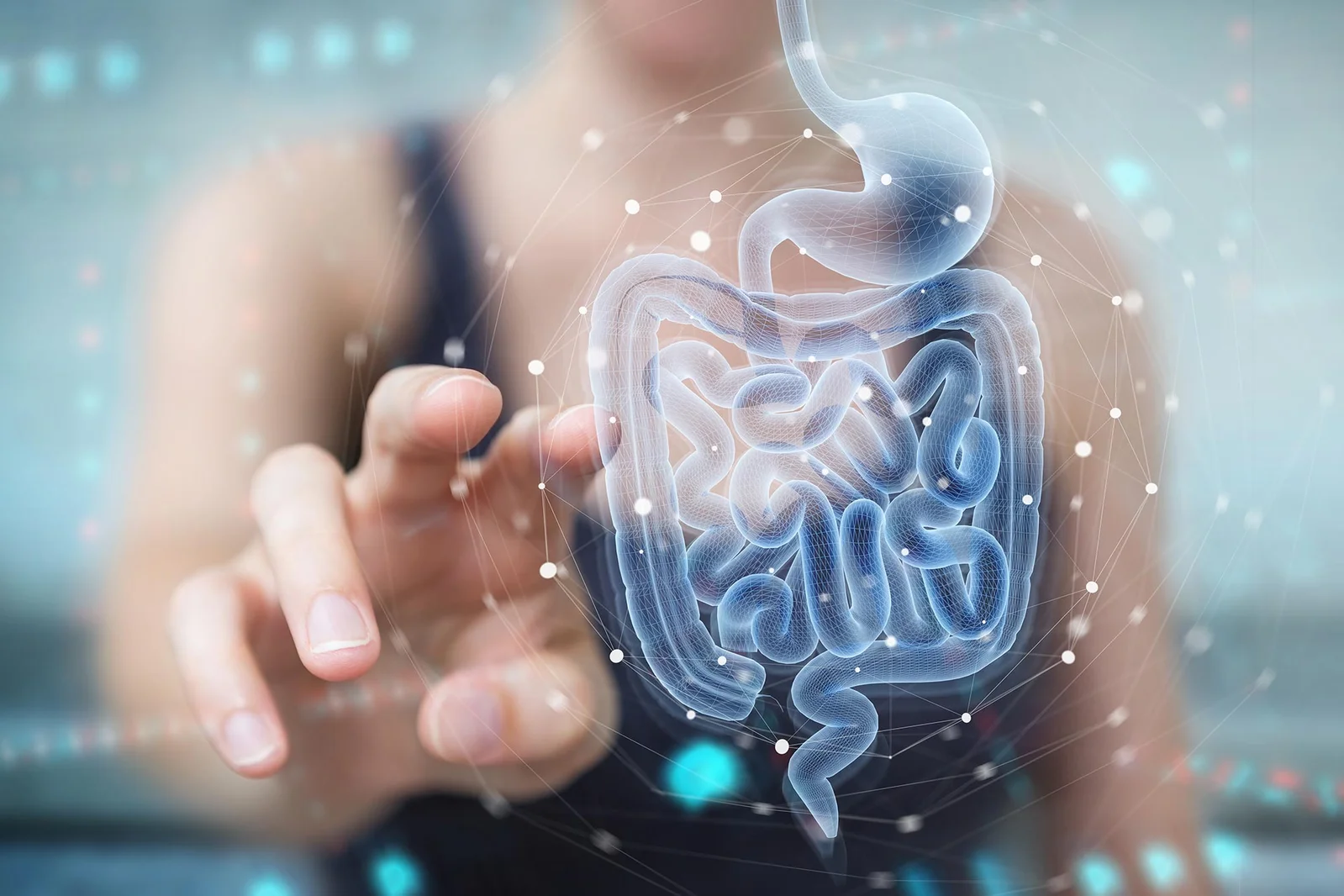
Immune Therapy Reboots Aging Gut, Delivering Year-Long Regeneration in Mice
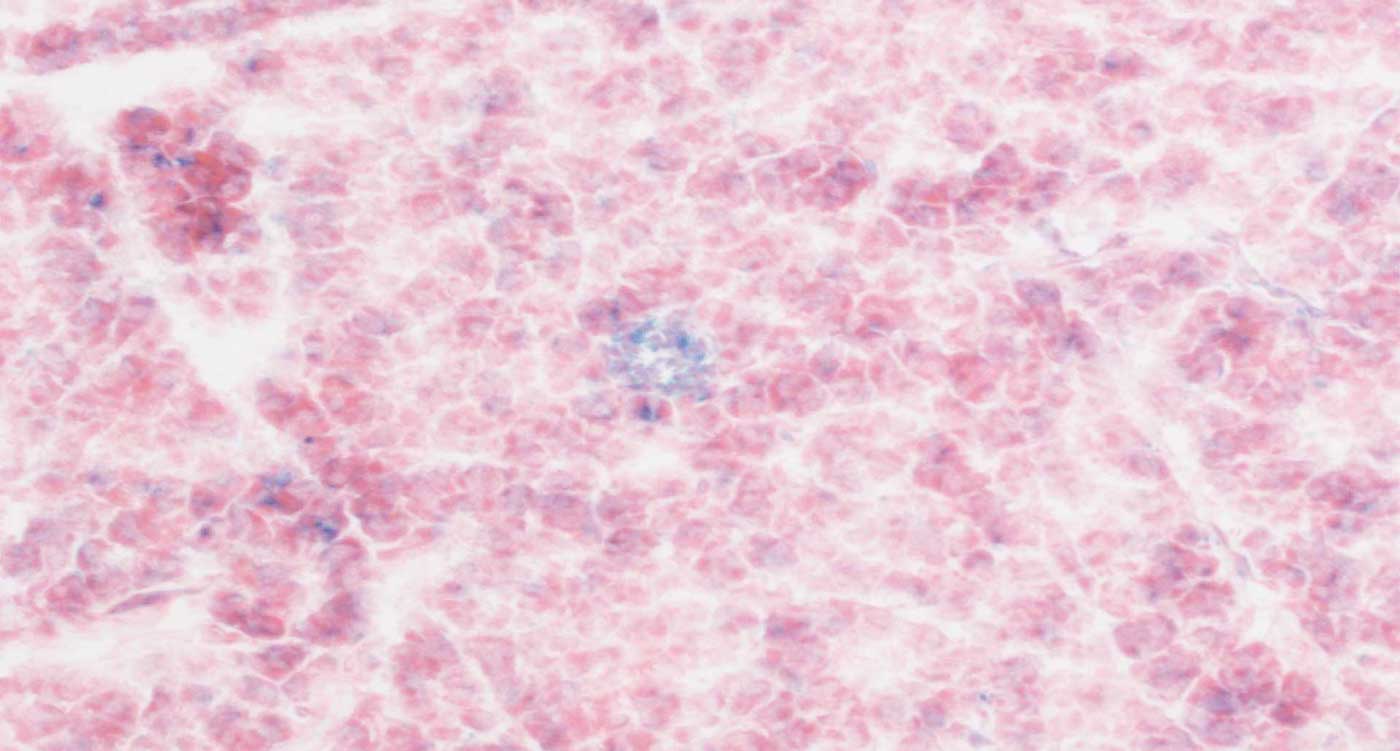
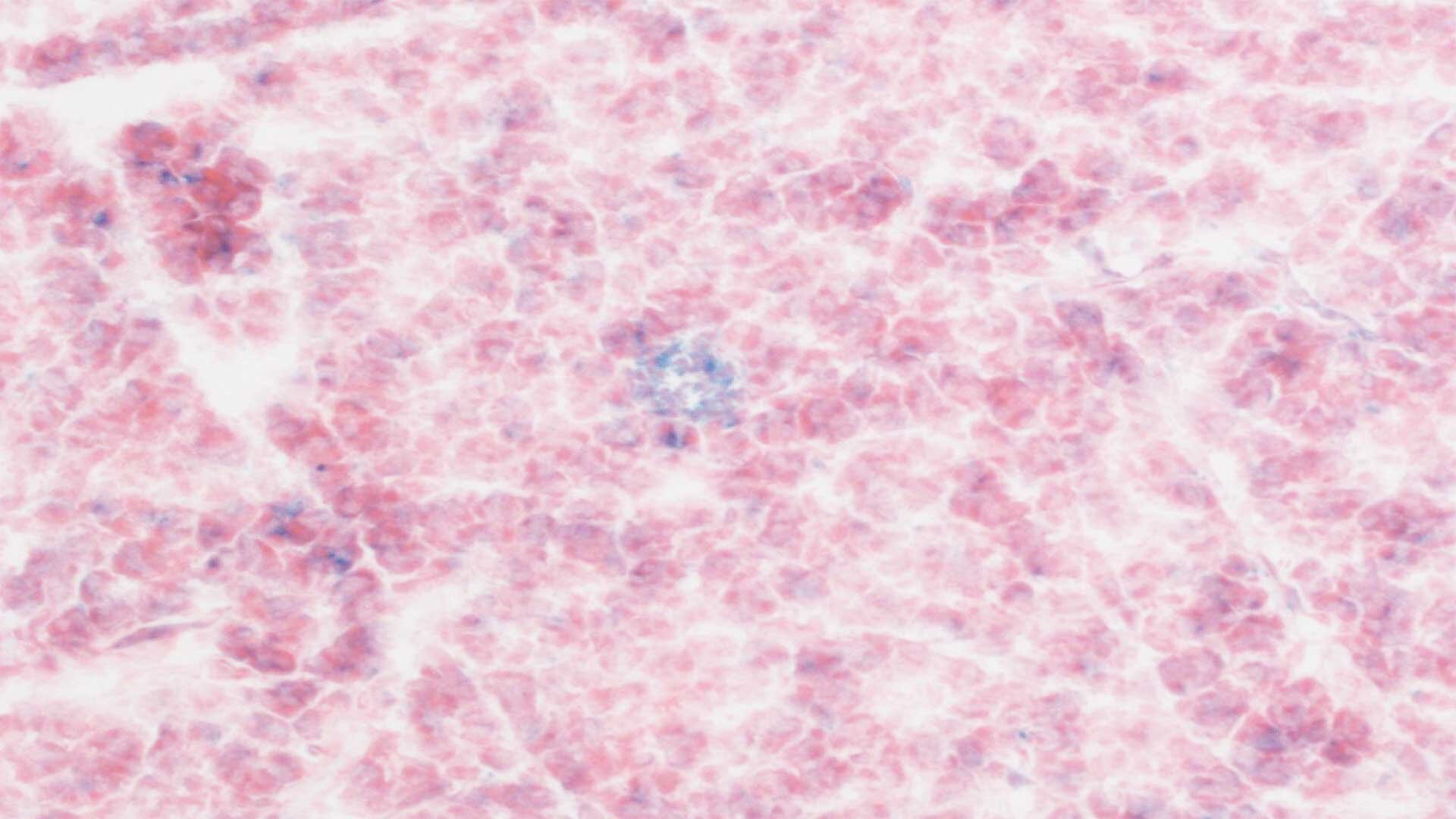
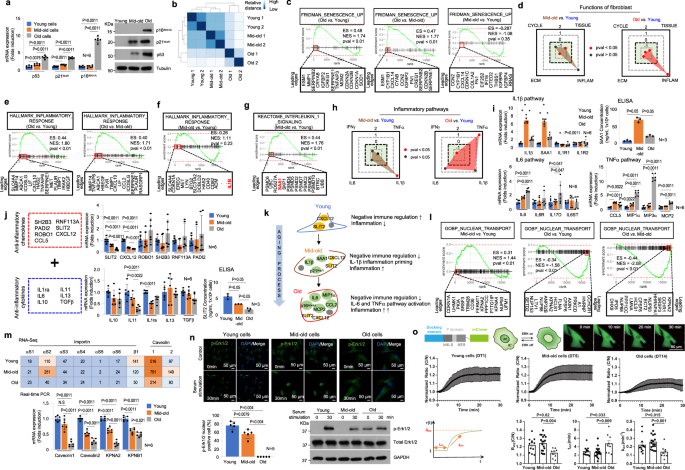
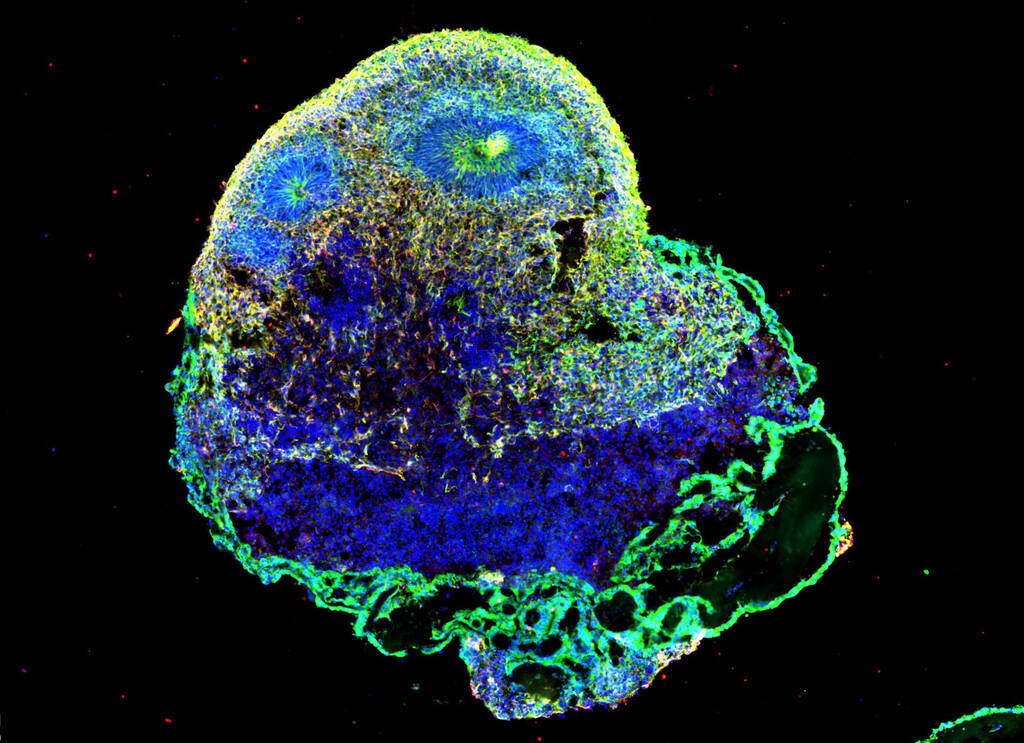
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory researchers used anti-uPAR CAR T cells to selectively clear senescent cells in aging intestinal tissue, boosting epithelial regeneration, reducing inflammation, and improving nutrient absorption in both young and old mice. After radiation-induced gut damage, treated mice recovered more fully, with benefits persisting for at least a year. Early data also show regeneration signals in human intestinal and colorectal cells, suggesting potential clinical trials to counter age-related gut decline.