
Revolutionizing Energy: A Petroleum-Free Gas Alternative
The article discusses a new gas alternative that aims to replace fossil fuels without using petroleum, promoting sustainable energy solutions and reducing environmental impact.
All articles tagged with #sustainable energy

The article discusses a new gas alternative that aims to replace fossil fuels without using petroleum, promoting sustainable energy solutions and reducing environmental impact.
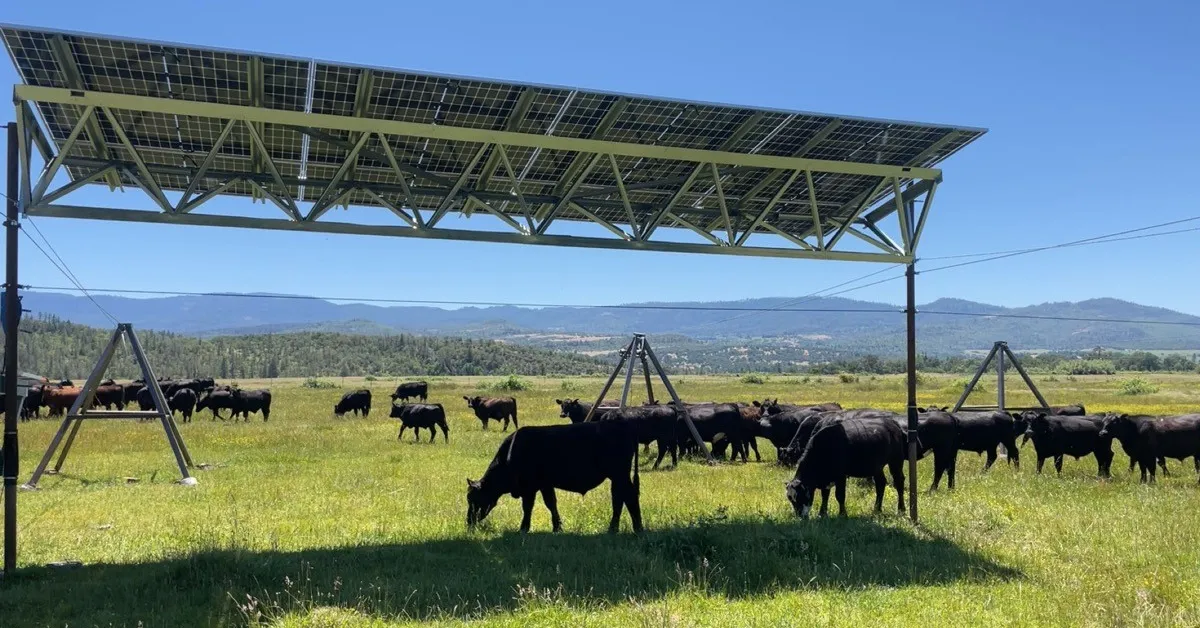

An Oregon cattle ranch has installed a unique, cattle-friendly solar array that provides ample clearance for grazing, supporting sustainable land use and creating additional revenue streams through agrivoltaics, with ongoing studies and plans to expand this innovative approach.

Scientists have discovered vast underground reserves of natural hydrogen that could provide up to 170,000 years of clean energy, offering a promising alternative to fossil fuels and potentially revolutionizing the global energy landscape, despite technical challenges in extraction and utilization.

Researchers have discovered vast underground reserves of natural hydrogen that could potentially power the planet for 170,000 years, offering a promising, environmentally friendly alternative to current hydrogen production methods, though challenges in extraction remain.

Experiments at San Diego's DIII-D National Fusion Facility have demonstrated that a new plasma shape called 'negative triangularity' can enhance the stability of tokamak fusion reactors, potentially paving the way for more efficient and sustainable nuclear fusion energy, which could provide nearly limitless low-carbon power.
