Can You Solve These Strange Medical Cases?
A weekly quiz series presents unusual medical cases for readers to diagnose, covering a range of rare and intriguing health conditions, encouraging engagement and learning about medical diagnostics.
All articles tagged with #health outcomes

A weekly quiz series presents unusual medical cases for readers to diagnose, covering a range of rare and intriguing health conditions, encouraging engagement and learning about medical diagnostics.

The U.S. healthcare system is characterized by high costs, lack of universal coverage, and poor performance in access, equity, and health outcomes compared to other high-income countries, leading to widespread personal and systemic challenges.

Research indicates that in older adults, later meal times, especially breakfast, are linked to health issues and increased risk of death, suggesting that maintaining consistent meal schedules could promote healthier aging.

A study from the University of Georgia, published in PLoS Genetics, reveals that genetic variations significantly influence individual health outcomes on a vegetarian diet. While vegetarians generally have lower cholesterol and reduced risks of heart disease and Type 2 diabetes, they may also experience lower Vitamin D levels and higher triglycerides. The research underscores the importance of personalized nutrition, considering genetic factors to optimize health, and identifies specific gene variants that affect calcium metabolism, hormone levels, and kidney function.
Researchers are using DNA sequencing of human feces to analyze the DNA of plant and animal species in order to reconstruct people's diets and understand the links between diet and health, potentially leading to personalized nutrition strategies and treatments for diet-linked diseases. This innovative approach provides valuable data for nutritional guidance and has the potential to revolutionize nutrition research, offering a more accurate and nuanced way to study the impact of diet on various health conditions.

