Post-Seizure Sleep May Strengthen Epileptic Networks
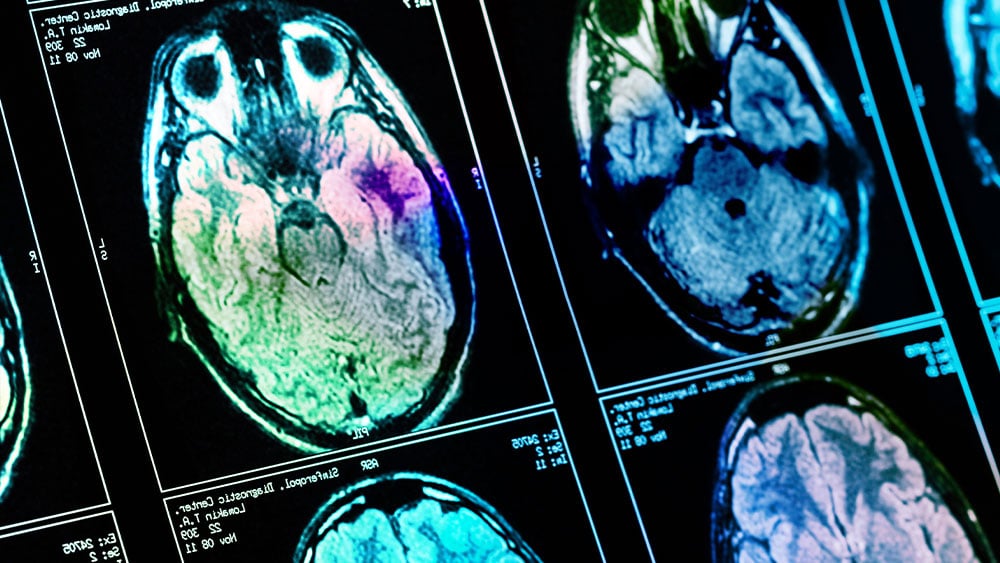
New Mayo Clinic findings indicate the brain may hijack memory-consolidation processes after a seizure, with nights of intensified deep (NREM) sleep and reduced REM sleep that strengthen seizure networks and potentially worsen epilepsy. This post-seizure consolidation could explain disease progression and points to a critical window for targeted neuromodulation therapies to disrupt the reinforced networks, an approach being explored by Mayo’s BIONIC initiative.