Drilling Into Antarctica’s Doomsday Glacier Ends in Setback but Yields Key Data
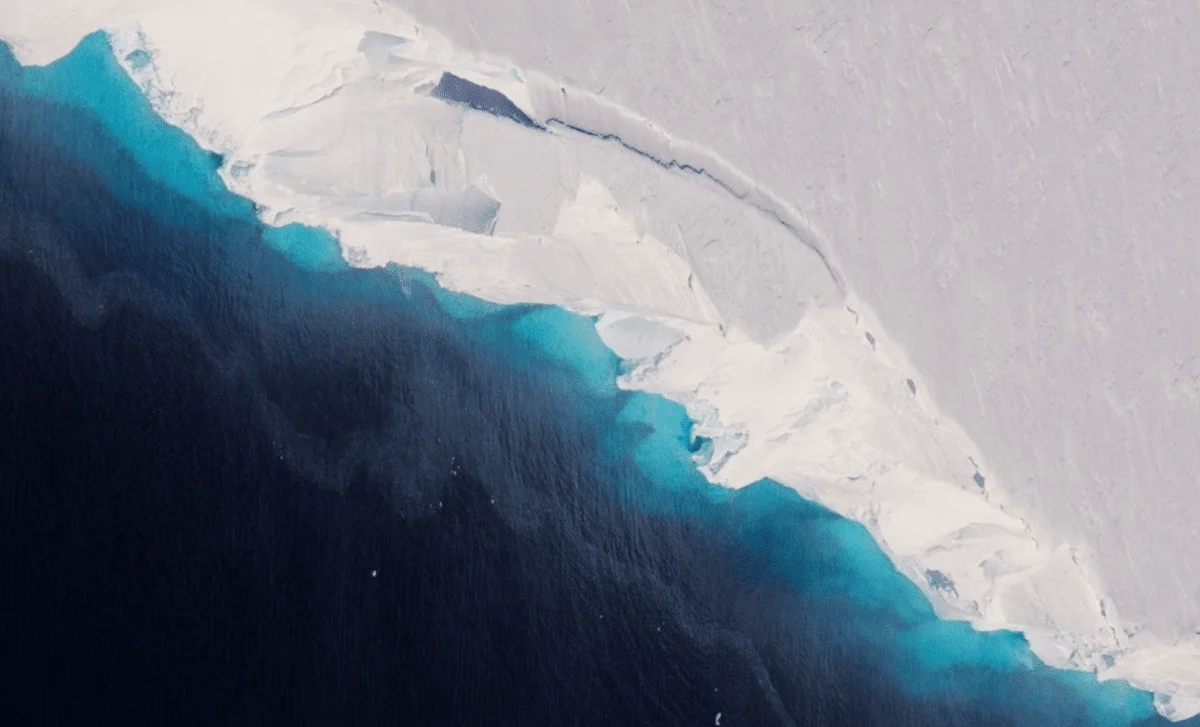
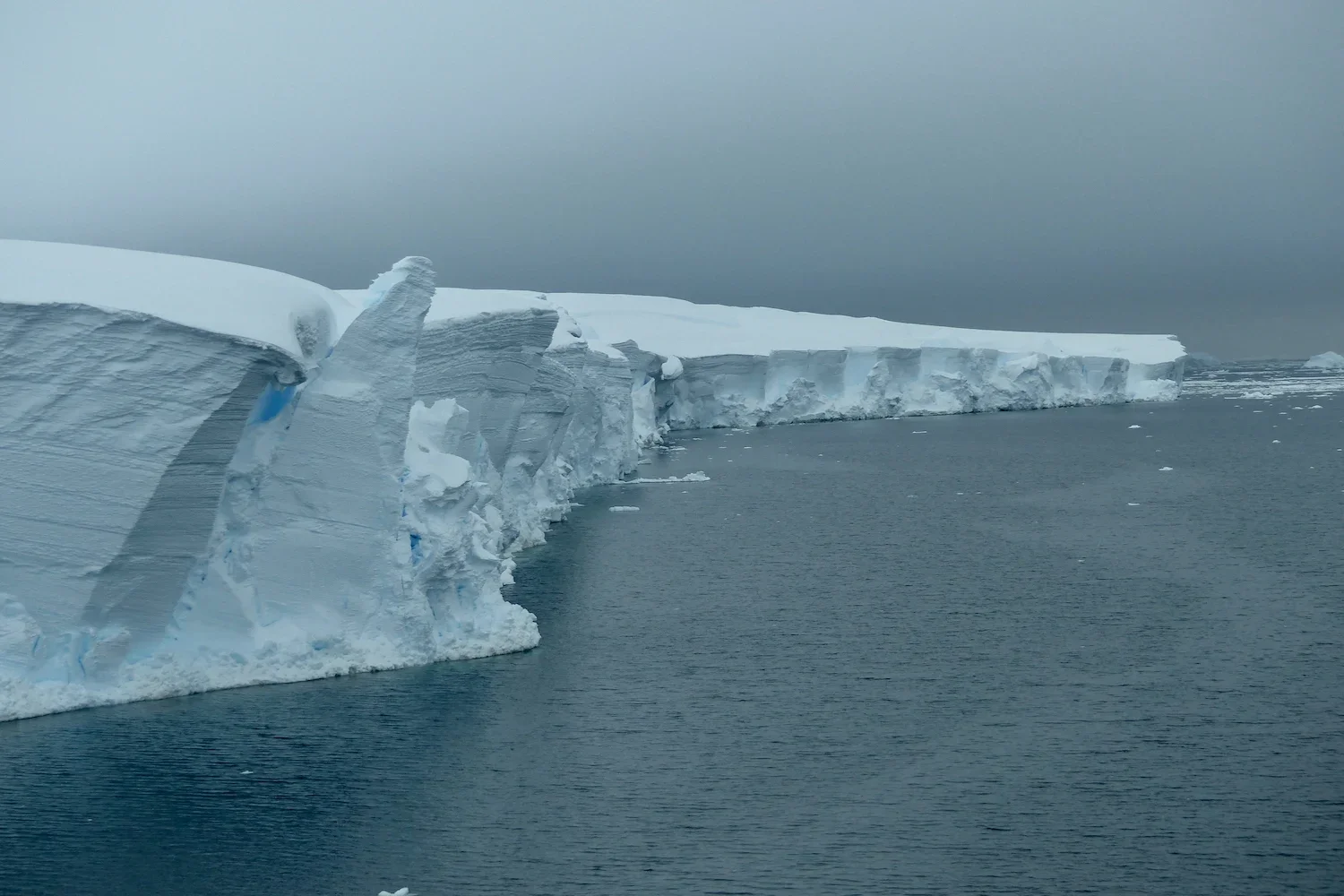
Scientists drilling into Thwaites Glacier with a hot-water borehole faced their instruments getting stuck about three-quarters of the way down and had to abandon the deployment, but the data recovered reveal warm, turbulent waters beneath the ice driving sub-ice melt. The findings improve understanding of the glacier’s instability, and researchers plan to return to continue studying it, given its potential to raise global sea levels by about 65 cm if it destabilizes.