A study using genetic data from over 3 million individuals, including those of European, Latin American, and African American ancestry, has revealed correlations between genetic variants related to alcohol consumption and a wide range of health outcomes. The research identified genetic variants that influence alcohol behaviors and found connections to both positive and negative health outcomes, including chronic conditions and certain cancers. The study emphasizes the importance of diverse genetic research to fully understand the multifaceted impacts of these genetic variants on human health and highlights the need for inclusive genetic studies to avoid exacerbating health disparities.

A new study published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition explores the safety and benefits of the Mediterranean diet (MED diet) in adults with cancer, indicating that the diet may help mitigate adverse effects of cancer treatment. The study found that participants adhering to the MED diet experienced favorable changes in body weight, BMI, metabolic and inflammatory markers, and quality of life. While the study highlights the safety and feasibility of the MED diet as a nutritional intervention for cancer patients, further research is needed to confirm its efficacy in preventing and managing chronic diseases in this population.
A study analyzing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) reveals that poverty combined with chronic inflammation leads to significantly worse health outcomes than either factor alone, with a 127% increased heart disease mortality risk and a 196% increased cancer mortality risk for those affected by both factors. The research suggests a need for healthcare professionals to screen socially disadvantaged individuals for chronic inflammation and consider appropriate treatments, emphasizing the synergistic relationship between poverty and inflammation in exacerbating health risks and reducing life expectancy in the U.S.
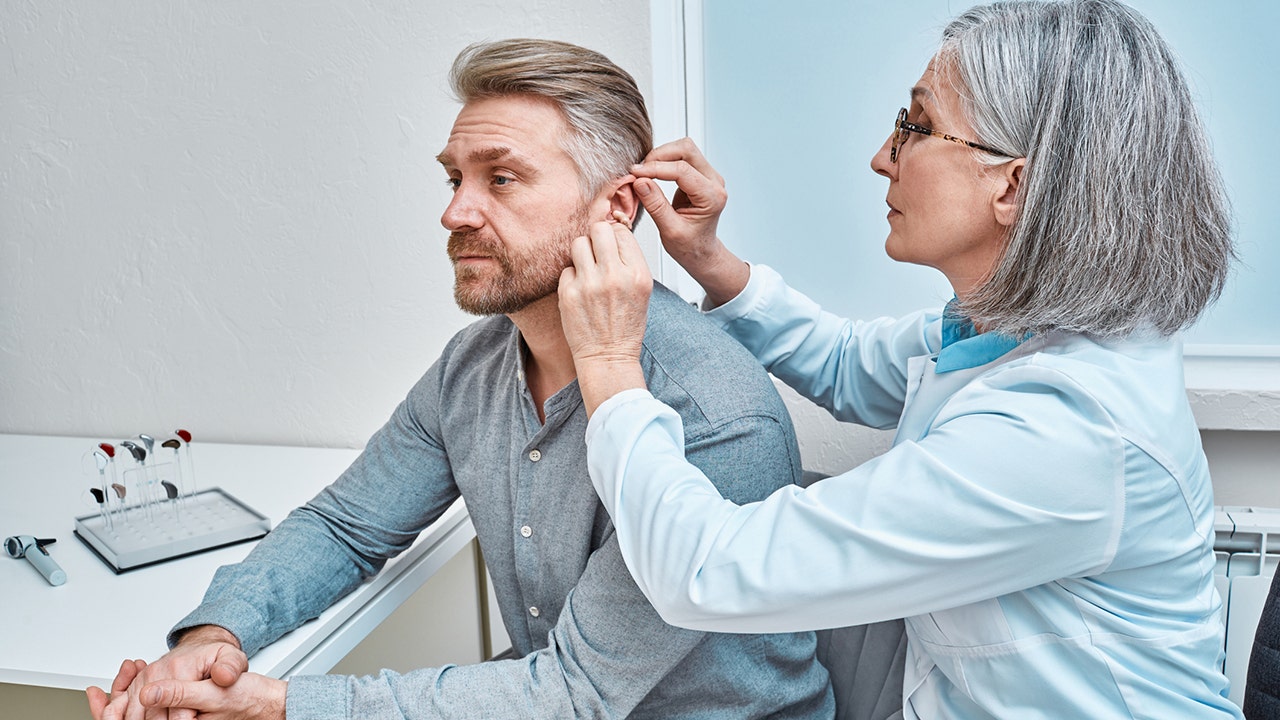