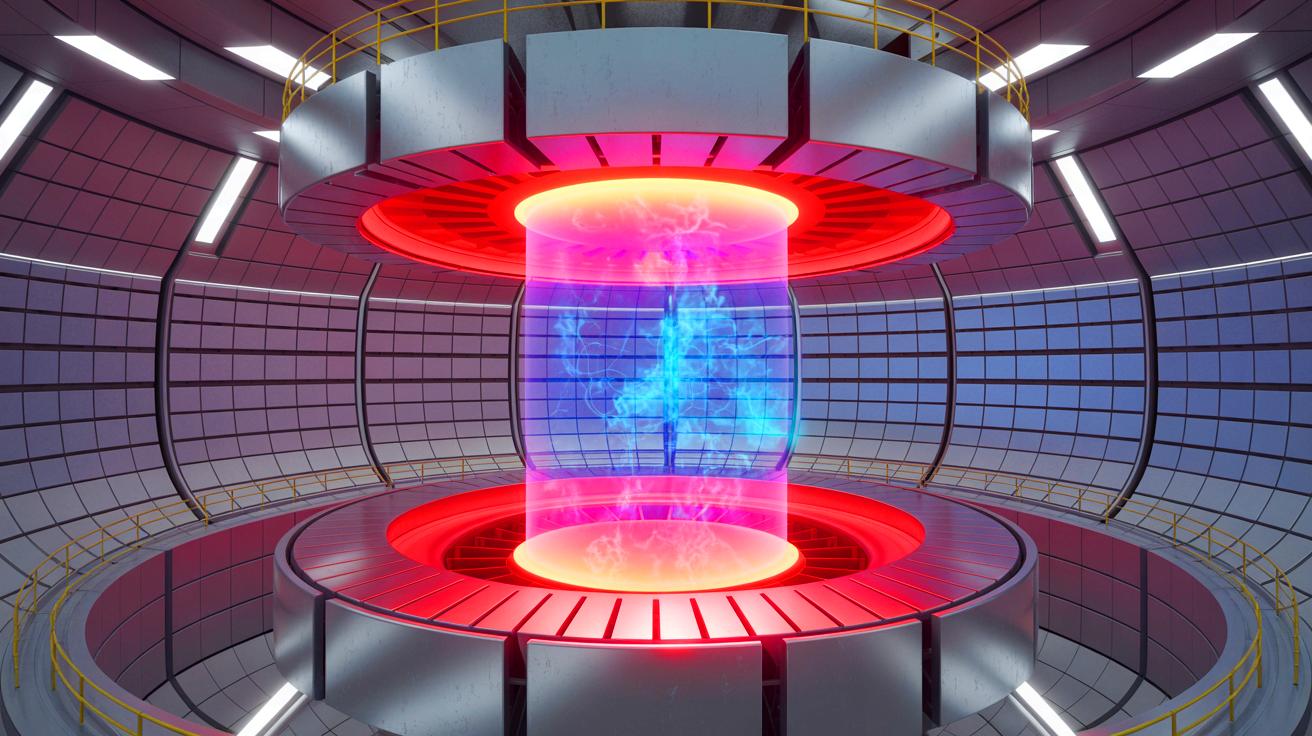
China's EAST reactor has set a new world record by maintaining plasma temperatures over 180 million degrees Fahrenheit for 1,066 seconds, marking a significant milestone in nuclear fusion research and the pursuit of clean, sustainable energy. This achievement demonstrates the potential for fusion to become a practical energy source, with global implications for energy security and environmental impact.
