Oral Bacteria May Accelerate Breast Cancer by Reaching Breast Tissue
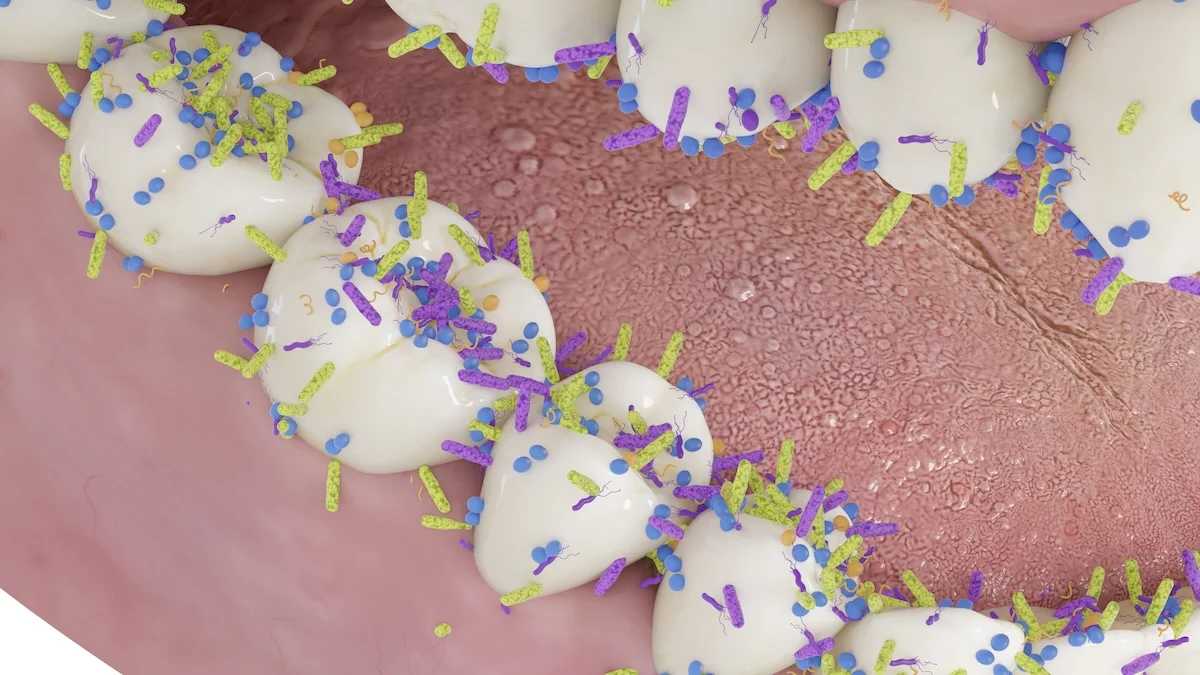
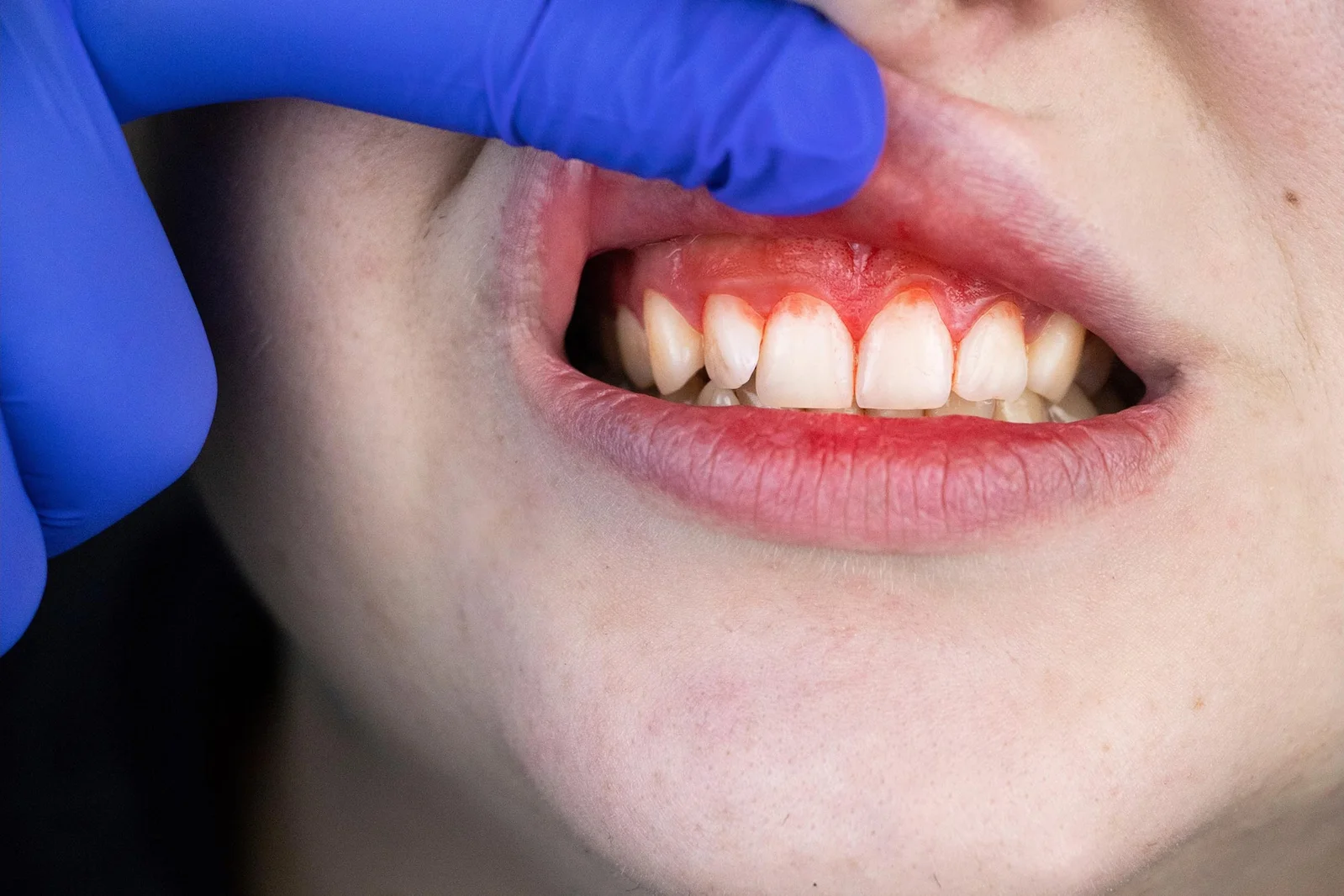
A Johns Hopkins study shows Fusobacterium nucleatum, a mouth bacterium linked to gum disease, can travel to breast tissue via the bloodstream, causing inflammation, DNA damage, and cell changes that accelerate tumor growth and spread in mouse models, with BRCA1-mutant breast cells especially vulnerable; findings suggest oral microbes may influence breast cancer risk and progression.