California’s Heat-Pump Gamble: High Bills Cloud the Clean-Energy Push
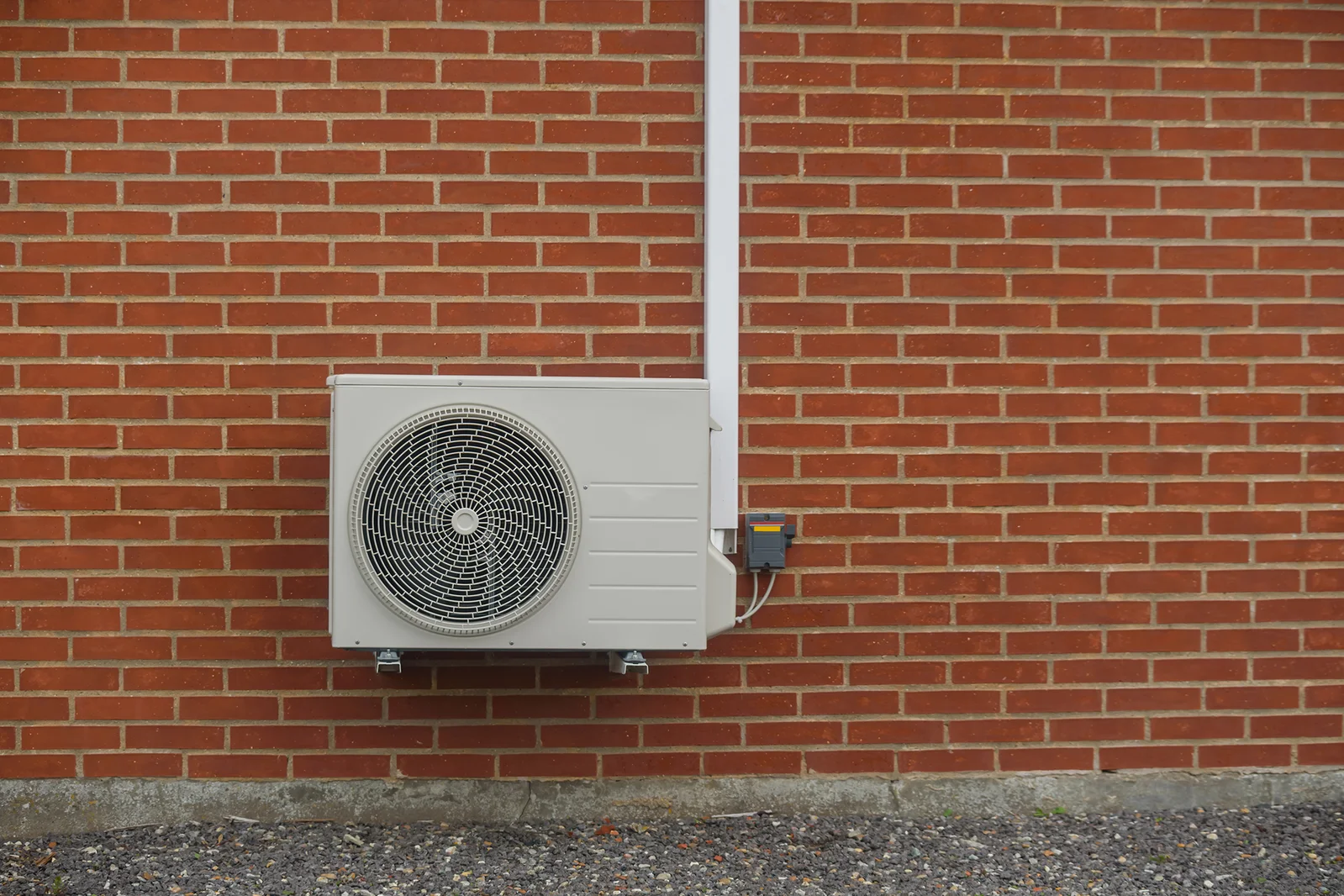
California is pushing to electrify home heating with heat pumps (aiming for six million installations by 2030), backed by rebates and easier permitting, but high electricity prices complicate the economics. A Harvard study finds regional differences: savings tend to occur in the South and Pacific Northwest, while the northern Midwest could see higher bills. In California, coastally favorable conditions are tempered by costly rates, larger or colder homes, and required electrical upgrades; solar can help, but upfront costs and rate plans largely determine whether heat pumps save money.