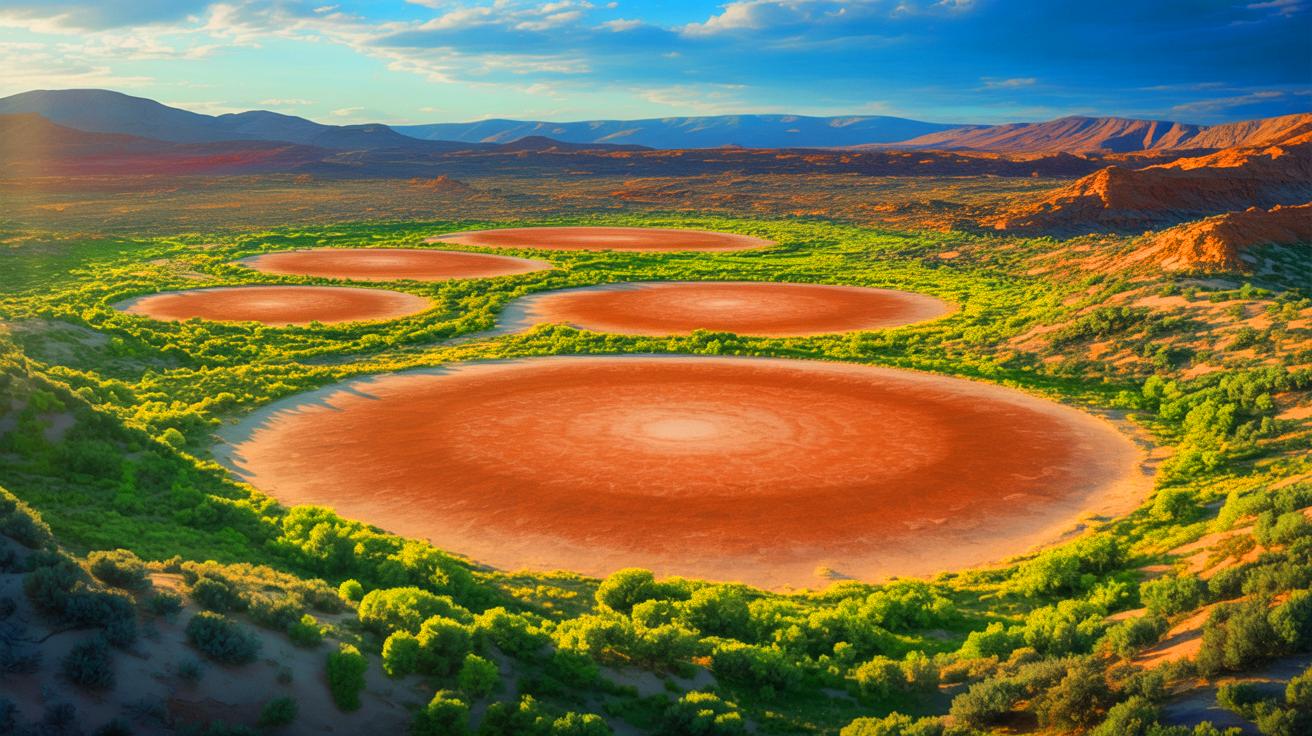

Scientists have discovered that mysterious fairy circles may indicate underground hydrogen reserves, offering a potential new method for exploring and harnessing clean, natural hydrogen as a sustainable energy source, which could revolutionize the global energy landscape.