A study by the Keck School of Medicine at USC found that regular use of hearing aids is associated with a 24% lower risk of mortality among individuals with hearing loss. The study, which followed nearly 10,000 patients over a 10-year period, revealed that even after adjusting for factors like age and medical history, the mortality risk remained significantly lower for regular hearing aid users. The findings suggest a potential protective role of hearing aid use against mortality and highlight the importance of addressing hearing loss to improve overall health outcomes and quality of life, potentially leading to a longer lifespan.
A new study reveals that Americans are taking more prescription drugs and staying on them for longer periods of time than ever before. The research estimates that babies born in 2019 will spend half their lives taking medications under doctor's orders. The study highlights a steep increase in prescription drug use among various demographics, with older, White women showing the highest increase. Factors contributing to this trend include the growing burden of obesity, longer survival with chronic conditions, and intensified treatment of high blood pressure and cholesterol. However, the study also raises concerns about the potential risks and negative interactions associated with taking multiple medications for extended periods. The need for further research on the long-term impact of sustained prescription drug use is emphasized.
A study presented at the annual conference of The American College of Chest Physicians found that cannabis consumers who contracted COVID-19 had lower rates of intubation, respiratory failure, and death compared to non-users. The study, based on hospital data, suggests that marijuana may inhibit viral entry into cells and prevent the release of proinflammatory cytokines. Cannabis consumers also had lower rates of complications related to COVID-19, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome and severe sepsis with multiorgan failure. However, further investigation is needed to understand the association between marijuana use and COVID-19.
New research published in the Journal of Criminal Justice reveals that contact with the criminal justice system, particularly probation and probation in combination with incarceration, disproportionately affects the health outcomes of Black Americans. The study, based on data from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health, found that Black Americans consistently reported poorer health outcomes compared to their White and Hispanic counterparts when associated with contact with the criminal justice system. Probation was identified as the strongest driver of lower self-rated health and chronic conditions among Black Americans, highlighting the need for further investigation into the long-term consequences of different types of contact with the criminal justice system and their impact on health.
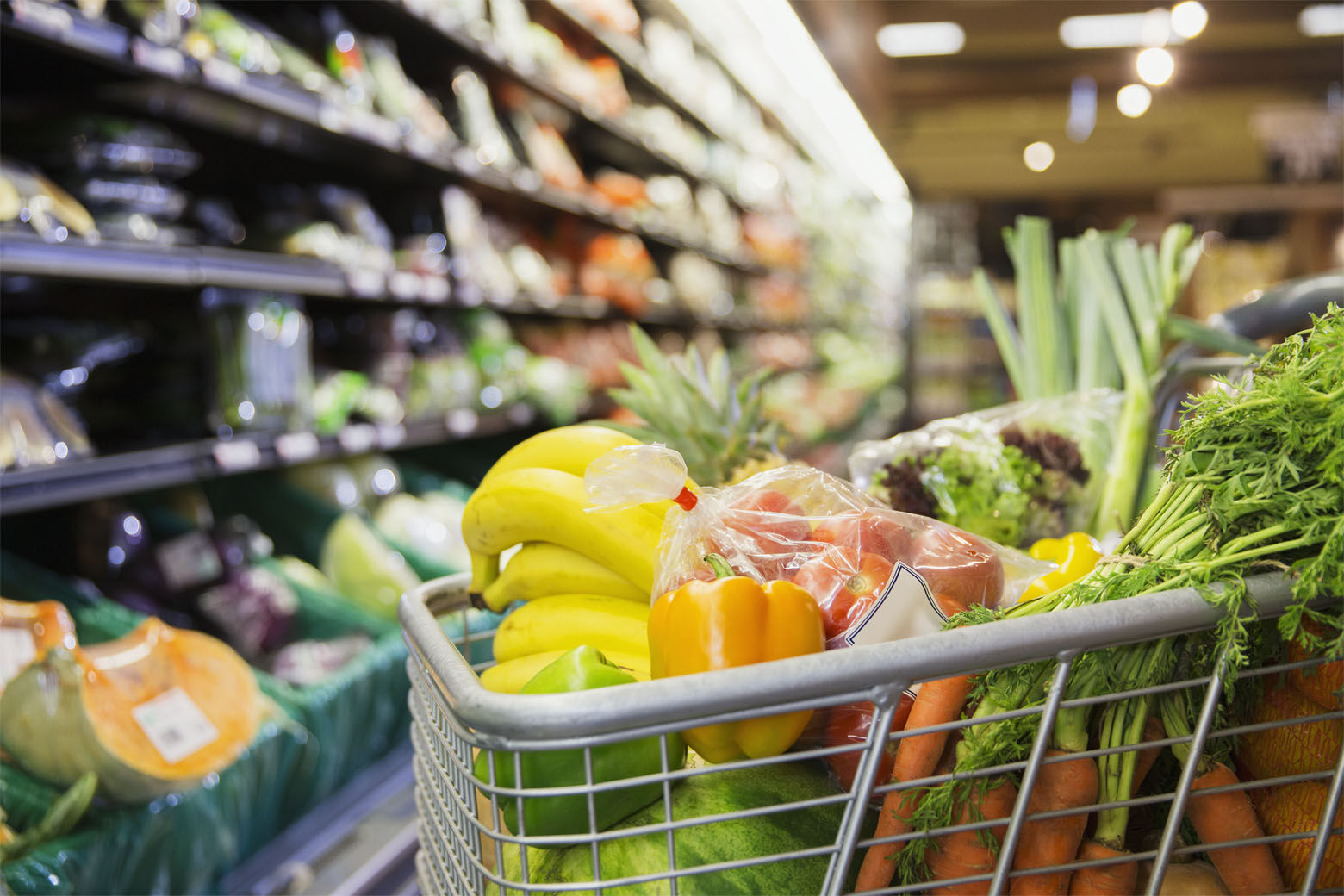

