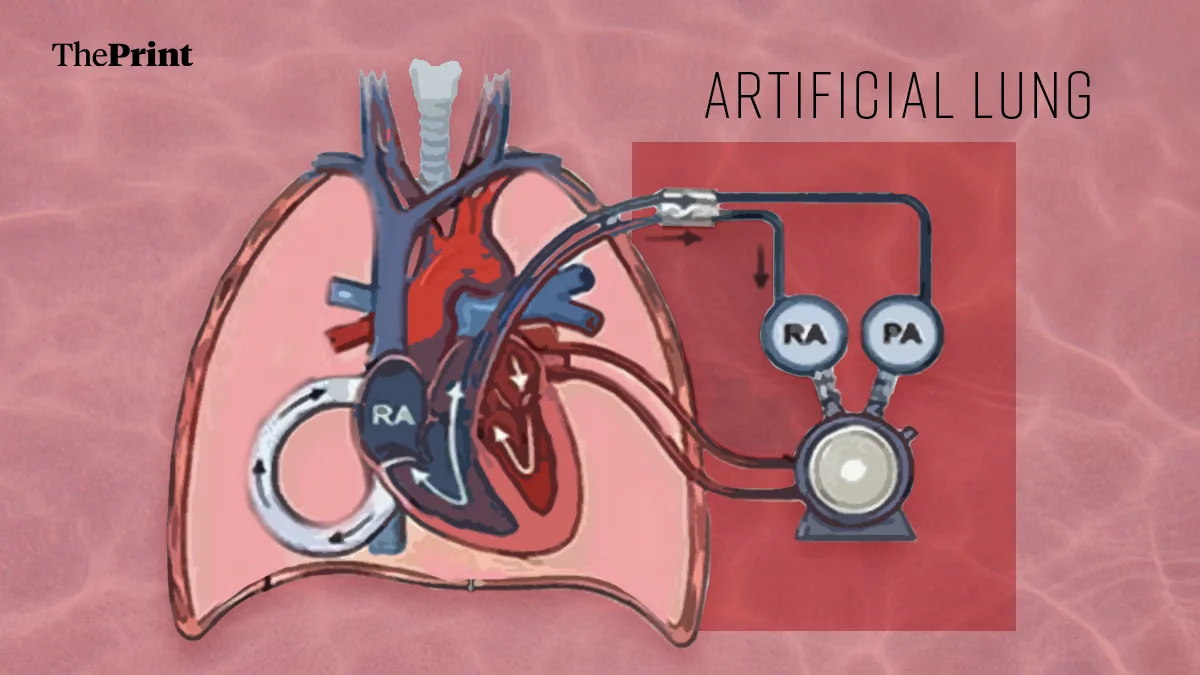
Two Days Without Lungs: A Case That Could Redefine Transplant Medicine
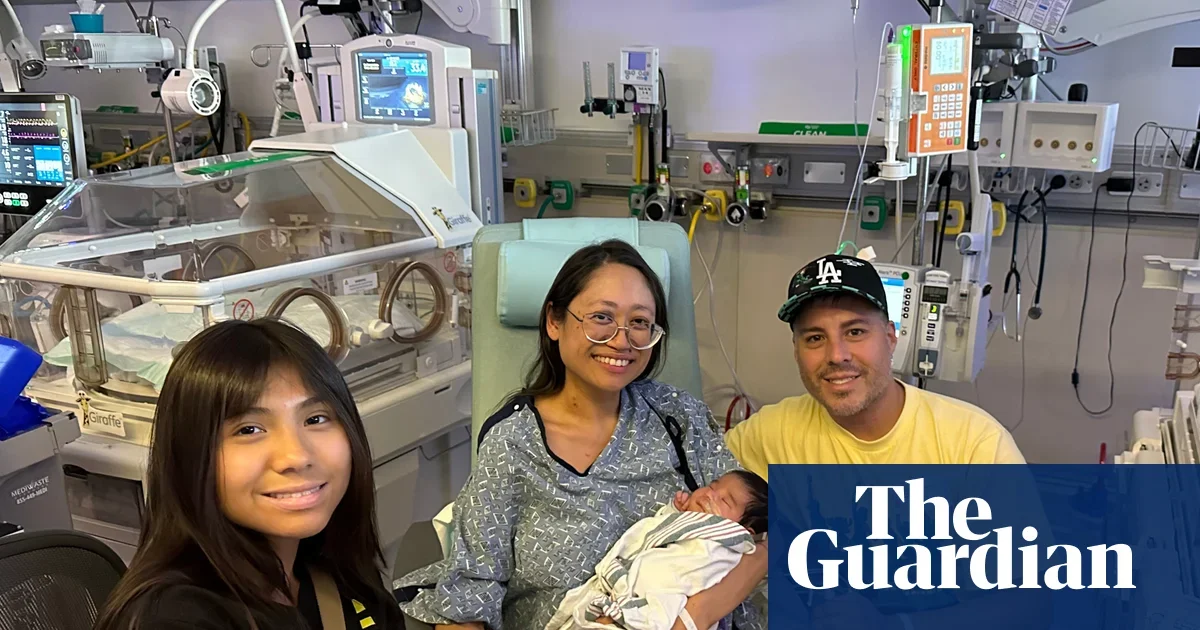
The article discusses a US patient who reportedly lived for two days without native lungs, supported by advanced extracorporeal technologies. It argues this could revolutionize transplant practice by extending bridging time and improving donor-lung utilization.