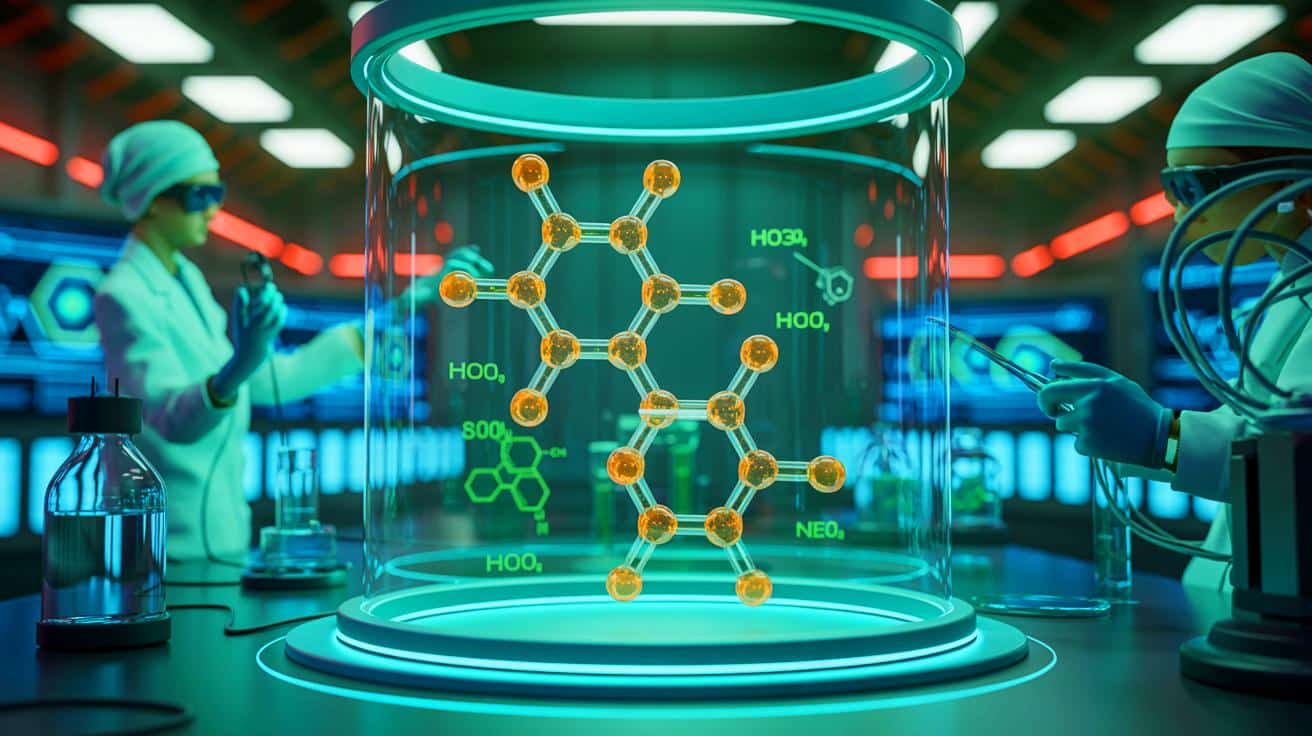
Swiss scientists at the University of Basel have developed a groundbreaking molecule capable of storing multiple charges, mimicking natural photosynthesis to produce carbon-neutral fuels like hydrogen and methanol, advancing sustainable energy technologies and addressing climate change.

Tesla's fourth 'Master Plan' lacks specifics and reads as vague and generic, failing to build on the concrete goals of its previous plans, and raising questions about the company's progress on its ambitious sustainability and automation objectives.
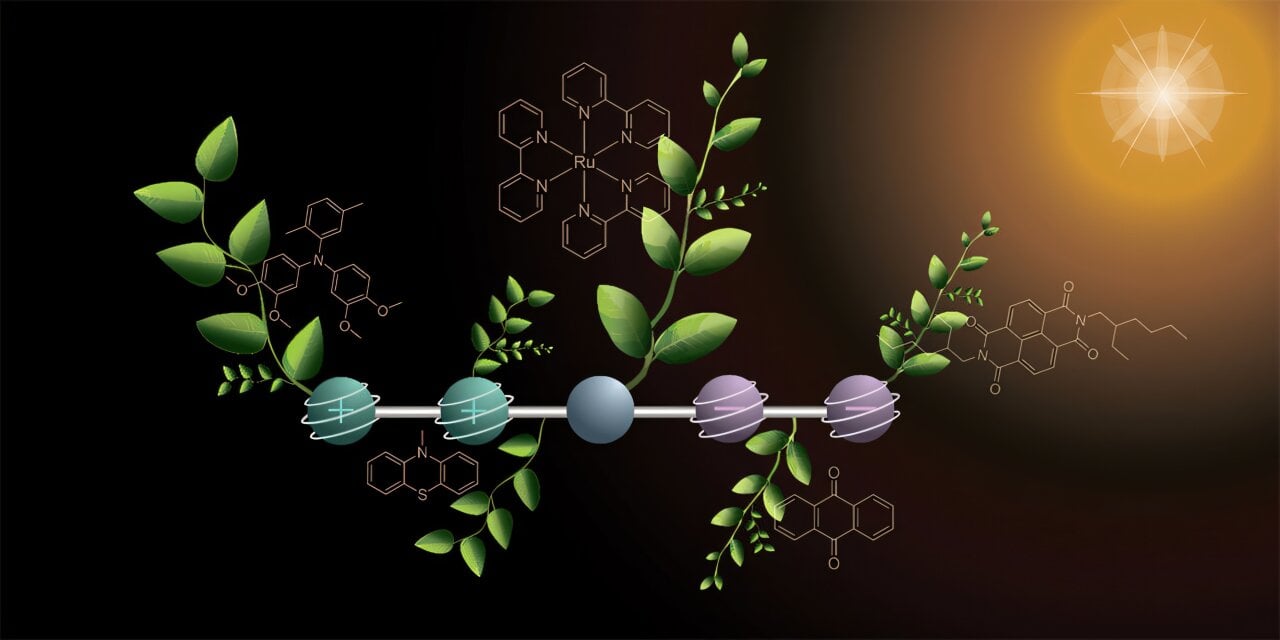
A Swiss research team has developed a novel molecule capable of storing four charges under light, mimicking natural photosynthesis, which could be a key step toward creating carbon-neutral fuels using sunlight.