Programs like DC Greens' Produce RX, which provides prescriptions for healthy foods to low-income individuals with diet-related chronic illnesses, are helping improve access to nutritious food and overall health outcomes. A recent study found that participants in such programs experienced increased consumption of fruits and vegetables, as well as improvements in blood pressure, obesity, and blood sugar. By providing prepaid debit cards for purchasing fresh produce, these programs not only address affordability barriers but also alleviate financial stress for families. The approach of prescribing fresh food as medicine is proving to be more effective and appealing to patients than traditional medications.
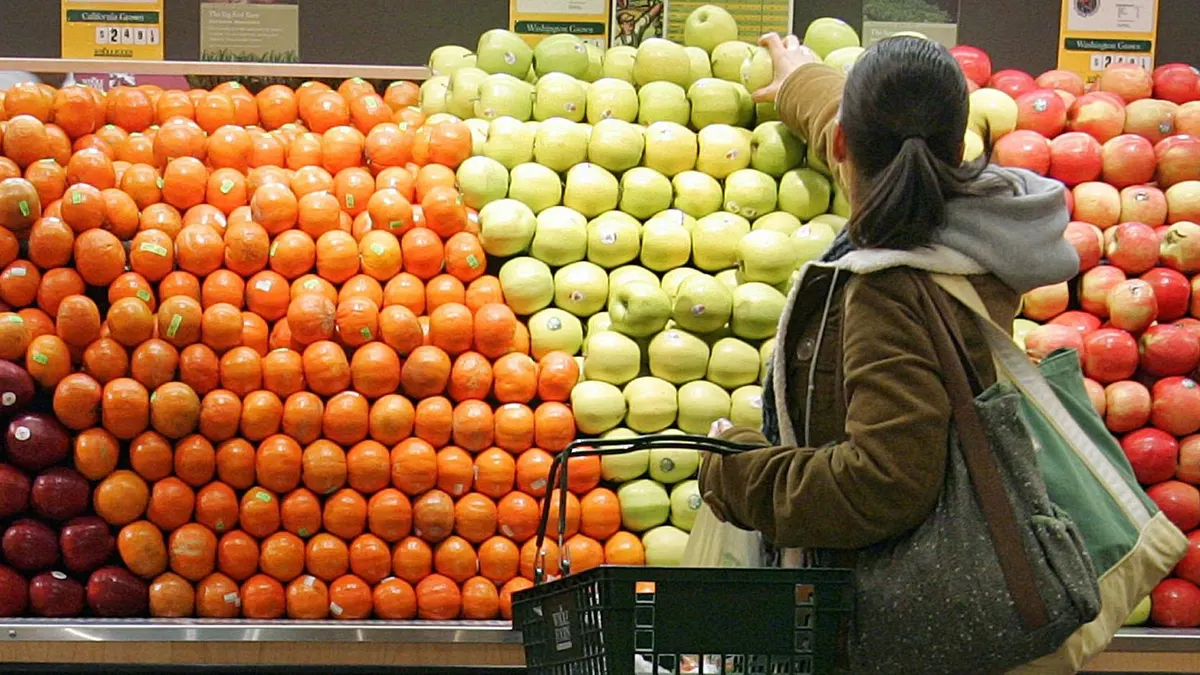

A new study from Tufts University shows that Americans who participate in "produce prescription" programs, where doctors prescribe fruits and vegetables alongside traditional medications and have those foods covered by health insurance or community grants, experience improved health outcomes and a reduced risk of stress and anxiety. Participants saw lowered blood pressure, reduced BMI, improved blood sugar levels, and reduced food insecurity. The study highlights the potential benefits of such programs in addressing obesity-related illnesses and the importance of increasing access to fresh produce for better overall health.

A multicentre French study found that recreational drug use was detected in more than 1 in 10 patients admitted to cardiac intensive care. Drug use was associated with significantly poorer outcomes, with users being nearly 9 times more likely to die or require emergency intervention. Cannabis was the most frequently detected substance, followed by opioids, cocaine, amphetamines, and MDMA/ecstasy. The study suggests the potential value of urine screening for selected patients with acute cardiovascular events to improve risk stratification in cardiac intensive care. However, larger studies are needed to establish a causal relationship and determine the best interventions following positive drug test results.