Researchers at NJIT used generative AI to discover five new porous materials that could enable more efficient, sustainable multivalent-ion batteries using abundant elements like magnesium and zinc, offering a promising alternative to lithium-ion technology and accelerating advanced materials research.
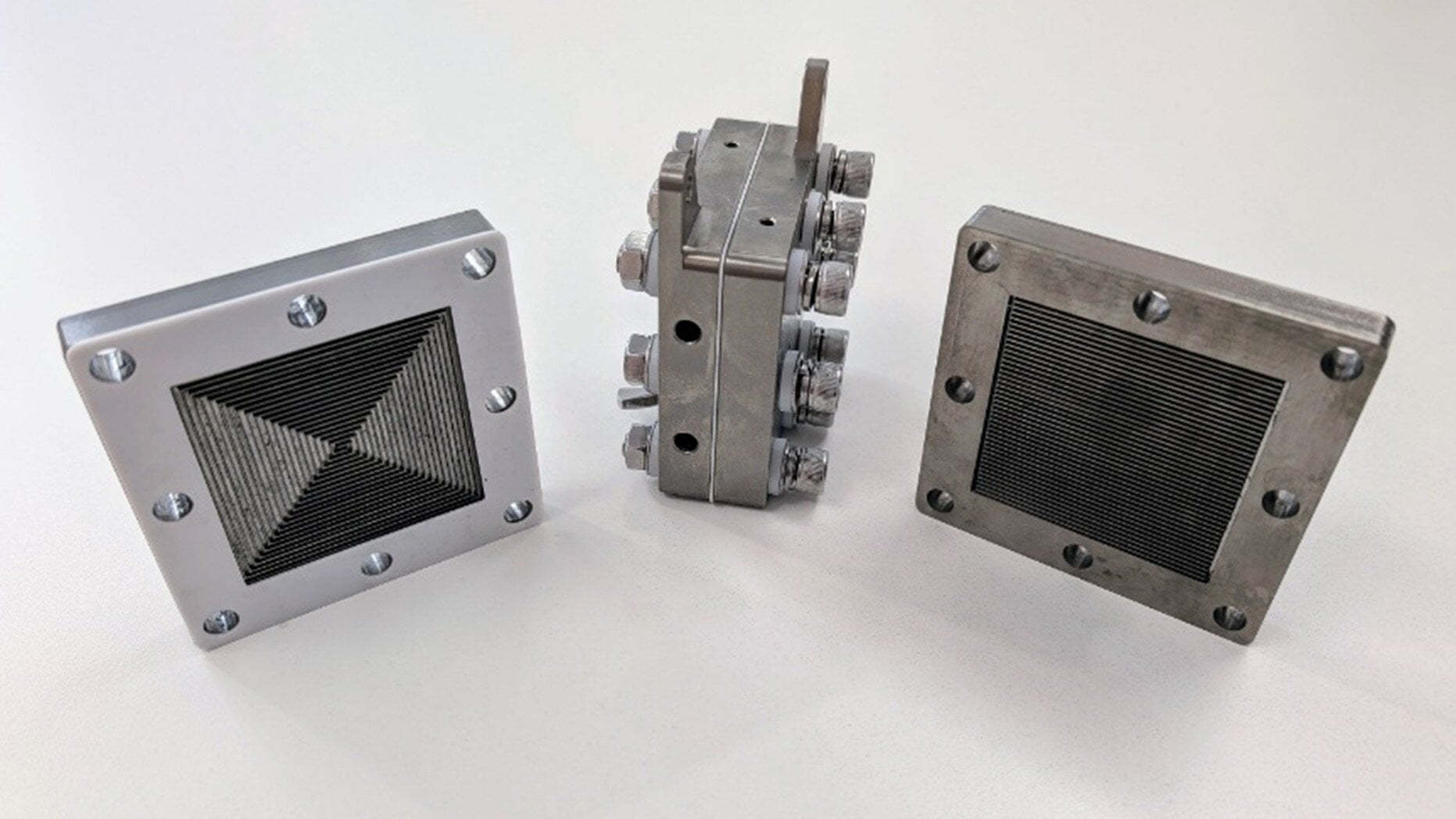
University of Sydney researchers have developed a new method to produce green ammonia directly from air using plasma and electrolysis, potentially revolutionizing sustainable fertilizer and hydrogen storage, and reducing reliance on the climate-intensive Haber-Bosch process.

Researchers from Korea have developed a new proton exchange membrane using SPAES that significantly reduces toluene crossover in hydrogen storage systems, potentially enabling more efficient and durable hydrogen fuel cells for eco-friendly vehicles by 2030, contributing to the hydrogen economy and reducing carbon emissions.
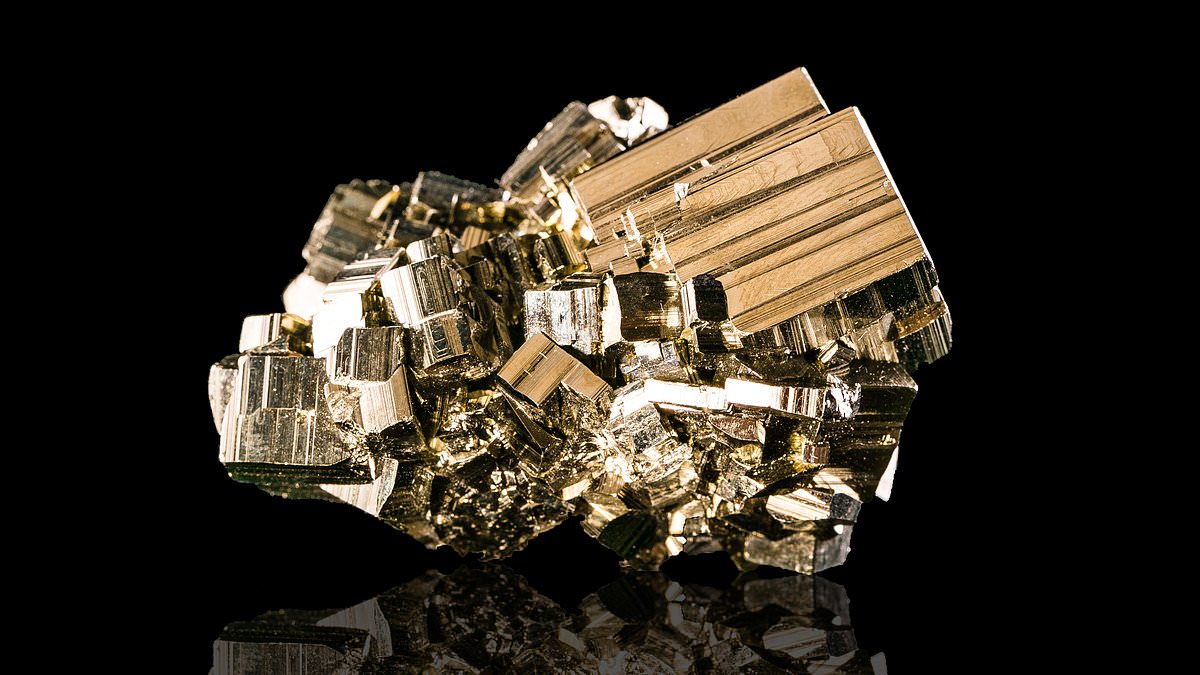

Scientists at West Virginia University discovered significant amounts of lithium in fool's gold, potentially opening up old industrial mines as a valuable source of the metal needed for green energy technologies like lithium-ion batteries. The discovery could help meet the soaring demand for lithium as the US transitions to green energy, offering a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective approach to lithium extraction compared to traditional methods. This unexpected finding in the Appalachian Mountains could play a crucial role in sustaining global green initiatives and reducing the negative environmental impact of mining for essential minerals.
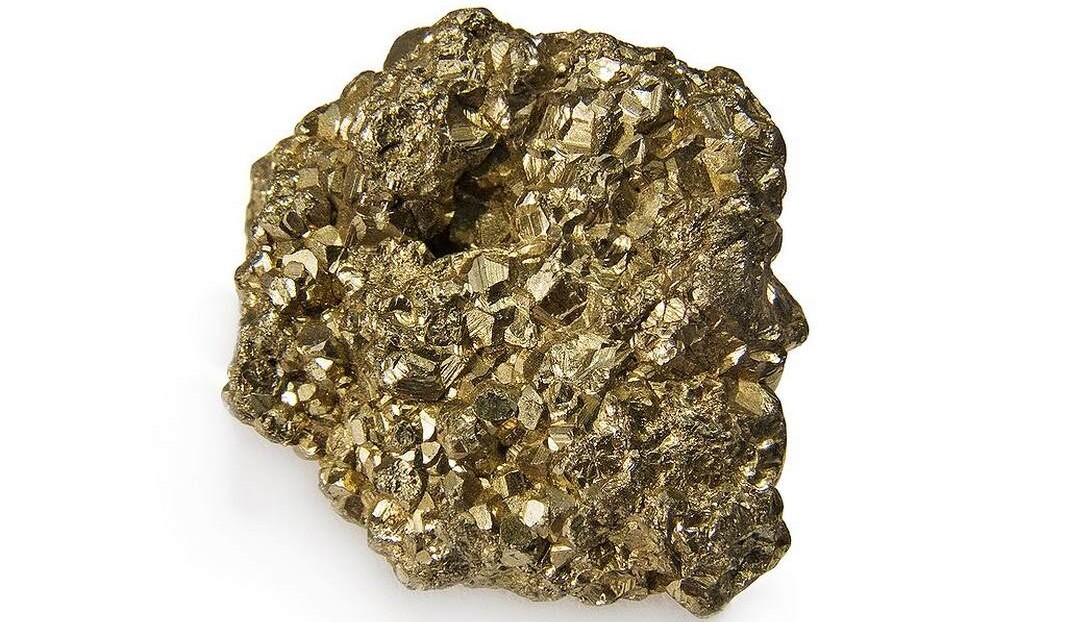

Scientists in West Virginia have discovered significant amounts of lithium within pyrite, or fool's gold, found in mine tailings, offering a potential sustainable source of the rare earth element for renewable energy technologies. This discovery could provide a steady supply of lithium without the need for environmentally harmful mining, as demand for the element skyrockets due to the transition to greener energy sources. The study suggests that certain shales containing pyrite could serve as a lithium source, potentially revolutionizing the way lithium is obtained for use in batteries and other applications.